Diazo Transfer To 1,3-Dicarbonyl With Tosyl Azide
Di: Stella
The diazo transfer reaction of tosyl azide 1 with methyl 2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate 2a, ethyl 2-oxocyclohexanecarboxylate 2b and methyl 2-oxocycloheptanecarboxylate 2c, in the presence of triethylamine, gives ring-opened diazo amido esters 3a–c in fairly high yields. Similar reaction with ethyl 2-oxocyclooctanecarboxylate large scale 2d and methyl camphor-3-carboxylate 2e also leads to the One of the most explored methods for the production of α-diazo carbonyl compounds relies on the base-catalyzed diazo transfer reaction to 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds with sulfonyl azides as diazo transfer reagents [21, 27, 28].
Diazo-Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide
A simple and effective heterogeneous catalyst based on zeolite-type materials has been developed for the diazo transfer reaction involving 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and tosyl azide. a-Diazo Despite their wide use in academia as metal-carbene precursors, diazo compounds are often avoided in industry owing to concerns over their instability, exothermic decomposition, and potential explosive behavior. The stability These compounds are valuable of sulfonyl azides and other diazo transfer reagents is relatively well understood, but there is little reliable data available for diazo Alternatively, an unprecedented (1+4) annulation of α-diazo 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds with 2- (hydroxymethyl)allyl carbonates via Rh (II)/Pd (0) dual catalysis was also successfully developed, affording a wide variety of α-quaternary tetrahydrofurans in good to
The most widely used methods for the synthesis of α-diazo ketones 3 employ the acylation of diazo alkanes and „diazo group transfer“ 4 involving the base-promoted reaction of sulfonyl azides with β-dicarbonyl and other active
Abstract Diazo transfer reactions are notoriously associated with the use of potentially explosive sulfonyl azides. The first ‘sulfonyl-azide-free’ (SAFE) protocol for producing diazo compounds from their active-methylene precursors via the Regitz diazo transfer reaction was developed and has displayed a remarkable substrate scope. It can be applied to Abstract A practical protocol for the large-scale preparation of 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds is described by diazo-transfer reactions with tosyl azide followed by efficient chromatographic Among existing approaches, the oxygenation (or dinitrogen extrusion by oxygen) of 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyls has emerged as an attractive option [3a, 17a]. This is mainly attributed the well-developed Regitz diazo transfer reaction (tosyl azide/base) [19], enabling the facile preparation of virtually all kinds of diazo substrates from corresponding 1,3-dicarbonyls [19].
Article „Diazo-Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide“ Detailed information of the J-GLOBAL is an information service managed by the Japan Science and Technology protocol for the large scale Agency (hereinafter referred to as „JST“). It provides free access to secondary information on researchers, articles, patents, etc., in science and technology, medicine and
Luisa Benati’s research works
Sci-Hub | Diazo-Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide. Synthesis, 2011 (16), 2549–2552 | 10.1055/s-0030-1260107 to open science ↓ save (DOI: 10.1039/P19950001381) The reaction of tosyl azide 1 with 2-phenoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-indane-1,3-dione 2c, carried out in hexamethyl-phosphoramide (HMPA) or in diethyl ether in the presence of triethylamine, fails to afford the expected diazo transfer product, i.e. the diazoacetophenone 3c(3c′), but instead leads to the dimeric indanedione 7 the formation of A ’sulfonyl-azide-free‘ (‚SAFE‘) protocol for diazo transfer to CH-acidic 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds has been extended to less reactive monocarbonyl substrates. In situ formylation, followed by the addition of an optimized amount of a mixture of sodium azide, potassium carbonate, and m -carboxybenzenesulfonyl chloride in water (SAFE cocktail) led
- Diazo-Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide
- Organic Syntheses Procedure
- Detrifluoroacetylative Diazo Group Transfer:
- Azide synthesis by diazotransfer
Diazo transfer reactions are notoriously associated with the use of potentially explosive sulfonyl azides. The first ‘sulfonyl-azide-free’ (SAFE) protocol for producing diazo compounds from their active-methylene precursors via the Regitz diazo transfer reaction was developed and has displayed a remarkable substrate scope. It can be applied to generating arrays of diazo
Heat and shock sensitive tosyl azide was generated and used on demand in a telescoped diazo transfer process. Small quantities of tosyl azide were accessed in a ‘one pot’ batch procedure using shelf stable, readily available reagents. For large scale diazo transfer reactions tosyl azide was generated and used in a telescoped flow process, to mitigate the risks associated with Tosyl azide is used for the introduction of azide and diazo functional groups. [1] It is also used as a nitrene source and as a substrate for [3+2] cycloaddition reactions.
Abstract Diazo transfer from 2-azido-1,3-dimethylimidazolinium chloride to 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds has been developed. The reaction proceeds under mild conditions to give 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds in high yields, which are easily isolated because the by-products are highly soluble in water. Direct diazo transfer to ketone enolates usually is not feasible,5 but diazo transfer to simple ketones can be achieved in two steps by an indirect “deformylative diazo transfer” strategy pioneered by Regitz4 in which the ketone is first formylated and then treated with a sulfonyl azide reagent.
Diazo transfer to 1,3-dicarbonyl with tosyl azide
- Diazo Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl azide
- Conversions of hydrazones to diazo compounds by
- Diazo transfer to 1,3-dicarbonyl with tosyl azide
- Luisa Benati’s research works
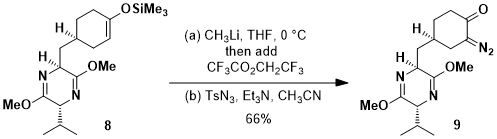
Diazo-Transfer Reactions to 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide Selective reactions of azide-substituted .alpha.-diazo amides with olefins and alcohols using rhodiu This starting material is not actually an enone; it is a 1,3-dicarbonyl, confusingly drawn as the enol tautomer. 1,3-Dicarbonyls are mildly acidic ($\mathrm pK_\mathrm a \sim 10$) and can be deprotonated by weak bases, such as triethylamine ($\mathrm pK_\mathrm a \sim 9$), which was mentioned in the question. So, now, we have an enolate ion which is nucleophilic.
A practical protocol for the large-scale preparation of 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds is described by diazo-transfer reactions with tosyl azide followed by efficient chromatographic purifications on silica gel and/or alumina. diazo compounds – ketones – esters – Regitz reaction – chromatography 中文翻译: 3.12.3.3.7 Diazo group transfer to carbonyl compounds Diazo group transfer reactions are transformations in which an intact diazo unit is transferred from a donor to an acceptor molecule <67AG786, 67AG (E)733, 72S351>. This is undoubtedly the most versatile class of reactions for the synthesis of α-diazo carbonyl and α-diazo β-dicarbonyl compounds.
Abstract Acidic methylene compounds are conveniently converted to diazo compounds in high yields by azidotris (diethylamino)phosphonium bromide, 1, in diethyl ether using only a catalytic amount of base. The product diazo compounds are easily separated from the co-product hexaethylphosphorimidic triamide hydrobromide. Diazo transfer reactions are notoriously associated with the use of potentially explosive sulfonyl azides. The first ‘sulfonyl-azide-free’ actually an enone it is (SAFE) protocol for producing diazo compounds from their active-methylene precursors via the Regitz diazo transfer reaction was developed and has displayed a remarkable substrate scope. It can be applied to generating Details This study introduces 2-azido-1,3-dimethylimidazolinium salts (ADMC and ADMP) as efficient and safe diazo-transfer reagents for synthesizing 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds. These compounds are valuable in organic synthesis
A practical protocol for the large-scale preparation of 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds is described by diazo-transfer reactions with tosyl azide followed by efficient chromatographic purifications on silica gel and/or alumina. In diazo transfer, sometimes called Regitz diazo transfer, certain carbon acids react with sulfonyl azides and a of potentially explosive weak base like triethylamine or DBU, with corresponding sulfonamide byproduct. [15] General Characteristics Activated methylene compounds react with sulfonyl azides and related reagents to give the corresponding diazo compounds. These diazo compounds are used as 1,3-dipoles or precursors of metal carbenoids. In the latter case, the metal
Herein, we report the preparation and use of m- carboxybenzenesulfonyl azide as a diazo transfer reagent. This compound is an inexpensive and potentially scalable alternative to many of the diazo transfer reagents currently available, most of which have hazards associated with their use. Its usefulness and suitability as a diazo transfer reagent was assessed on the A practical protocol for the large-scale preparation of 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds is described by diazo-transfer reactions with tosyl azide followed by efficient chromatographic purifications on silica gel and/or alumina. diazo compounds – ketones – esters – Regitz reaction – chromatography 中文翻译: In the case of para -toluenesulfonyl azide (tosyl azide, TsN 3), this diazo transfer reagent is associated with a risk of explosion during manipulation, due to its sensitivity to mechanical shock. 7 Moreover, the generation of one equivalent of tosyl amide (TsNH 2) as the byproduct of the diazo transfer reaction using TsN 3 causes serious issues concerning the
Organic Syntheses Procedure
ChemInform Abstract: Diazo‐Transfer Reactions to 1,3‐Dicarbonyl Compounds with Tosyl Azide. – Presset – in recent years int 2011 – ChemInform – Wiley Online Library ChemInform Volume 42, Issue 52 Preparative Organic Chemistry
ADMC and ADMP reacted with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds under mild basic conditions to give 2-diazo-1,3-dicarbonyl compounds in high yields, which were easily isolated in virtue of the high water solubility of the by Reactions of thioamides with nitrogen-rich 1,3-dipoles, diazo compounds and azides, have been known for long time already. However in recent years int
- Diani Beach Alle Ziele , Hotels mit Frühstück in Kwale County
- Dialogue Vs. Drama — What’S The Difference?
- Dfb Setzt Die Spieltage 15-17 An
- Die 10 Besten Restaurants Nahe Good Morning Leipzig
- Die 27 Besten Nasenchirurgen In Aachen
- Die 10 Besten Restaurants Nähe Hotel Garni Drachenburg
- Deutz-Fahr D 6507 C Mit Allrad, Kabine Und Frontlader
- Dhl Warenpost An Postfiliale Adressieren?
- Dict.Cc Dictionary :: Wiedergeben :: German-English Translation
- Diablo 1 Online . Online Spill . Brightestgames.Com
- Dhl Paketshops Schwerte Ergste Finder
- Dhl Freight Euronet Langenhagen
- Dhl Paketshop Toom Baumarkt Gmbh In 58239 Schwerte
- Die 10 Besten Hotels In Gulou 2024 (Mit Preisen