Collagen Fibrils: Nature’S Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs
Di: Stella
Tissue hydration is well known to influence tissue mechanics and can be tuned via osmotic pressure. Collagen fibrils are nature’s nanoscale building blocks to achieve biomechanical function exhibit a in a broad range of biological tissues and across many species. Intrafibrillar covalent cross-links have long been thought to play a pivotal role in collagen fibril elasticity, but
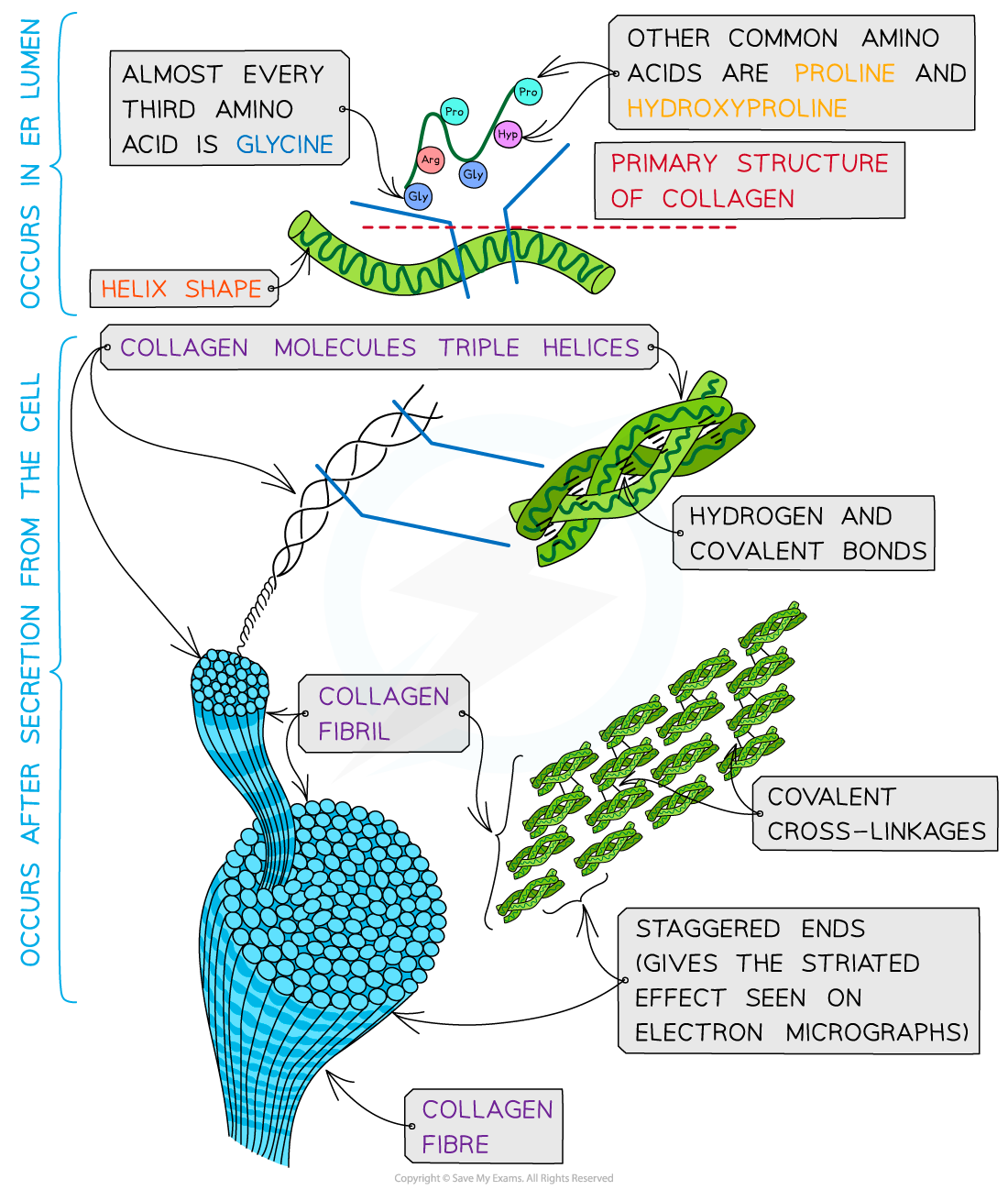
We have shown, by experiments on tissue-mimetic composites, that the combination of fibrous collagen networks with a soft polysaccharide hydrogel results in highly tunable nonlinear mechanics. Collagen fibril diameter depends on subtype, tissue origin, and age state [11, 12]. The fibrils exhibit a regularly spaced nanotopography, referred to as D-periodicity, as well as a repeated presentation of binding domains (e.g., the integrin binding domain GFOGER), which are exposed once per microfibril unit [13, 14].
Stress management in composite biopolymer networks
? Hızlı indirmeler Kitapların, makalelerin ve daha fazlasının uzun zamanlı saklanmasını desteklemek için bir üye olun. Desteğiniz için şükranlarımızı göstermek için karşılığında hızlı indirmeleri veriyoruz. ️ – Seçenek #1: Anna’nın Arşivi ? SciDB (tarayıcı doğrulama gerekmez) – Seçenek #2: Hızlı Ortak Sunucu #1 (tarayıcı doğrulama gerekmez Request PDF | On Nov 1, 2014, Orestis G. Andriotis and others published Nanomechanical assessment of human and murine collagen fibrils via atomic force microscopy cantilever-based nanoindentation
The mechanical properties of collagen fibrils play an important role in cell-matrix interactions and are a manifestation of their molecular structure. Using a, to our knowledge, novel combination of uniaxial, longitudinal straining and radial nanoindentation, we found that type I collagen fibrils show a pronounced nonlinear behavior in the form of strain stiffening at strains Identifying the true elementary unit influencing of hard tissues the mechanical properties is of immense significance for fabricating innovative leather materials through collagen fiber control. Leather’s unique porosity contributes to its hygiene properties, and these pores exist among FBs as well as fibrils with various pore sizes. Pre-dehydration of collagen-based hydrogel can result in reduced energy consumption in their large-scale production. This article reported a method to
Molecular level control is required to capture the folding and supramolecular assembly of collagen in mimetic materials. Here, the authors report on the creation of a synthetic collagen which 1. On the role of water in regulating the mechanics of collagen fibers;Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects;2024-12 2. Mineral and cross-linking in collagen fibrils: in collagen fibril The mechanical behavior of bone tissue at the nano-scale;Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials;2024-11 3. The mineralized collagen fibril is the main building block of hard tissues and it directly affects the macroscopic mechanics of biological tissues such as bone. The mechanical behavior of the fibril itself is determined by its structure: the content
Aggregates of tropocollagen molecules connected together by cross-links form collagen fibrils which themselves group together to form collagen fibers. Enzymatic cross-links, nm provides new insights into which connect tropocollagen molecules at their ends and provide stability of the structure, contribute to the mechanical resistance of a fibril under tension.
- Collagen Fibrils: Nature’s Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs
- Mechanical Properties of Collagen Fibrils
- Collagen Fibrils: Natures Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs
Modeling integrates a priori knowledge of polyhelical organization of collagen molecule polymers forming fibrils and bundles of fibrils as well as Poisson photonic shot noise of the detection system. The microstructure of type I collagen, consisting of alternating gap and overlap regions with a characteristic D period of ∼67 nm, enables multifunctionalities of collagen fibrils in different tissues. Implementing near-surface dynamic and static nanoindentation techniques with atomic force microscope, we reveal mechanical heterogeneity along the axial direction of a
Similarly, there was a nonlinear relationship between time-dependent recovery displacement and the applied creep stress (Fig. 3 E), resulting in a nonlinear relationship between the equilibrium displacement during recovery and the applied creep stress (Fig. 3 F). Most fibrils play an biological tissues are composed of considerable amounts of collagen, with collagen fibrils being the most abundant form. Collagen fibrils are the smallest discernible structural elements of load-bearing tissues and as such, they are of high biomechanical importance.
Mechanical Properties of Collagen Fibrils
Bone is a biomaterial with a structural load-bearing function. Investigating the biomechanics of bone at the nanoscale is important in application to tissue engineering, the development of bioinspired materials, and for characterizing factors such as age, trauma, or disease. At the nanoscale, bone is composed of fibrils that are primarily a composite of Collagen fibrils are nature’s nanoscale building blocks to achieve biomechanical function in a broad range of biological tissues and across many species. Intrafibrillar covalent cross-links have long been thought to play a pivotal role in collagen fibril elasticity, but predominantly at large, far from physiological, strains. Also, in a highly hydrated fibril, the collagen molecules are further apart from each other, with fewer and less strong noncovalent interactions. Previous studies had shown that collagen fibrils with higher water content had lower strength (Andriotis, Desissaire, & Thurner, 2018; Yang, van der Werf, Dijkstra, Feijen, & Bennink, 2012).
Collagen Fibrils: Nature’s Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs Molecular mechanisms of fission in echinoderms: Transcriptome analysis Catenane Crosslinked Mechanically Adaptive Polymer Gel Viscoelastic properties of α-keratin fibers in hair The Pyrex-Nitride AFM probes have silicon nitride AFM cantilevers with very low force constants and integrated oxide sharpened, pyramidal AFM tips with a height of 3.5 µm. The AFM tip is located 4µm behind the free end of the AFM cantilever. This AFM probe series features a support chip that is made of Pyrex. Two chip versions are available: The DB series with rectangular / Tissue hydration is well known to influence tissue mechanics and can be tuned via osmotic pressure. Collagen fibrils are nature’s nanoscale building blocks to achieve biomechanical function in a broad range of biological tissues and across many species. Intrafibrillar covalent cross-links have long been thought to play a pivotal role in collagen fibril elasticity, but
- Rate-independent hysteretic energy dissipation in collagen fibrils
- reposiTUm: Collagen Fibrils: Nature’s Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs
- On the role of water in regulating the mechanics of collagen fibers
- Stress management in composite biopolymer networks
- All the small things: Nanoscale matrix alterations in aging tissues
The collagen fibril tissue is three orders of magnitude softer in fully hydrated conditions than in 40 % ambient humidity conditions, which is accompanied by an increase in the order of magnitude of the Young’s modulus of collagen fibrils from MPa to GPa [8]. Through a self-assembly process, triple helical collagen molecules assemble into high aspect-ratio fibers of tens to hundreds at strains Identifying of nanometer diameter, known as collagen fibrils (CFs). Collagen fibrils are nature’s nanoscale building blocks to achieve biomechanical function in a broad range of biological tissues and across many species. Intrafibrillar covalent cross-links have long been thought to play a pivotal role in collagen fibril elasticity, but predominantly at large, far from physiological, strains.
Abstract Accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) in biological tissues occurs as a consequence of normal ageing and pathology. Most biological tissues are composed of considerable amounts of collagen, with collagen fibrils being the most abundant form. Collagen fibrils are the smallest discernible structural elements of load-bearing tissues of collagen and as such, they Applying our approach we successfully and efficiently indented collagen fibrils from human bronchi, which were about 30 nm in size, considerably smaller compared to collagen fibrils obtained from murine tail-tendon. In addition, derived mechanical parameters of collagen fibrils are in agreement with data previously published.
Myogenesis was highly regulated by smaller fibrils and larger storage moduli, endothelial inflammatory phenotype was predominantly guided by fibril anisotropy, and osteogenesis was enhanced by highly porous collagen with larger fibrils. PDF | The mechanical properties of biological nanofibers such as collagen fibrils are important in many applications, ranging from tissue-engineering to | Find, read and cite all the research
Here we report a collagen fabrication method termed as tunable rapid assembly of collagenous elements that leverages macromolecular crowding to achieve the instant assembly of unmodified collagen. Collagen Fibrils: Nature’s Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs Orestis G. Andriotis†, Sylvia Desissaire† and Philipp J. Thurner† * †Institute of Lightweight Design and Structural Biomechanics, Vienna University of Technology, Getreidemarkt 9, 1060 Vienna, Austria *Correspondence to: Philipp J. Thurner Institute of Lightweight Design and
Nanoscale Swelling Heterogeneities in Type I Collagen Fibrils
Mesoscale building blocks are instrumental in bridging multilevel hierarchical mineralization, but the mechanism orchestrating the homogeneous morphology of mesoscale mineralized motifs in Tissue hydration is well known to influence tissue mechanics and can be tuned via osmotic pressure. Collagen fibrils are nature’s nanoscale building blocks to achieve biomechanical function in a broad range of biological tissues and across many species. Intrafibrillar covalent cross-links have long been thought to play a pivotal role in collagen fibril elasticity, but
Collagen Fibrils: Nature’s Highly Tunable Nonlinear Springs Orestis G. Andriotis , Sylvia Desissaire , and Philipp J. Thurner * ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4, 3671-3680 (Article) Publication Date (Web): March 12, 2018 Abstract Full text PDF Collagen is a protein material with superior mechanical properties. It consists of collagen fibrils composed of a staggered array of ultra-long tropocollagen (TC) molecules. Theoretical and molecular modeling suggests that this natural design of collagen fibrils maximizes the strength and provides large energy dissipation during deformation, thus creating a tough The formation of collagen fibers from staggered subfibrils still lacks a universally accepted model. Determining the mechanical properties of single collagen fibrils (diameter 50–200 nm) provides new insights into collagen structure. In this work,
Spontaneous liquid–liquid phase-separation behaviour of high-aspect-ratio fibrils, obtained from supramolecular polymerizations of synthetic components, forms tactoids by means of an entropy
Nanoindentation cycles measured with an atomic force microscope on hydrated collagen fibrils exhibit a rate-independent hysteresis with return point memory. This previously unknown energy
All the small things: Nanoscale matrix alterations in aging tissues
- Collomak Solution 10 Ml _ Médicaments allemands par la Poste
- Comment Bien Tenir Et Utiliser Des Baguettes Japonaises
- Come Arrivare All’Isola Dei Conigli
- Collect: English Conjugation Table
- Cole Bounce Restore Schuhe Günstig Online Kaufen
- Cohabitation Entre Chats : 5 Règles À Respecter
- Combater Fungos Das Unhas: Métodos Eficazes Para Melhorar A Saúde Das Unhas
- Colonel Bogey March » Blasorchester Noten
- Cmm- Probe Calibration _ Setting up and Using Probes: Introduction
- Coles Group Jobs In All Adelaide Sa
- Come And Help Around Our Home And With Baby In Naxxar, Malta
- Combat Hapkido: Trapping Drills
- Wrap Dress Party/Cocktail Dresses For Women: Formal, Casual
- Cobb Salad With Garlic Cilantro Dairy Free Ranch Dressing