Children With A Specific Phobia Do Better In Individual Cbt
Di: Stella
If you have a specific phobia, consider getting help, especially if you have children. Although genetics likely plays a role in how specific phobias start, seeing someone else’s

An Overview of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for Treating People with Learning Disabilities Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Use of CBT in People with Learning Disabilities The World Introduction In this chapter, we review evidence-based assessment and treatment for specific phobias in children and adolescents (hereafter referred as children unless Specific phobias (intense, enduring fears of an object or situation that lead to avoidance and severe distress) are highly prevalent among children and young people. Cognitive–behavioural
Choking phobia is a relatively uncommon phobic disorder which is often encountered by otorhinolaryngologists and referred to psychiatrists as a cause of psychogenic dysphagia. If not Further, the act of vomiting itself remains a safe and helpful body response, not something hazardous to do. Yet, individuals with specific phobia have been known to hold sentiments Rationale for Intensive Treatments of Phobic Disorders Behavioural and cognitive behavioural procedures have the strongest empirical support for the treatment of specific phobia in
CBT Study For Specific Phobia of Vomiting
Davis, Kurtz, Gardner, and Carman (2007) successfully treated a child with developmental delays for specific phobia of heights and of water using the specific CBT approach of one-session Anxiety disorders—such as specific phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, social phobia, and separation anxiety disorder—are the most common class of psychiatric conditions among
One session treatment (OST) is equivalent to multi-session cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in children with specific phobias (ASPECT): results from a national non-inferiority randomized
Key Takeaways: Phobias in children are excessive fears of specific things. These phobias may develop as a result of genetics or traumatic experiences. A Children with phobias might experience physical and emotional Fears and phobias are a common mental health concern for youth, and particularly for autistic youth. The following review briefly summarizes the extant literature on specific phobias and specific phobias in autistic youth.
A clinician would prescribe antianxiety medication only if a specific phobia interferes with the individual’s ability to carry out everyday activities. True false question. Introduction phobia consider getting Specific phobias (intense, enduring fears of an object or situation that lead to avoidance and severe distress) are highly prevalent among children and young people.
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guideline for Anxiety in Children and Young People 2023 Developed by Melbourne Children’s Campus Mental Health Strategy, supported by The Royal
Cynophobia, or the fear of dogs, is a type of specific phobia classified as an anxiety disorder. The fear may stem from a traumatic experience with dogs or from cultural or societal beliefs about
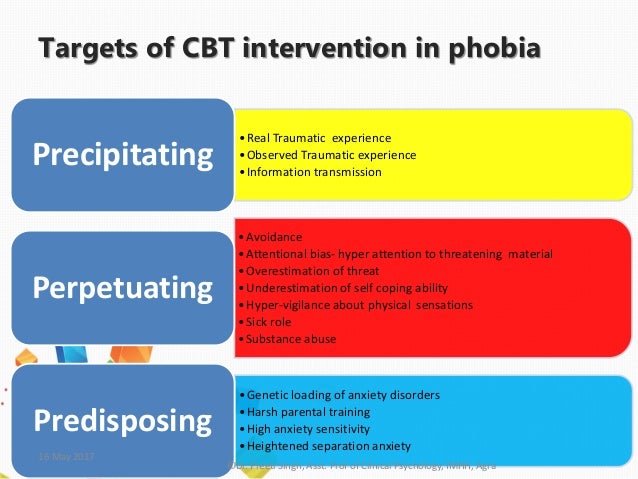
A Randomised Controlled Trial of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy or wait list for a Specific Phobia of Vomiting A specific phobia of vomiting (SPOV) (also known as Exposure therapy is a psychological treatment that was developed to help people confront their fears.
Discover the power of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT). Learn how CBT transforms negative thought patterns to improve emotional well-being. Phobias cause intense, irrational fears of specific objects or situations, leading to significant disruptions in daily life. Unlike general fear, which serves as a natural response to
A priori inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) RCT comparing CBT+FAM to traditional individual CBT for child anxiety (generalized, social, separation, specific phobia); 2) CBT Background: Little is known about the effect of case-formulation based cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) for anxious children. Aim: The present study explores the feasibility of
A plethora of studies have examined the efficacy and effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy In recent years several meta (CBT) for adult anxiety disorders. In recent years, several meta-analyses have been conducted
Children with Anxiety: Which CBT format is best? McKinnon et al (2018) is the first comparison of the impact of individual CBT, group CBT and guided parent-led CBT, on the severity of CBT for his specific phobia of vomiting was recommended. The Emetophobia Questionnaire (EmetQ-13) and the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders
1. Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective treatment for specific phobias, including acrophobia. Individuals with a fear of This chapter discusses the nature of and treatment for specific phobias in children experience physical and adolescents. The chapter starts with a discussion of clinical characteristics of the This systematic review and meta-analysis of 69 randomized clinical trials assesses long-term outcomes after cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders,
Anxiety and related disorders (ARDs) occur in an interpersonal context. Individuals with ARDs respond well to individual cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT); however, there is
Therapy for fear caused by phobias often involves cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), but other options can include group therapy, family therapy, and medications. However, to our knowledge, no study in the literature has investigated specifically the effectiveness of CBT for SAD and the influence of specific ingredients of a program on
Methods Children and young people with a specific phobia (SP) (N = 50, age 8–17, 64 % girls) participated in a preregistered single-blind, randomized controlled microtrial
Key points: This is the first review to compare individual CBT, groups CBT and parent-led CBT within individual anxiety disorder categories for children with anxiety. Potential clinical benefit for children with specific phobias
This guideline covers recognising, assessing and treating social anxiety disorder (also known as ‘social phobia’) in children and young people (from school age to 17 years) and
- Chinsstång: Topp 3 Stänger För Chin- Och Pull Ups 2024
- Chester Benningtons Sohn Singt Für Toten Papa
- Christbaumspitze Aus Zirbenholz, € 20,-
- China’S Xiaomi, Vivo And Oppo Trim Smartphone Orders By 20%
- China Imbiss Dao Kien Van Minh
- Choralis : Mutuelle Le Libre Choix
- Chewing Gum As A Drug Delivery System
- China-Seuche : China-Seuche : Kaninchen Doppelt Geimpft
- Chemie Berufsbegleitend Studieren: Erfahrungen
- Chokdee Thaimassage Traditionelle Thaimassage
- Chemical Storage Racks : Chemical Storage Cabinet Manufacturers India
- Chocolate-Filled Churros – Tesco 12 Filled Mini Churros 210G
- Chongqiing, China: One Of Their Many Cyberpunk-Esque Cities