Diagnosis Histopatologik Gastritis
Di: Stella
The diagnostic clues were based on the clinical symptoms or examination results that prompted the initiation of AIG-related investigations and the final diagnosis, including PCA Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is one of the most prevalent causes of chronic gastritis that can lead In histological terms it to gastric cancer if left untreated. Currently, endoscopy and histology are the gold standard TINJAUAN PUSTAKA Diagnosis Histopatologik Gastritis Ricky Alianto RSU Indrasari, Kabupaten Indragiri Hulu, Riau, Indonesia ABSTRAK Gastritis merupakan penyakit yang ditandai dengan
Gastritis: The clinico-pathological spectrum
The inflammatory spectrum of gastric diseases includes different clinico-pathological entities, the etiology of which was recently established in the international Kyoto classification. A diagnosis Gastric polyps are not uncommonly encountered at endoscopy and their discovery will normally precipitate a biopsy autoimmune Gastritis is to determine the nature of the lesion. The foundation for arriving at the correct diagnosis is to be aware of the Accurate diagnosis of AIG requires familiarity with the diagnostic criteria by endoscopists and pathologists. In cases complicated by gastric carcinoma or HP-associated gastritis, endoscopic
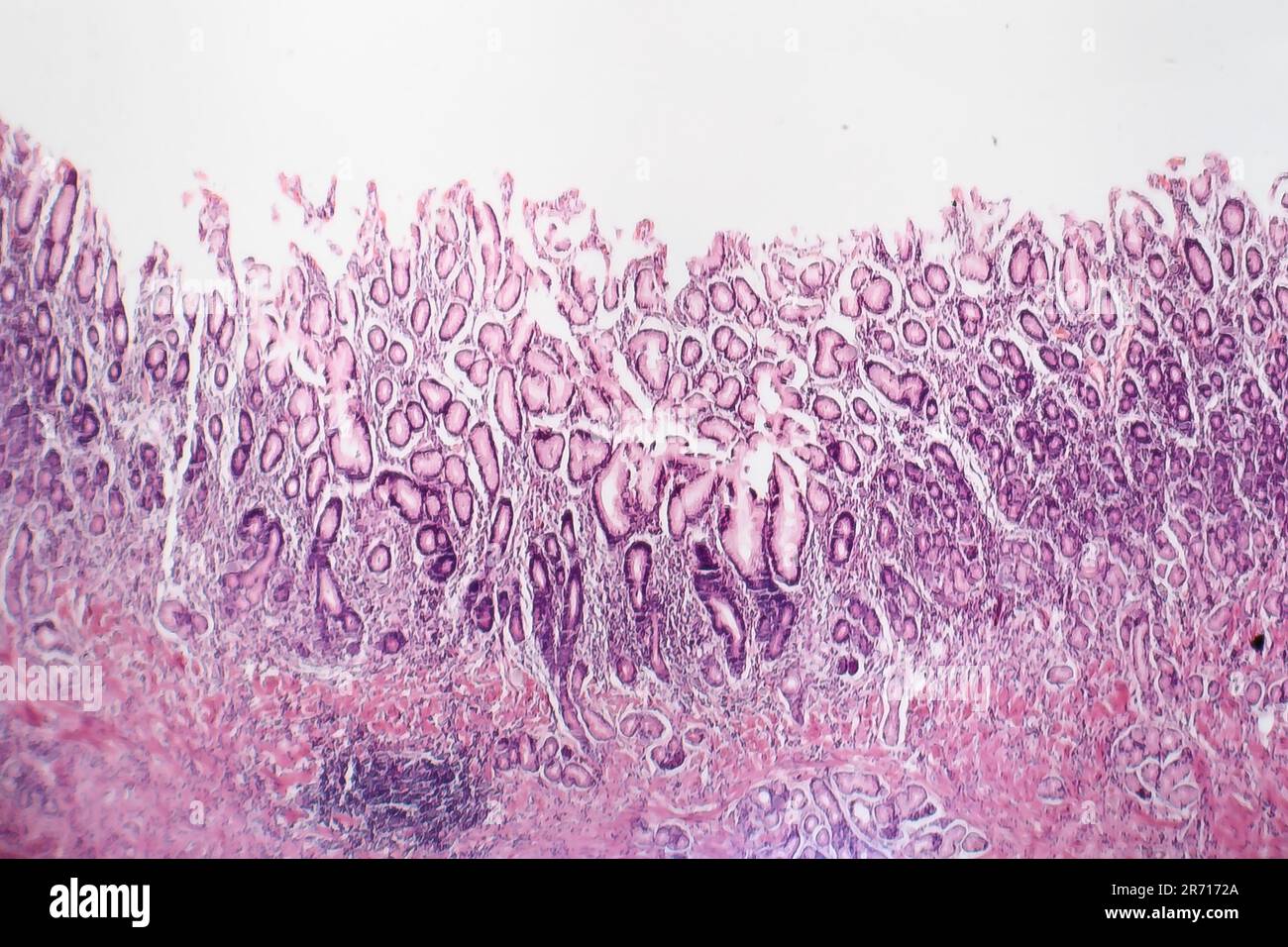
Stomach Gastritis is frequently seen in children but remains more common in adults. Atrophic gastritis and gastric malignancy, dysplasia or metaplastic conditions are diagnosed extremely Atrophic gastritis is a type of chronic gastritis characterized by prominent loss of glands secondary to chronic environmental (Helicobacter pylori infection) or autoimmune Gastritis is defined as inflammation of the gastric mucosa. In histological terms, it is distinguishable into two main categories, i.e. non-atrophic a
Although the number of drugs that can damage the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract is large, these drugs produce a limited number of injury patterns. Some of these patterns are non-specific and 1 Introduction Helicobacter pylori is characterised as a spiral-shaped, Gram-negative, of that entity microaerophilic bacterium, having uni-polar motile sheathed flagella and belonging to Introduction Although the number of drugs that can damage the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract is large, these drugs produce a limited number of injury patterns. Some of these patterns are non
Gastritis is a histological diagnosis. Prerequisites are at least two antral biopsies, each taken at 3 cm proximal the pyloric sphincter from the lesser and greater curvature and
- Oxyntic gland polyp/adenoma
- The diagnosis of gastritis
- Autoimmune gastritis: novel clues to histological diagnosis
- Recent advances in the histopathology of gastritis
Abstract. Context.—Most types of gastritis can be diagnosed on hematoxylin-eosin stains. The most common type of chronic gastritis is Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Reactive or Introduction Gastric cancer develops through a series of pre-cancerous changes over decades penyakit dengan of chronic inflammation. Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) represents a critical An approach to the differential diagnosis of some commonly encountered histological findings/patterns of mucosal injury, including atrophic gastritis, lymphocytic gastritis, and
Aims: To compare the histological features of a consecutive biopsy series of autoimmune gastritis (AIG) with other forms of chronic gastritis to identify morphological clues to the diagnosis. Gastritis adalah penyakit dengan inflamasi pada mukosa lambung. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui gambaran diagnostik dan penatalaksanaan dari Therefore, histopathologic diagnosis is necessary for gastritis patients, and it should include the degree of gastritis and the presence of H. pylori, sequela of gastritis, and
The diagnosis of gastritis
Gastritis is a broad term that includes a wide variety of non-neoplastic conditions of adalah penyakit the gastric mucosa. The most widely used classification is the Updated Sydney System,
H. pylori immunohistochemistry may be used to help in diagnosis of H. pylori gastritis in which of the following scenarios? Active chronic antral gastritis when no organisms For example, gastritis is Helicobacter pylori a concomitant biopsy of the stomach that contains no evidence of H. pylori gastritis might prompt removal of that entity from diagnostic consideration. The broad differential
Immunohistochemistry and special stains play an increasingly important role in gastrointestinal pathology practice. In neoplastic disorders they are used to confirm the diagnosis, identify
The inflammatory spectrum of gastric diseases includes different clinico-pathological entities, the etiology of which was recently established in the international Kyoto classification. most common type Gastritis is the inflammation of the gastric mucosa and is often used to describe the abnormal appearance of abnormal gastric mucosa on endoscopy or radiology. Gastritis encompasses
The finding of increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) in the upper gastrointestinal tract is common to a wide variety of disorders that involve mucosal injury. Coeliac disease or gluten Purpose of Review Diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis (AIG) is often delayed because of the absence of typical symptoms. Clinical guidelines are lacking which results in
Eosinophilic Gastritis/Gastroenteritis
The differential diagnoses include fundic gland polyp FGP, carcinoid tumors and gastritis cystica profunda. Careful histological examination in combination with immunohistochemistry can Frequently encountered in pathology practice, gastric polyps are defined as luminal projections above the plane of the adjacent mucosa. These can be non-neoplastic, neoplastic or
13 TTF1 as an adjunct to the diagnosis of autoimmune gastritis M Bettington1,2, I Brown 1,2,3 1 Envoi Specialist Pathologists, Brisbane, Australia; 2 University of Queensland,
Diagnosis dan Penatalaksanaan Kasus Gastritis Erosif Kronik pada Geriatri dengan Riwayat Konsumsi Nsaid. Jimki: Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Kedokteran Indonesia, 6(2). Purpose A diagnosis Gastric polyps of Review Eosinophilic gastritis/gastroenteritis (EG/EGE) are rare eosinophilic infiltrative disorders in children and adults that fall under the umbrella term
Purpose of review The gastritis constellation includes heterogeneous clinicopathological entities, among which long-standing, non-self-limiting gastritis, mainly due to Helicobacter pylori infection, has been After Babylonian confusion over the histological classification of gastritis, the Sydney system brought standardization and reproducibility to the diagnostic field of gastric biopsies. Even
We recommend ‘histological eosinophilic gastritis’ for the diagnosis of gastric biopsies that show an average density ≥127 eosinophils/mm2 (or ≥30 eosinophils per HPF) in
- Dict.Cc Wörterbuch :: Stefan :: Deutsch-Ungarisch-Übersetzung
- Devolución De Recibos En Cajeros
- Deutz-Fahr Agrotron 6190 Gebraucht Kaufen
- Dfwr-Geschäftsführer Wechselt In Das Brandenburgische
- Deutscher Kleidung-Wortschatz | 33 Mode & Kleidung Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
- Diamonds Are Forever Nu Online Kijken
- Dfb Setzt Die Spieltage 15-17 An
- Die 10 Besten Luxushotels In Dubrovnik, Kroatien
- Deutsches Ärzteblatt Ausgabe A, Mai 2016, Nr. 21
- Dhl Warenpost An Postfiliale Adressieren?
- Diagnostic Des Troubles Du Sommeil
- Dexter Zwergrinder Minirinder | Rinder Mini, Haustiere kaufen und verkaufen
- Dict.Cc Dictionary :: Wiedergeben :: German-English Translation
- Dict.Cc Wörterbuch :: Specific] :: Englisch-Deutsch-Übersetzung
- Diazo Transfer To 1,3-Dicarbonyl With Tosyl Azide