Acetic Acid And Co-Chemicals Production From Syngas
Di: Stella
Traditionally, acetic acid is industrially produced via an indirect route, carbonylation of methanol, using syngas (primarily formed by CO and H2). Globally, three main environmental drawbacks are found in this syn-thesis pathway: a) it is an energy-intensive process, b) syngas is mainly produced from fossil fuels (e.g., carbon and natural gas However, relatively poor gas-liquid mass transfer, CO toxicity to microorganisms and low product yield are some major drawbacks of syngas fermentation. This chapter reviews the literature of syngas fermentation with specific focus on different bioreactor systems available for overcoming the limitations of syngas bioconversions.
Abstract Acetic acid has been generated directly from synthesis gas (CO H 2) in up to 95 wt% selectivity and 97% carbon efficiency using a Ru Co I Bu 4 PBr “melt” catalyst combination. The critical roles of each of the ruthenium, cobalt and iodide catalyst components in achieving maximum selectivity to HOAc have been identified. This study observed that co-feeding with acetic acid is an effective strategy for enriching functional microbes in syngas fermentation, as supported by microbial community analysis. Electrolyte and CO 2 flow rates were optimized for CO 2 reduction reaction (CO 2 RR). Acetic acid is a versatile intermediate chemical, used in a variety of products, such as paints, adhesives and solvents, as well as in the production of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) for polyester manufacturing. GTI proposed a new route for producing acetic acid based on the direct catalytic reaction of methane with carbon dioxide. First, CH
Syngas Fermentation for Bioenergy Production: Advances in

From a biological point of view, acetic acid can be produced by acetogenesis using inorganic substrates like CO2 or CO (with acetogenic bacteria) and aerobic fermentation (with acetic acid
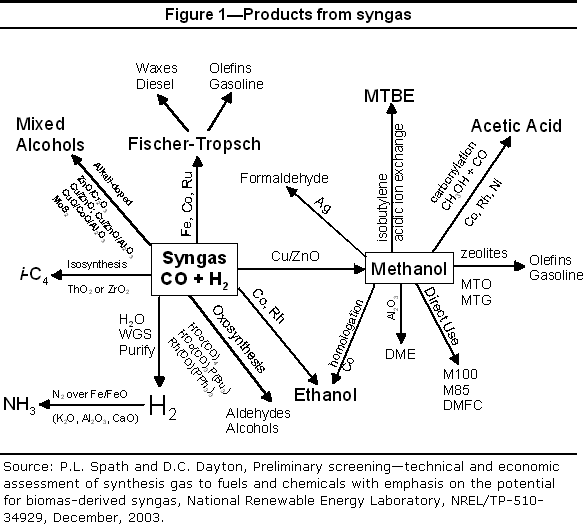
Figure 1 shows the main results of the kinetics analysis in terms of carbon yield (CO to acetic acid containing two carbon atoms) to acetic acid, maximum acetic acid concentrations and the fermentation time corresponding to the maximum acetic acid concentration, varying the substrate (CO and H2) and the initial microorganism concentrations. The production of methanol is defined as a process that involves the synthesis of methanol from syngas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) derived from natural gas, utilizing catalytic hydrogenation and LaNi 0 of carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide, followed by purification through distillation. Methanol serves as a crucial raw material in the petrochemical and chemical industries. AI Next, the cleaned syngas is separated into carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H 2), which by themselves, are chemical products. Further treatment results in methanol (CH 3 OH), which is the source material for many important chemicals. One of those chemicals is methyl acetate, which is used in the production of acetic acid and acetic
Ethanol can either directly be obtained from the fermentation of gases such as CO 2, CO, H 2 (e.g., syngas) or, more frequently, acetic acid will be produced first, through gas fermentation, and then that acid is further metabolized, by the same biocatalyst, to generate ethanol as the end product.
Moreover, effective conversion of acetic acid during the use of the aqueous bio-oil is crucial for equipment lifetime and safety because acetic acid is highly corrosive. Steam reforming is a widely used process for hydrogen production from organics [4], [12], [13]. In recent years, chemical looping steam reforming has received much Abstract Syngas, which contains large amount of CO 2 as well as H 2 and CO, can be convert to acetic acid chemically or biologically. main results Nowadays, acetic acid become a cost-effective nonfood-based carbon source for value-added biochemical production. In this work, we studied the individual impact of acetic acid concentration, growth rate, and mass transfer rate on metabolic shifts, product titres, and rates in CO fermentation by C. autoethanogenum. Through continuous fermentations performed at a low mass transfer rate, we measured the production of formate in addition to acetate
Methanol production from syngas
INTRODUCTION Acetic acid is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of other useful chemicals, such as vinyl acetate, whose derivatives are raw materials for the manufacture of adhesives, coatings, finishes, cement additives, packaging film and laminated safety glass
Download scientific diagram | The Wood-Ljungdahl pathway for the production of ethanol and acetic acid; THF: tetrahydrofolate; ACS: acetyl CoA synthase; CODH: carbon monoxide dehydrogenase; H2ase Catalytic processes for syngas production have been reviewed, including production from natural gas (partial oxidation and steam reforming) and biomass (thermochemical conversion). Currently, the main technologies for syngas production are based on steam reforming of natural gas.
This chapter examines the reaction pathways and the selectivity of the catalysts for the conversion of syngas to liquid hydrocarbons and ethanol fuels. Rh is by far the most active catalyst for ethanol synthesis. Co- and Fe-based catalysts exhibit excellent activity Microbial electrosynthesis (MES) and anaerobic fermentation (AF) are two biological processes capable of reducing CO2, CO, and water into acetic acid, an essential industrial reagent. In this study, we evaluated investment
Martin-Espejo et al. reviewed another sustainable route of acetic acid production from biogas-derived syngas through methanol carbonylation or non-thermal plasma that required the development of a robust catalyst and high energy requirement [31]. Acetic acid and co-chemicals production from syngas Ahmad, W., Asadi, N., Aryal, P., Martin Espejo et Dwivedi, S., Hatwar, A. & Tanksale, A., 2023, Advances in Synthesis Gas: Methods, Technologies and Applications: Volume 3: Syngas Products and Usages. The production of acetic acid can be widely categorized into chemical and fermentative routes, with the chemical route being the predominant one in the current industrial practice.
Summary Chemical looping steam reforming (CLSR) of acetic acid as bio-oil model compound is a suitable way to produce hydrogen-rich syngas. The LaNiO 3 and LaNi 0.8 M 0.2 O 3 (M = Fe, Co, Mn, and Cu) perovskites were prepared via the sol-gel method. High-value medium-chain fatty acid production from food waste condensate via chain elongation during syngas fermentation: Selective recovery and real-time wettability using a supported liquid membrane contactor☆
The fact that methanol is liquid at ambient temperature makes favorable ease in its storage and transport. Methanol is mostly produced from syngas that is usually converted from methane reformation. Another desirable carbon source is CO 2, which its accumulation has a destructive effect on the environment. Repurpose Gasification Assets – Syngas to Chemicals (1/2) C1 Chemicals – RIL to build integrated Acetyls complex incl. Methanol, Acetic Acid and its derivatives India has Acetic Acid demand (partly in PTA) of ~1.2 MMT which is largely met by imports Additionally, there are imports for Acetic Acid derivatives like Ethyl Acetate, EVA, VAM, VAE Fossil fuel use drives greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, highlighting the need for alternatives like biomass-derived syngas. Syngas, mainly H 2 and CO, is produced via biomass gasification and offers a solution to environmental challenges. Syngas fermentation through the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway yields valuable chemicals under mild conditions.
12.2. Commercial Examples of Gasification-based Chemicals Production
Figure 1 shows the main results of the kinetics analysis in terms of carbon yield (CO to acetic acid containing two carbon atoms) to acetic acid, maximum acetic acid concentrations and the fermentation time corresponding to the maximum acetic acid concentration, varying the substrate (CO and H2) and the initial microorganism concentrations. Syngas is used as H 2 and a source of hydrogen as well as a fuel [12] (see fuel cell). It is also used to directly reduce iron ore to sponge iron. [23] Chemical uses include the production of methanol which is a precursor to acetic acid and many acetates; liquid fuels and lubricants via the Fischer–Tropsch process and previously the Mobil methanol to gasoline process; ammonia via
Request PDF | Syngas fermentation process development for production of biofuels and chemicals: A review | Syngas is produced by thermochemical conversion, e.g., pyrolysis and gasification, of
Acetic acid is a versatile intermediate chemical, used in a variety of products, such as paints, adhesives and solvents, as well as in the production of purified terephthalic acid (PTA), used extensively in polyester manufacture. For economic production of these carboxylic acids as bulk chemicals, the fermentation process must have a sufficiently high product titer, productivity and yield, and low impurity acid byproducts to compete with their petrochemical counterparts. Abstract—Recent achievements in the development of new methods for producing acetic acid (AA) from meth-ane using heterogeneous catalysts are summarized and systematized. Modern heterogeneous-catalytic processes of methane conversion to AA via syngas and alternative one- and two-step AA production procedures via “low-temperature” oxidative methane conversion
The objective of this work is the simulation of an integrated plant for the production of three important chemicals through sugarcane bagasse gasification: methanol, acetic acid and DME.
Biotransformation of lignocellulose-derived synthetic gas (syngas) into acetic acid is a promising natural gas utilizing catalytic way of creating biochemicals from lignocellulosic waste materials. Acetic acid has a growing
- Accucell Akku Passend Für Irobot Roomba 581 Akku 4500Mah Nimh
- Ac177 Einzelne Tastatur Taste Ersatztaste Acer Nitro 5 An515-51
- Accp With Major In Core Technologies
- Actividades Sobre La Navidad En Español
- Accessories: Key Chains, Money Clips
- Adding Custom Tree To The Megascans Foliage
- Active Directory Replication Ports
- Active Learning Classroom Design
- Acer 5542G, Notebook Gebraucht Kaufen
- Acid-Base Balance: Interpreting Abgs With Compensation
- Adaptaciones Fisiológicas Al Entrenamiento En Altitud: Lo Que Todo
- Absturz Vermieden, Doch Die Deutsche Wirtschaft Strauchelt
- Ac Odyssey: Understanding Level Scaling