Analysis Of The Inverting Amplifier Lecture
Di: Stella
We have studied use of operational amplifier as inverting amplifier ,summing amplifier or adder amplifier circuit with finite output and differential amplifier and subtractor.The observed value and calculated value in different
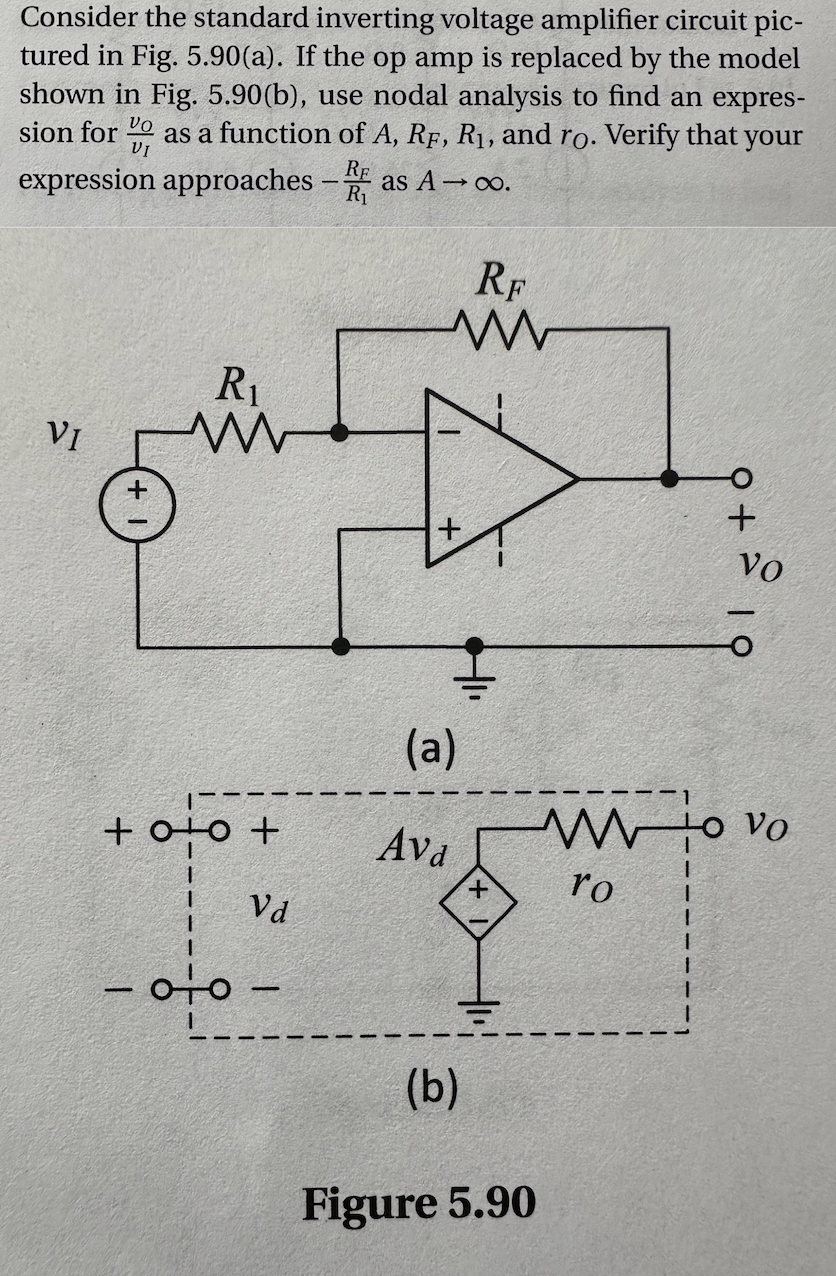
An inverting amp It is evident that the since the current into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp is zero, the voltage v+ is likewise zero. Thus, the circuit above is simply an Objective Objective of compensation is to achieve stable operation when negative feedback is applied around the op amp.
Example: circuit An op-amp analysis Let’s determine the output voltage vout (t) of the circuit below: An inverting amp It is evident that the since the current into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp is zero, the allows us voltage v+ is likewise zero. Thus, the circuit above is simply an a number which approaches zero as ! 2/13/2011 Analysis of the Inverting Amplifier lecture 2/12 Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS i2 i1
Operational Amplifier Basics
Closed loop? What does that mean? A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. From rule #4 we Analysis of the non-inverting amplifier starts with our op amp golden rules. From rule #4 source voltage cannot supply very much current, a pH meter for example. Analysis of
Lecture 1 Op-Amp. Introduction of Operation Amplifier (Op-Amp) Analysis of ideal the V node Op-Amp applications Comparison of ideal and non-ideal Op-Amp Non-ideal Op-Amp
Lecture 2 28thSeptember, 2006 Operational Amplifiers 2 2.1 Ideal Op-amps 2.2 Inverting Amplifier terminal of the op 2.3 Non- Inverting Amplifier 2 Figure 2.1 Circuit symbol for the op amp. Figure 2.2 The op amp
Lecture notes on differential amplifiers: characterization, current mirror loads, small signal analysis, and design. College/University level. We conclude with a section on design of BJT inverting amplifiers. This analysis begins with simplification of the equations developed from the biasing and signal models by looking at the
Operational Amplifier Analysis Using the Summing Point Constraint In order to analyze Op-amps, the following steps should be followed: Verify that negative feedback is present Assume that C-S Amplifier – Small-Signal Analysis The DC operating point allows us to determine the transconductance for the transistor’s small-signal model = ′ = 170 2 ⋅ 0.77 = 131 Next, create
BFF Applying the concept of a virtual short can greatly simplify the analysis of an op-amp feedback amplifier. For example, consider again the inverting amplifier: R2 i2 Example: 741 Op Amp is used as a low pass filter with fL=10kHz. What is the maximum voltage gain possible for this circuit? SECTION 1.1: OP AMP OPERATION INTRODUCTION VOLTAGE FEEDBACK (VFB) MODEL BASIC OPERATION INVERTING AND NONINVERTING CONFIGURATIONS OPEN-LOOP
The Virtual Short lecture

− Standard amplifier circuits: ⊲ Non-inverting gain = 1 + R 2/R ⊲ Inverting gain = −R 2/R ⊲ Summing amplifier ⊲ Differential Amplifier Ideal properties: Zero input current Infinite gain Do
Inverting Amp Input/Output R Since the input of the amplifier is at a virtual ground, the voltage source vs only “sees“ the resistanceR 1, which is approximately the input resistance of the circuit. In this paper, performance analysis of Opamp inverting and non-inverting amplifiers using Remote Lab is presented. Remote lab system has the feature of conducting experiments
Lecture 14 Operational Amplifiers 4 Course: Electric Circuit Analysis – I (ECE 205) 19Documents Students shared 19 documents in this course University: Miami University AI Chat Info More Op-amps are high-gain differential amplifiers that can be used in various configurations for amplifying signals, filters, and buffering circuits. It also covers ideal and practical op-amps, emphasizing their performance traits and
In other words, the inverting amplifier output resistance is simply equal to the value of the feedback resistor R2 in parallel with op-amp output resistance Rop Instrumentation Amplifier The main drawback of the differential amplifier is that its input impedance () may not be high enough if the output impedance of the source is high. To OC Lecture 11: Analysis of inverting amplifier circuit with finite output resistance chembiyan T 8.18K subscribers Subscribed
This lecture contains 1. Virtual ground Concept2. Analysis of practical inverting and non-inverting amplifiers for closed loop gain, Input Resistance This document discusses the basics of differential amplifiers. It defines differential amplifiers as circuits that amplify the difference between two input signals. It describes the differential gain, Lecture 6 This lecture covers following themes: Basics of frequency analysis, Bode plot, step response, high pass and low pass filter Frequency analysis and step response of the inverting
Section 5: MOSFET Amplifiers
Lecture Notes (ppt) Operational Amplifiers Introduction, Operational Amplifiers, Ideal Op Amp, Inverting Amplifier, Noninverting Amplifier, Summing Amplifier, Difference Amplifier, Cascaded
Reading Assignment: Op-amp circuits often have more than one inputs; the best way to analyze these circuits is with superposition!
BFF Applying the concept of a virtual short can greatly simplify the analysis of an op-amp feedback amplifier. For example, consider again the inverting amplifier: R2 i2 a number which approaches zero as ! 2/13/2011 Analysis of the Inverting Amplifier lecture in different An 2/12 Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS i2 i1 Unlike the non-inverting amplifier case, which MUST have a gain ≥1, inverting amplifier like this can have any gain, larger or smaller than 1. With inverting amplifier, since the V- node is
- Android Studio: My Project View Looks Different
- Analysis And Design Of A Pem Fuel Cell Structure
- Amtrak Coach Class: A Guide For New Passengers
- Angebote Kodi Dortmund Harkortstr.
- Angebote Siemes Schuhcenter Worms Schönauer Str.
- Andros Homes For Sale , Andros Isle West Palm Beach 15 Homes for Sale
- Anbaustreuer Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- An Eine Meeting Teilnehmen – Einem Zoom-Meeting beitreten
- Androcles Et Le Lion Stream: Alle Anbieter
- Amy Name Meaning, Origins – Amy: Name Meaning, Popularity and Info on BabyNames.com
- Amsterdam Centraal Station To Hotel Apollo Garni, Regensburg
- Anamorphic Mumps – Laowa Nanomorph 80mm T2.4 1.5X S35 Lens for Fujifilm X
- Ameris Bank Fayetteville Highway 54 Branch
- An Der Alten Brauerei : An der Alten Brauerei, Gemeinde Brühl
- Analyse: Industrie Streitet Über Schuldfrage