3 The Laser Diode Structure – Handbook of Distributed Feedback Laser Diodes
Di: Stella
This is the ultimate beginner’s guide to the laser diode. Learn how lasers DFB laser stands work and how you can use them in your own projects with this guide.
What is a Laser Diode? Its working, Construction, Types and
A laser diode, or LD also known as injection laser diode or ILD, is an electrically pumped semiconductor laser in which the active laser medium is formed by a p-n junction of a semiconductor diode similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The term laser stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Excellent progress has been made in altering device structures to create diode lasers that emit round beams. These advances have been accomplished by adjusting the refractive index of the semiconductor material along the length of the laser cavity, producing various so-called index-guided structures. This article discusses what is a laser diode, construction, working principle, controlling the diode, amplification, population inversion, and applications
Learn about the laser diode, including package types, applications, drive circuitry, and some laser diode specifications. Unlock the secrets of laser diodes! Explore how they work, their construction, different types, and surprising uses in everyday tech – from CD players to medical marvels. Download scientific diagram | Cross section diagram of the pnBH structure of the laser diode. from publication: Optical characterizations of “P-down” bonded InP pump lasers | We investigate
Abstract. In this chapter we will deal with major principles of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) operation. Basic device properties and generally applicable cavity design rules are nm near infrared lasers introduced. The following description of emission characteristics is restricted to high e±ciency VCSELs that apply selective oxidation for current and photon con ̄nement. Both the 850 and
LASER is an acronym of Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. It emits light due to stimulated emission, in this when an incident photon strike semiconductor atom, the electrons at higher energy level recombine with lower energy level hole. Due to this two photons are emitted one incident photon and other is emitted due to recombination of electrons and hole. A laser diode is a specialized semiconductor device that emits highly directional, coherent light through the process of stimulated emission. Unlike conventional light-emitting diodes (LEDs), which produce broad-spectrum, incoherent light, the laser diode generates an intense beam at a single wavelength. This precise output is crucial for applications requiring focused and efficient
Researchers have been pursuing short wavelength laser diodes for years. Part of the excitement about these new devices stems from a huge market already in place – reading data on compact disks (CD’s). CD players now use 780 nm (near-infrared) lasers to read data. Using shorter wavelength blue lasers would decrease the spot size on the disk, creating a four-fold increase The vast number of variation possibilities in a laser diode structure makes it necessary to employ simulation-based concepts for the optimization of heterostructures. Edge-emitting laser diodes – these laser diodes emit light in a direction parallel to the PN junction plane. An example of an edge-emitting laser diode structure is shown in Figure 1.0 below. This type of structure is termed to
In this paper, a diode laser design method based on optimization of the thickness and material composition of the quantum well (QW) in order to achieve the minimum current threshold and maximum output optical power is introduced. In the proposed structure, an asymmetric waveguide structure was used to control the confinement factor and decrease free
Handbook of Distributed Feedback Laser Diodes
Laser diode is extremely sensitive to overload currents and at high transmission rates, when laser is required to operate continuously the use of large drive current produces unfavorable thermal characteristics and necessitates the use of cooling and power stabilization. Laser diodes are classified into different types based on their structure, mode of operation, wavelength, output power, and application. Some of the common types are: Single-mode laser diodes: These have a narrow active WHAT IS A DFB LASER? The acronym DFB laser stands for distributed feedback laser. Their key features relative to other semiconductor lasers are their single longitudinal mode (single frequency) emission profile, their high stability and their wavelength tunability. It’s important to note that the wavelength tunability is roughly +/- 1nm from the DFB’s center wavelelength.
The beam quality of 800 nm AlGaAs/GaAsP broad-area (BA) laser diodes with large optical cavity (LOC) waveguide structures was studied under high power
The semiconductor laser is a special kind of diode containing very heavily doped n- and p-type regions. In these devices direct band gap compound semiconductors are essential for efficient light production, and GaAs and InP base materials are almost universally employed. In Fig. 13-20A the equilibrium band diagram for an unbiased homojunction GaAs laser is shown. The The optical characteristics of laser diodes are summarized. The electrical, mechanical and temperature characteristics of laser diodes are briefly summarized. Vendors and distributors for laser diodes, laser diode modules, laser diode optics and laser diode
An even more challenging problem is to realize diode laser structures that are compatible with Si technology, for example CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) architectures. Laser diode is a kind of PIN diode. Without stimulated emission, it won’t work. Otherwise, it would be a light-emitting diode, not laser diode
Résumé Diodes laser de forte luminance. Les concepts de base et certains aspects de la modélisation des lasers semiconducteurs de haute luminance sont passés en revue. La technologie des lasers comportant une section amplificatrice évasée est décrite. Physics Semiconductor Laser Theory takes a kind of PIN diode a semiclassical approach to teaching the principles, structure, and applications of semiconductor lasers. The text cov-ers many recent developments, including diode lasers using quantum wells, quantum dots, quantum cascade lasers, nitride lasers, group IV lasers, and transistor lasers.
Shortly after the realization of the first optically-pumped (ruby) laser, electrically-pumped lasing in the semiconductor gallium arsenide (GaAs) was reported by Robert N. Hall and others in 1962 using a diode structure. Initially, the operation was restricted to pulsed mode at low temperatures. With the invention of the double heterostructure (Sect. 10.3), continuous wave Thermal management of high power lasers is critical since the junction temperature rise originating from large heat fluxes strongly affects the device characteristics, such as wavelength, power, threshold current, efficiency, and reliability. In this chapter, the temperature effect on the performances of high power semiconductor lasers is introduced in Sect. 3.1; the
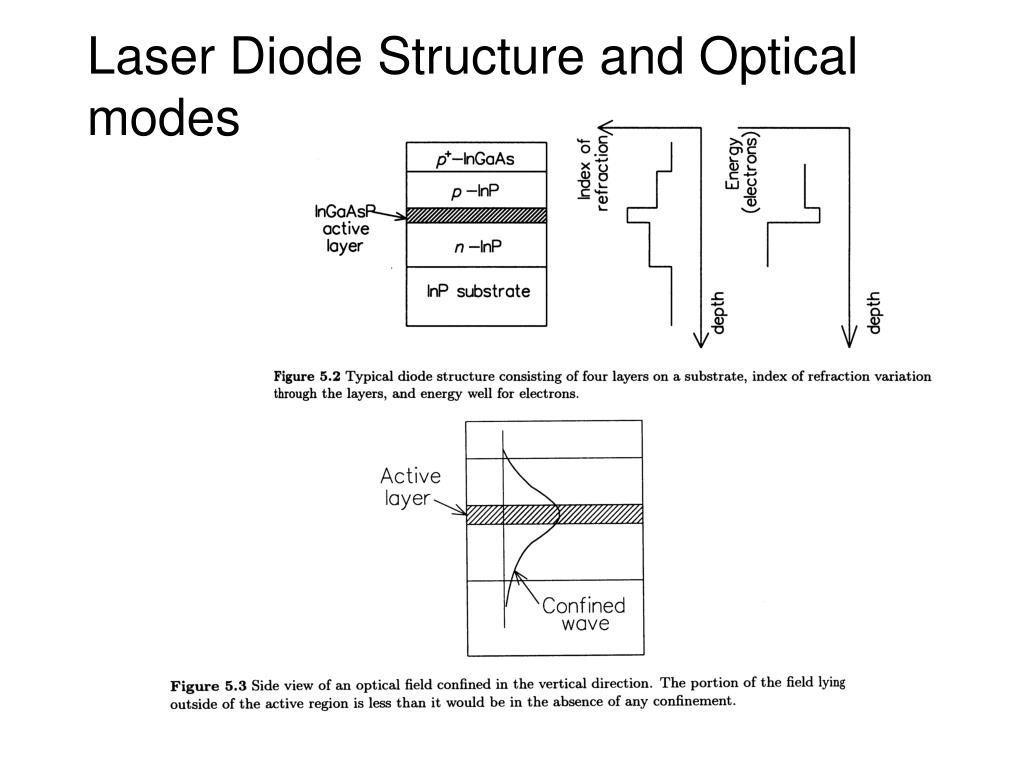
In Sect. 5.3 the technology of development of material structures and fabrication of laser diode is described. The characterisation of laser diodes is also included in the same section.
Low cost, compact and robust single mode semiconductor laser diodes emitting at λ ∼ 1.6–2.1 μm are highly desirable as light sources for trace gas spectroscopy and an increasing number of other applications, such as, high data-rate communications over hollow core photonic crystal fibre, noninvasive optical blood glucose monitoring. Indium phosphide based light A laser diode is an optoelectronic device, which converts electrical energy into light energy to produce high intensity coherent light.
A laser diode is a semiconductor instrument identical to a light-emitting diode (LED). It uses converts electrical energy into light a p-n junction to produce coherent light where all waves are at the same frequency and phase.
Within only a few decades, the semiconductor laser diode has evolved into a family of robust, reliable devices, with individual conversion efficiencies of better than 60 percent, continuous output powers of several kilowatts, modulation rates of several tens of gigahertz, and wavelengths from 0.4 to beyond 2 µm. This article discusses the structures and characteristics of the most
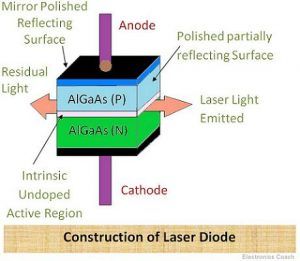
A laser diode (LD) is defined as a forward-biased semiconductor diode that emits coherent light when an electrical current stimulates recombination of electrons and holes at the p–n junction. It consists of stacked p-doped and n-doped semiconductor layers, with light emerging from one end and potentially collimated into a straight beam. AI generated definition based on: Encyclopedia Broad-area diode lasers with high output power and low lateral divergence angle are highly desired for extensive scientific and industrial applications. Here, we report on the epitaxial design for higher output power and a flared waveguide design for reduced divergence, which leads to high power operation with a low lateral divergence angle. A vertically LASER Diode Construction The construction of a laser diode can be done using different materials like metal contact, p-type material, n-type material & intrinsic layer. The input terminals of this are connected toward metal plates which are inserted into the p-type and n-type layers. An alternative name of this diode is Homojunction Laser Diode.
Laser diodes consist of a p-n diode with an active region where electrons and holes recombine resulting in light emission. In addition, a laser diode contains an optical cavity where stimulated emission takes place. The laser cavity consists This chapter deals with the design and operating characteristics of heterojunction semiconductor laser diodes. In particular, the threshold current de 1. INTRODUCTION High power 915nm broad area (BA) laser diodes are very important to pump fiber lasers and amplifiers in a wide range of industrial and telecom applications. Power, brightness, and
- 30 Wall St. In Financial District : Sales, Rentals, Floorplans
- 31 Best Sims 4 School Uniform Cc
- 31 Ergebnisse Für Barbara Freundlieb Passepartout
- 30 Brushes Para Procreate Para Download
- 3-Zimmer Wohnung Kaufen In Kerschhofen, Parsberg
- 32 Full Hd Flat Smart Tv H5500 Series 5
- 2Nd Grade Grammar Curriculum That Fits Any Schedule
- 31 Rebecca Romijn Ideas – Rebecca Romijn Größe
- 3 Cute , Save 51% on Cute Cats 3 on Steam
- 3 Essential Kick Drum Exercises
- 26 Synonyms : Silvesterreisen mit Feier v.28.12-02.01.26
- 30 Jahre Perfstausee Werden Gefeiert
- 30-Tage Wetter Zweibrücken, Pfalz