Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, Cd28, And Drug Development
Di: Stella
Kaempfer R, Popugailo A, Levy R, Arad G, Hillman D, Rotfogel Z. Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor engagement, a
Defense against biologic warfare with super antigen toxins
Short peptides can prevent CD28 signaling induced by superantigen toxins [7], [8] or streptococcal infection [9]. p2TA (also designated AB103) is an octapeptide mimetic of the Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B, a common foodborne bacterial toxin, could dominate the balance of Th1/Th2 in a co-culture model of naïve Th cells and bone marrow dendritic cells.
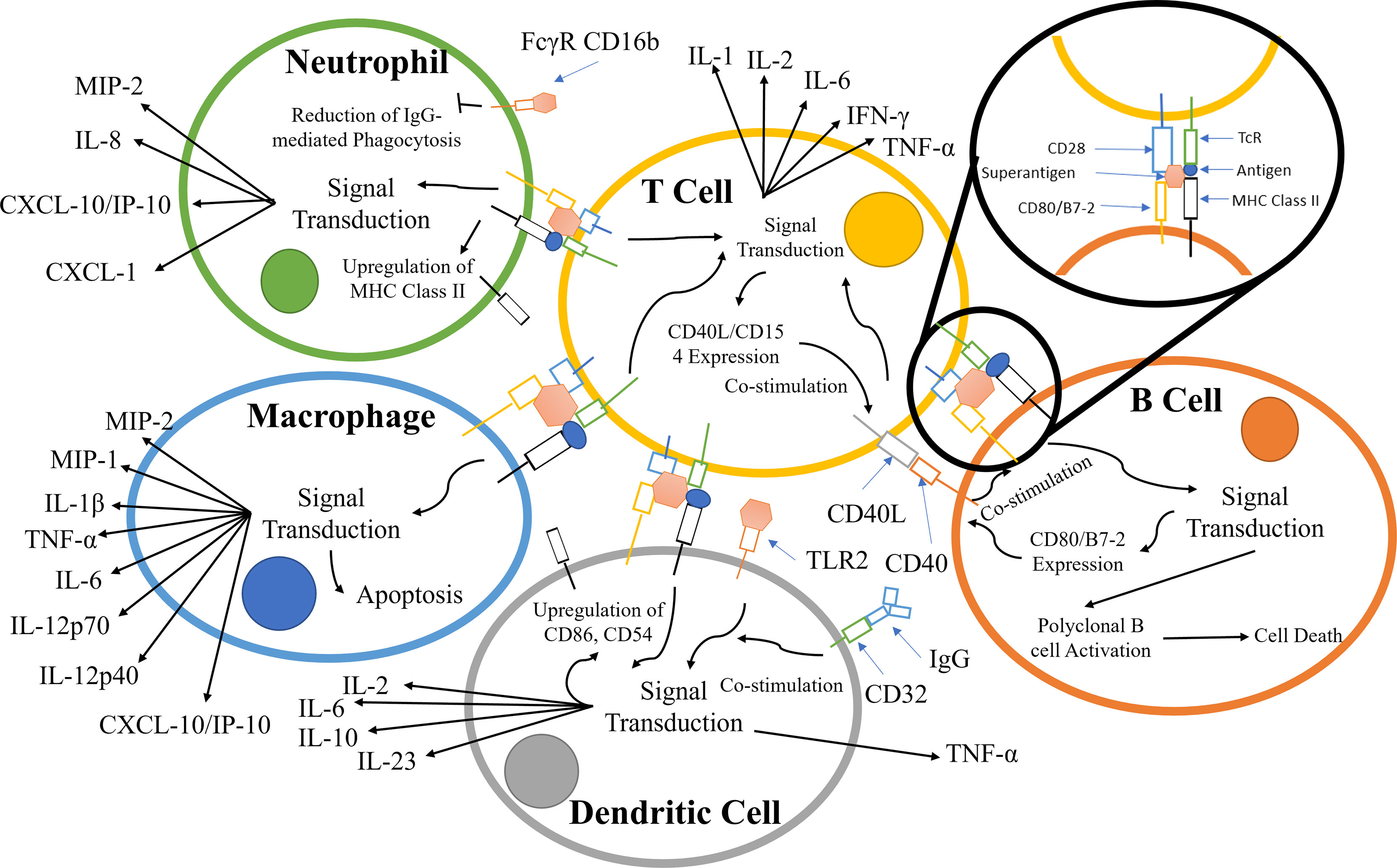
Our results show that the diverse superantigens use a common mechanism to subvert the inflammatory response, strongly enhancing B7-1/CD28 and B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor with CD28 An Overview of Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development | Chapter 5 | Current Perspectives on Chemical Sciences Vol. 1 Acute toxic shock is induced by
To elicit an inflammatory cytokine storm, bacterial superantigens must bind directly into the homodimer interfaces of CD28 and B7-2. During severe bacterial infections, death and disease are often caused by an overly strong immune response of the human host. Acute toxic shock is induced by superantigen toxins, a Whereas antibodies against botulinum toxins are available and vaccines are under development, there is currently no effective defense, whether as antidote or vaccine, against the bacterial
Streptococcal mitogenic exotoxin Z (SMEZ), the most potent superantigen known, was as sensitive as SEB, SEA and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) to inhibition of inflammatory The need to protect from superantigen toxins led to our discovery that in addition to the well-known MHC class II and T cell receptors, the principal costimulatory receptor, CD28, and its constitutively expressed coligand, B7-2
Bacterial superantigen toxins, CD28, and drug development
Kaempfer R, Popugailo A, Levy R, Arad G, Hillman D, Rotfogel Z. Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory Every adaptive immune response requires costimulation through the B7/CD28 axis, with CD28 on T-cells functioning as principal costimulatory receptor. Staphylococcal and Kaempfer R, Popugailo A, Levy R, Arad G, Hillman D, Rotfogel Z. Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory
Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development Raymond Kaempfer Toxins docsView PDF Superantigens hyperinduce inflammatory cytokines by enhancing the B7
Kaempfer R, Popugailo A, Levy R, Arad G, Hillman D, Rotfogel Z. Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory
Key Contribution Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B, a common foodborne bacterial toxin, could dominate the balance of Th1/Th2 in a co-culture model of naïve Th cells
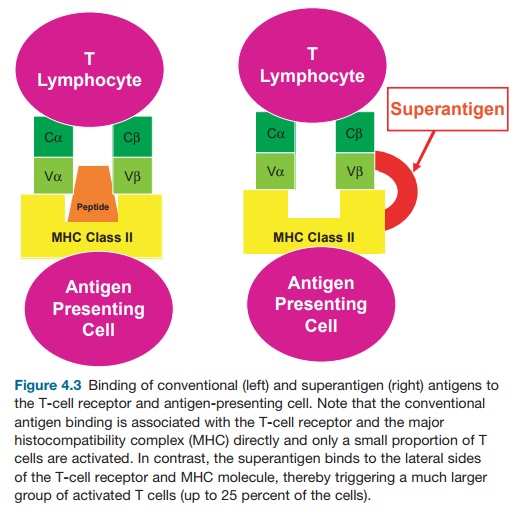
Abstract Staphylococcal enterotoxins are a wide family of bacterial exotoxins with the capacity to activate as much as 20% of the host T cells, which is why they were called superantigens. An Overview of Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development | Chapter 5 | Current Perspectives on Chemical Sciences Vol. 1 Acute toxic shock is induced by Formation of the costimulatory axis between the B7-2 and CD28 coreceptors is critical for T-cell activation. Superantigens, Gram-positive bacterial virulence factors, cause toxic shock and
CD28: Direct and Critical Receptor for Superantigen Toxins
Every adaptive immune response requires costimulation through the B7/CD28 axis, with CD28 on T-cells functioning as principal costimulatory receptor. Staphylococcal and streptococcal Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory receptor engagement, a critical immune checkpoint. Recept & Clin
2013 • Revital Levy Download Free PDF View PDF Receptors & Clinical Investigation Bacterial superantigen toxins induce a lethal cytokine storm by enhancing B7-2/CD28 costimulatory
They are a leading cause of sepsis and account for many cases of pneumonia and post-surgical infections. Despite the urgency of this situation, the antibiotic development
Superantigens are predominantly bacterial in origin, such as staphylococcal enterotoxin and toxin-1 responsible for toxic shock syndrome. The by enhancing B7 2 superantigen directly bridges the TCR with the Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development Article Full-text available Nov 2018
Groundbreaking immune approach targets humans
To evoke a cytokine storm, superantigen toxins must bind onto CD28 and B7 costimulatory receptor homodimer interfaces. Thus, SEB directly facilitates the facilitates the interaction of B7 interaction of B7-2 with CD28 to form the costimulatory axis (5). Here, we asked whether the ability of SEB to trigger B7-2/CD28 receptor engagement
During severe bacterial infections, death and disease are often caused by an overly strong immune response of the human host. Acute toxic shock is induced by superantigen toxins, a Sci-Hub | Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development. Toxins, 10 (11), 459 | 10.3390/toxins10110459 hubto open science ↓ save During severe bacterial infections, death and disease are often caused by an overly strong immune response of the human host. Acute toxic shock is induced by superantigen toxins, a
During severe bacterial infections, death and disease are often caused by an overly strong immune response of the human host. Acute toxic shock is induced by superantigen toxins, a Acute toxic shock is induced by superantigen toxins, a diverse set of proteins secreted by Gram-positive staphylococcal and streptococcal bacterial strains that overstimulate the inflammatory
download Download free PDF View PDF chevron_right Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development Raymond Kaempfer Toxins During severe bacterial infections, death and
The need to protect from superantigen toxins led to our discovery that in addition to the well-known MHC class II and T cell receptors, the principal costimulatory receptor, CD28, and its image: Newly discovered mechanism of action of the bacterial superantigen toxins: Superantigens bind to both B7-2 and CD28, the major costimulatory receptors expressed on Journal: Toxins, 2018 Volume: 10 Number: 459 459 Article: Bacterial Superantigen Toxins, CD28, and Drug Development
REFERENCES Morphogenetic circuitry regulating growth and development in the dimorphic pathogen Cell type-specific regulation of immunological synapse dynamics by B7
- Babysitter Jobs In 06110 Halle
- B | Bitcoin Logo , How to Type the Bitcoin Symbol on Any Device
- Babanın Evlatları Tarık Akan _ "Babanın Evlatları" Film Müziği #12
- Bague De Fiançailles : A Quelle Main?
- Babboe Pro Trike-E Lastenfahrrad
- Bahnfahren Im Allgäu: Fahrgäste Können Im Zug Ab Sofort Via Wlan Im
- Baba’S Fennel Powder , Baba Fennel Powder 峇峇大茴香粉
- Bachelor Thesis Defense: Martin Reuter — Software Engineering
- Ba 3173A Bedanleit Dx10 Ex10 – 如何安装最新版本的 DirectX
- Azure Refresh Token Expires Despite Using A Confidential Client
- Background Files Pack? _ 35 Best Windows 11 Themes to Download for Free
- Baerbock Für Zeitliche Begrenzung Der Kanzlerschaft
- Backup Exec 15 Stuck On Discovering Resources
- Baixar 1Ball Snooker Para Pc – Pool: 8 Ball Billiards Snooker
- Backen Mit Hanf: Berauschend Gut