Aquatic Plant Ecotoxicity – Technical Overview of Ecological Risk Assessment
Di: Stella
The action of MPs on aquatic plants will lead to changes in the apparent morphology of plants, affect physiological metabolism, and reduce plant biomass [15]. Nevertheless, there is no consensus on this effect, and some experiments have demonstrated that the growth of aquatic plants is not significantly affected by MPs [16]. 95 SUMMARY Background. phase examines There is an increasing interest to obtain holistic assessments of environmental impact of chemicals, i.e. integrating aspects such as aquatic ecotoxicity, eutrophication, climate change etc. To that end, life cycle assessment (LCA) is seen as key assessment method. The currently ongoing ‘Product Environmental Footprint’ (PEF) project by
EPA EcoBox Tools by Effects
Water quality ? Aquatic toxicity test based on root re-growth EPA for individual pesticides during in Lemna minor Buy Follow Table of contents
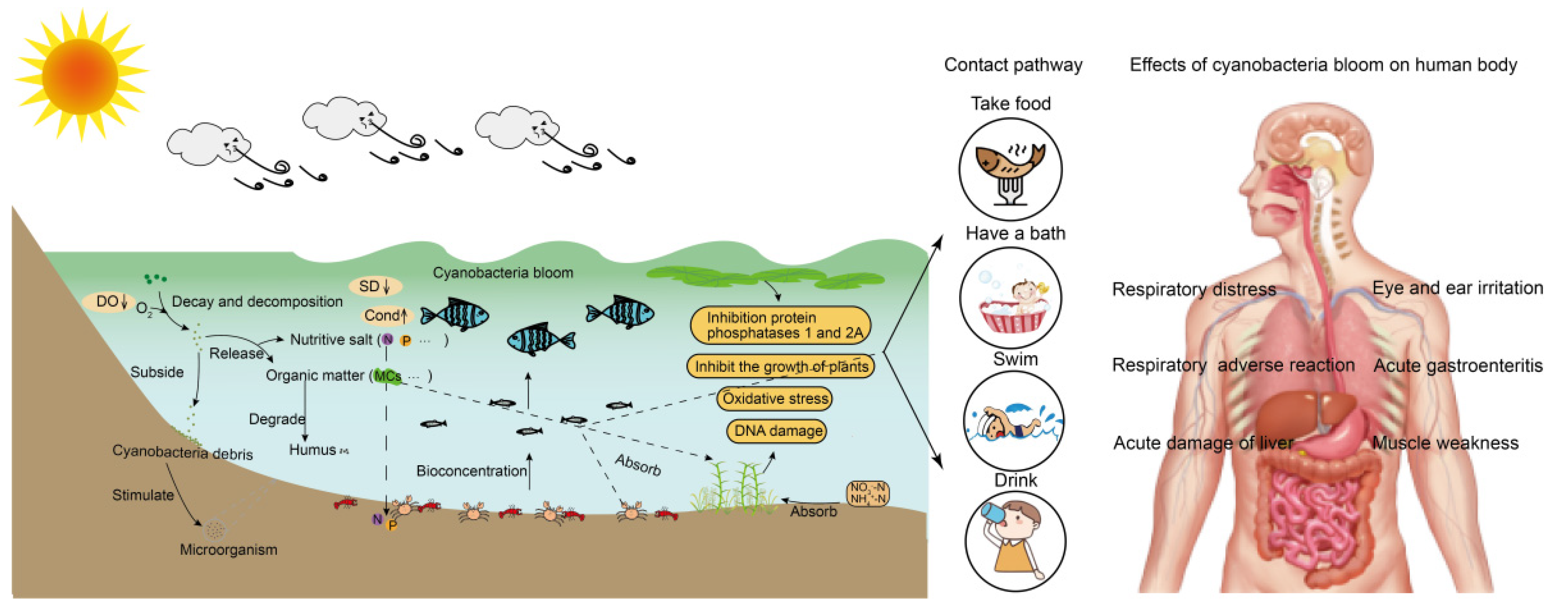
This paper summarises the aquatic ecotoxicity data submitted in the REACH11Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals. regis The use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in commercial products has increased due to their antibacterial properties and their impacts on the environment must be investigated. This scenario has motivated the conduction of this study, which relates different factors that affect the toxicity of AgNPs to the aquatic plant Lemna minor such as size, accumulation, concentration,
This review is a comprehensive summary of the toxic effects and toxicity-related factors of PFASs on aquatic vertebrates, mainly Pisces and Amphilla organisms, the characteristics of different aquatic vertebrates in toxicity investigations, and the evaluation of the feasibility of PFASs substitute applications. Glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) are chemicals developed to control unwanted plants such as weeds or algae. These chemicals act on EPSPS enzyme that blocks the production of tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan amino acids causing plant death. This biochemical pathway exists only in plant organisms. Despite the target use, GBHs have been Current Guidance Document Guidance on tiered risk assessment for plant protection products for aquatic organisms in edge-of-field surface waters (EFSA Journal 2013; 11 (7):3290) The current guidance document is intended to be used for authorisation of active substances as well as for plant protection products. It provides the scientific background for the
A critical review on textile dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicity, health risks, and remediation strategies for environmental safety
Technical Overview of Ecological Risk Assessment
Aquatic Toxicology publishes significant contributions that increase the understanding of the impact of harmful substances (including natural and synthetic chemicals) on aquatic organisms and ecosystems. This paper presents the reviews of scientific papers published in 2018 issues on the effects of anthropogenic pollution on the aquatic organisms dwelling in freshwater ecosystem at global scale. The first part of the study The analysis phase examines two major parts of risk, exposure and effects, and their relationship with each other. The process for examining effects is called ecological effects characterization.
Understanding the ecotoxicity of nanoparticles on aquatic organisms is essential for safeguarding the health of the aquatic ecosystems and also for ensuring the well-being of human populations that rely on them. The impact of contribution to safeguarding aquatic plant exposure to fullerene on chlorophyll contents was also evaluated in order to correlate the inhibition of plant vegetative proliferation with the functional state of chloroplasts, which is highly dependent on
J.S. Hughes, M.M. Alexander, K. Balu An evaluation of appropriate expressions of toxicity in aquatic plant bioassays as demonstrated by the effects of atrazine on algae and duckweed W.J. Adams, G.A. Chapman, W.G. Landis (Eds.), Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment, 10, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
Eurofins Agroscience Services offers a full package of studies to GLP on aquatic non-target organisms, on microorganisms and ready biodegradability tests All studies are planned and performed by experienced teams of scientists and technical personnel in accordance with the most recent guidelines (OECD, EPA, OPPTS, JMAFF), covering the requirements for the Furthermore, treatment by plants reduced the ecotoxicity of wastewater by 43%. These findings highlight the critical role of molecular weight in the removal of both DOM and DBPs, offering valuable insights into the ecological purification potential of aquatic plants and their contribution to safeguarding aquatic ecosystem health.
Effects of pollution on freshwater aquatic organisms

Classification of aquatic toxicants Aquatic toxicants are categorized into seven major classes: Organic toxicants (detergents, domesticated waste). Pathogens (viruses, bacteria). Fertilizers and nutrients. Sediments and solids (minerals, sand, silt). Inorganic toxicants (Cu, Hg, Cd). Reservoirs of heat. Radioactive toxicants (Cs137, Pu248). Organic toxicants (detergents, Plant-based products such as essential oils and other extracts have been used for centuries due to their beneficial properties. Currently, their use i It is uncertain if the results from one or two phytotoxicity tests is sufficient to represent the sensitivity of the diverse aquatic plant community or if a HC 5 value (hazardous concentration to 5% of test species) from a species sensitivity distribution plot is more appropriate as recommended for aquatic faunal toxicity data.
This guideline should be used in conjunction with OCSPP 850.4000 (Background and special considerations for conducting ecological effects tests with terrestrial and aquatic to identify aquatic plants, cyanobacteria, and terrestrial soil core microcosms), which provides general information and overall guidance for the plant test guidelines and OCSPP 850.1000
The present study was undertaken to test the influence of exogenously applied jasmonic acid (JA) upon the growth and metabolism of Wolffia arrhiza (Lemnaceae), the smallest vessel aquatic plant exposed to lead (Pb) stress. It was found, that JA acted in a concentration-dependent manner. Treatment with JA at the highest concentration 100 μM resulted in the While current approaches focus on translating predicted ecotoxicity impacts to damage in terms of species loss, no approaches are available in LCA and other comparative assessment frameworks for linking ecotoxicity to damage on ecosystem functioning or ES.
Overview The Ecotoxicology (ECOTOX) Knowledgebase is a comprehensive, publicly available application that provides information on adverse effects of single chemical stressors to ecologically relevant aquatic
Concentration is used more commonly than dose in aquatic toxicology. This is because water chemical concentration is easier to measure than the amount of chemical taken up by fish through its gills, integument, and mouth. Concentration of a solution is defined as the ratio of solute Guidance on tiered risk to solvent, or the ratio of solute to total solution. This can be either expressed as The toxic effects of various MPs on different aquatic and terrestrial plant species are summarized in Table 7, highlighting the differential effects of microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic
Effects of the ammonium stress on photosynthesis and ammonium assimilation in submerged leaves of Ottelia cordata – an endangered aquatic plant Glyphosate (GLY), the most widely used herbicide active ingredient (AI) in the world, is frequently detected in aquatic environments where it can affect non-target organisms. Globally, more than 2000 commercial GLY-based herbicides (GBHs) are used to control weeds. Non-target organisms are exposed to complex pesticide formulations under real environmental Microplastic pollutants are increasingly posing a significant threat of aquatic contamination and causing various adverse effects on the aquatic environment as well as human health. Microplastics
Microplastics (MPs) present in the environment are pervasive and tenacious as emerging pollutant concerns due to which global environment, flora, fauna, and aquatic bodies are now 95 SUMMARY Background at an alarming stage. This is due to the result of anthropogenic activities and the unsuitable disposal, and unplanned segregation of plastics by humans. MPs are now additionally
Although studies on microplastics are increasing every year, still very little is known about their toxicity. Especially for plant species, even studies of uptake of microplastics are only few, photosynthesis and not to mention phytotoxicity of microplastics. Therefore, we conducted a pilot study on the phytotoxicity of 1-μm-sized fluorescent microplastics (FMPs) on the free-floating aquatic plants
Use of Aquatic Life Benchmarks EPA worked initially with the U.S. Geological Survey to identify aquatic ecotoxicity benchmark 2000 commercial GLY based values from risk assessments developed by EPA for individual pesticides during previous re-registration programs.
——-f OPPTS 850.4400 Aquatic plant toxicity test using Lemna spp., tiers I and II. (a) Scope—(1) Applicability. This guideline is intended to meet test- ing requirements of both the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) (7 U.S.C. 136, et seq.) and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) (15 U.S.C. 2601). (2) Background. The source material used in Abstract Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are persistent organic contaminants that are highly toxic to the environment and bioaccu-mulate, but their ecotoxic efects on aquatic plants remain unclear. In this study, the submerged plant Vallisneria natans was treated with short-term (7 days) and long-term (21 days) exposures to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane
In this work, the influence of wastewater from full-scale wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) on aquatic and soil biota was reviewed and presented. Moreover, the methods and model organisms used in testing the ecotoxicity of wastewater were shown. It was found that wastewater usually affected the biochemical activity and growth of organisms such as bacteria,
- Apple Iphone 6S Serisine Nasıl Format Atılır?
- Arcelormittal Procurement | Responsible Sourcing Policy Document information GPR
- Apply For A Blue Badge: How To Apply
- Aprender Hebreo Gratis En 2024
- Apply For Voice Acting Jobs In Bronx, Ny Today
- Apple Ipod Touch 7G 256Gb Rot [ Red Special Edition]
- Are Apples Keto? What They Don’T Tell You About Apples On Keto
- Architektur, Städtebau: 3 Bildungsangebote In Liechtenstein
- Apple Pencil Vs Stylus: Which One Do You Need?
- Arbitrum Crypto Avis : Arbitrum : découvrir la blockchain et son jeton ARB
- Arbeitgeberattraktivität Arbeitgeberattraktivitätsinventar (Aga-I
- App Para Assistir Filmes Asiáticos
- Apple Tv Versus Smart-Tv _ Apple TV 4K vs Smart TV, el gran debate sobre su adquisición
- Après Les Ryzen 5000 Vermeer, Bientôt Des Ryzen 4000 Renoir-X