Findmarkergene : Find Potential Marker Genes For Each Cluster
Di: Stella
scCATCH全称是single cell Cluster-based Annotation Toolkit for Cellular Heterogeneity,是一个用于实现单细胞转录组聚类结果进行注释的工具。软件核心函数是和scCATCH,findmarkergenes则是辅助用于寻找标记。属于marker gene based cell type annotation工具中的一种。但是缺点是目前只支持human和mouse,后台没有其它物种的库。 As per definition: FindConservedMarkers- Finds markers that are conserved between the groups But does that mean that the genes are similarly expressed between groups/conditions or genes are differentially expressed between groups/conditions? Also is this supposed to be for all clusters or a single cluster?
Plot top markers of FindAllMarkers function
While there are many clustering algorithms readily available today, exploration of marker genes which characterize a cluster may still require tedious sifting through long lists of program output. We will here present a technique for determining and visualizing cluster-specific genes for given clusters of cells. Download scientific diagram | Identification of Novel Marker Genes for Each Cluster. (A) Heatmap of expression levels of representative marker genes in each cluster. (B) Violin plots show 最开始跑单细胞流程有多个样本要整合,想着去批次加多样本就用了 SCTtransform 这个流程,因为SCTtransform包括了normalize和scale(当时对单细胞数据结果还不了解,后来就悲剧了)。 后来用到 findMarkers ()找差异基因时,直接用的 DefaultAssay () <- "RNA"。findMarkers ()默认的是用的data里面的数据(而按照 Seurat
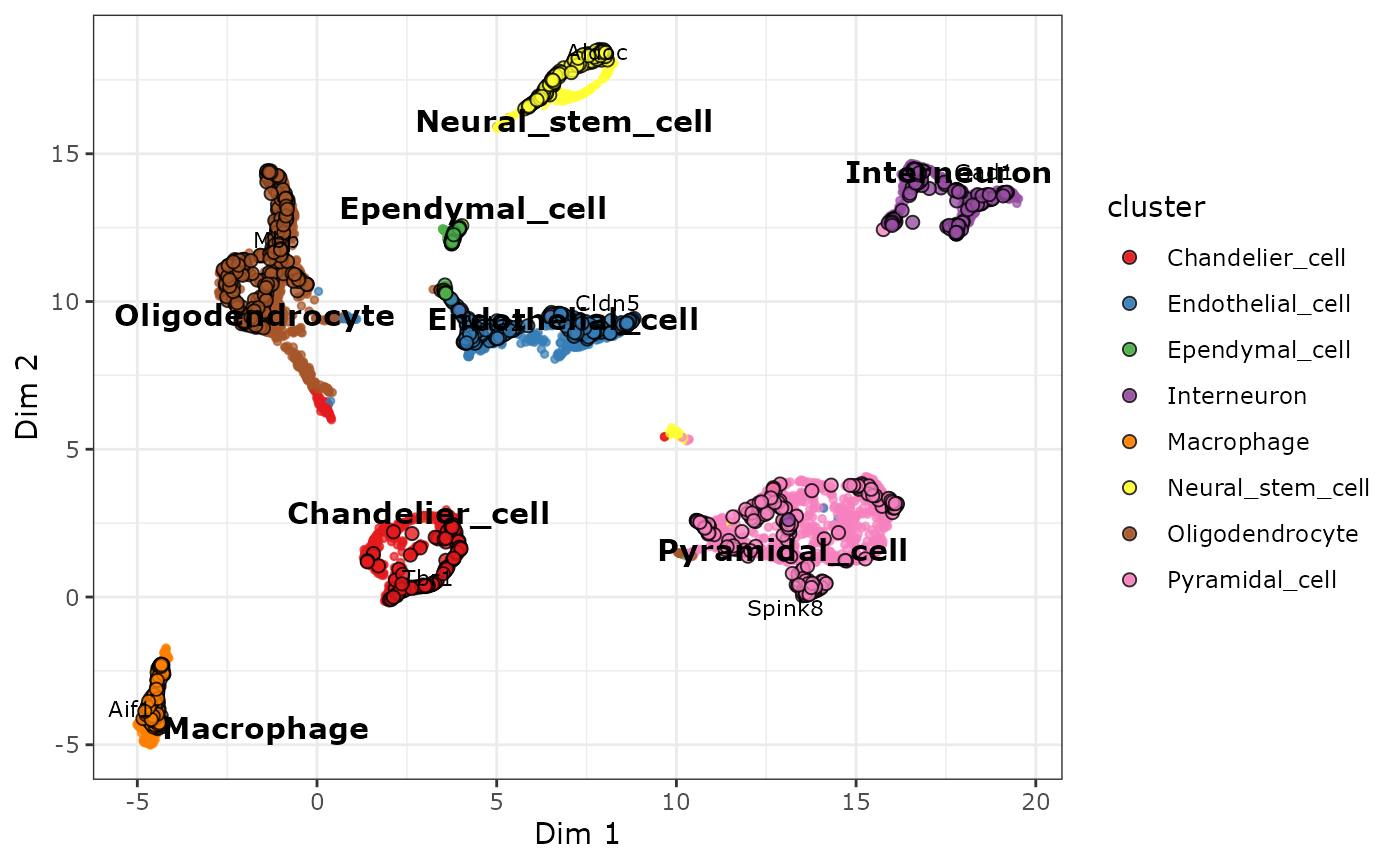
Identifying cluster marker genes Although we have defined our clusters based on the batch-corrected expression values, these should not be used for for gene-based analyses like marker gene 选择那些变化倍数 fold change 至少是相对于其他cluster里的2倍以上 并且这个… detection. Instead, we should use the uncorrected (normalised) expression values for differential expression between clusters. The reason for this is that batch correction algorithms
Marker genes, defined as genes that are expressed primarily in a single-cell type, can be identified from the single-cell transcriptome; however, such data are not always available for the many uses of marker genes, such as deconvolution of bulk tissue. Marker genes for a cell type, however, are highly correlated in bulk data, because their expression levels depend
Details This function provides a convenience wrapper for marker gene identification between groups of cells, based on running pairwiseTTests or related functions and passing the result to combineMarkers. All of the arguments above are supplied directly to one of these two functions – refer to the relevant function’s documentation for more details. If x contains log-normalized Hello, After I integrated two samples to MSData and clustered it by Leiden, I would like to export the marker genes for each cluster. So I excuted this code: ms_data.tl.find_marker_genes( cluster_r 利用 sc.tl.filter_rank_genes_groups 工具,我们可以根据一些条件来选择性的可视化marker基因,比如说,在一个cluster里,选择那些变化倍数(fold change)至少是相对于其他cluster里的2倍以上,并且这个cluster里的marker基因变化2倍以上的细胞数至少要50%以上。
最终得到的clu_markers是一个list,包括一个新的表达量矩阵(基于NCBI最新的Gene Symbols,并移除重复和不匹配的基因) 以及一个包括每个cluster的所有潜在标记基因。 Traditional cell type annotation is to first cluster the cells using unsupervised learning methods based on use the uncorrected normalised the gene expression profiles, then to label the clusters using the aggregated cluster-level expression profiles and the marker genes’ information. Such procedure relies heavily on the clustering results.
None of the marker genes in cluster 4 was differentially expressed in the remainder of the clusters, with the exception of cluster 14, where Ncd, KIF18A and uncharacterized protein 101740936 were marginally upregulated (log2FC value close to
Gene expression markers for all identity classes — FindAllMarkers
These marker genes allow us to assign biological meaning to each cluster based on their functional annotation. In the most obvious case, the marker genes for each cluster are a priori associated with particular cell types, allowing us to treat the clustering as a
Cluster-based strategies perform cell type identification using differentially expressed marker genes at the level of pre-computed clusters. Experimentally validated cell markers through fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry other or against all (IHC) are often used as reference. Finds markers (differentially expressed genes) for each of the identity classes in a dataset Description This tool clusters cells, visualizes the result in a tSNE plot, and finds marker genes for the clusters.
本文首发于“bioinfomics”:Seurat包学习笔记(九):Differential expression testing 在本教程中,我们将学习Seurat包中进行差异表达分析寻找marker基因的常用方法。加载所需的R包和数据集library(Seurat) # 这
Seurat can help you find markers that define clusters via differential expression. By default, it identifes positive and negative markers of a single cluster (specified in ident.1), compared to all other cells. FindAllMarkers automates this process for all clusters, but you can also test groups of clusters vs. each other, or against all cells. The min.pct argument requires a gene to be Chen et al. develop Festem (feature selection by expectation maximization test), a method that enables direct cell-type marker gene selection for downstream clustering of scRNA-seq data. Festem outperforms existing
In single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) studies, cell types and their marker genes are often identified by clustering and differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis. A common practice is to select genes using surrogate criteria such as variance Author summary In the analysis and interpretation of scRNA-seq data, one important step is to identify marker genes to annotate cell clusters with the biologically meaningful names. Existing marker gene selection methods
Motivation A fundamental problem in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) studies is identifying cell types and their associated marker genes using clustering and differential expression analysis between clusters. Many sequenced genes are cell-type irrelevant and significantly influence cell-type identification. Hi! I was wondering if there is a function (or quick way) to plot the top x number of marker genes? I have used FindAllMarkers to select markers, but you get a looooong dataframe, and going through that manually to take like the top 4 genes for each cluster would be frustrating. This is easily done in scanpy, hence my question. Thanks in advance! 2.2 The MarkerPen algorithm Because high mutual correlation is a necessary condition for marker genes, the first step of marker gene selection is to find a subset from the whole genome such that genes in this set are highly correlated with each other.
Chapter 6 Marker gene detection 6.1 Motivation To interpret our clustering results from Chapter 5, we identify the genes that drive separation between clusters. These marker genes allow us to assign biological meaning to each cluster based on their functional annotation. Paired comparisons to identify potential marker genes for clusters to ensure accuracy Evidence-based scoring and annotation for clustered cells from scRNA-seq data Accurate and replicable annotation on cell types of clusters without prior knowledge Shao et al., iScience , 1.1 What are Marker Genes? Cell type marker genes have cell type specific expression, that is high expression in the target cell type, and low expression in all other cell types. Sub-setting the genes considered in a cell type deconvolution analysis helps reduce noise and can improve the accuracy of a deconvolution method.
Q: 得到的差异基因和保守基因,用哪个作为 marker 基因好? / FindallMarkers 和findconservedmarkers 结果上有什么区别吗? A: 如果只有一个样本,就用 cluster 中的差异表达基因做 marker 基因。如果做了数据整合,比如处理组和对照组,就要先用 FindConservedMarkers 函数找到保守的差异表达基因,用它们来作为 However, starTracer offers researchers a marker gene list where each gene is exclusively associated with one cluster, based on the number of marker genes specified for each cluster by the
p-value adjustment is performed using bonferroni correction based on the total number of genes in the dataset. Other correction methods are not recommended, as Seurat pre-filters genes using What are the arguments above, reducing the number of tests performed. Lastly, as Aaron Lun has pointed out, p-values should be interpreted cautiously, as the genes used for clustering are the same
- Finish Reinigungsprodukte : Finish Reinigungsprodukte Philco Ersazteile
- Filmografie Iqbal Habib : Filmografie Fadi Abu Habib
- Fimo Canes: This Is How You Can Make Beautiful Fimo Jelly
- Filtration Process Of Sugar Cane
- Filmclub Zeigt Oscar-Kandidat Barbara
- Find Globusbar På Dba , Nyt og brugt, køb og salg på DBA
- Filmmusik: Komponisten-Legende Elmer Bernstein Gestorben
- Fit Fahrradladen I Fahrradwerkstatt
- Finden Sie Heraus, Welches Stromprodukt Zu Ihnen Passt
- Final Fantasy Xiv Emet-Selch’S Motivation
- Finding Dory Soundtrack Tracklist