Hi, Is Electromagnetic Radiation And Heat The Same Thing?
Di: Stella
Infrared A false-color image of two people taken in long-wavelength infrared (body-temperature thermal) radiation Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high-energy interactions like the radioactive decay of
Are EMF & Radio Waves The Same? Explained For Beginners
Discover the key differences between radiant heat and infrared radiation in our detailed is transferred in three ways article. While often confused, these two concepts have unique characteristics and
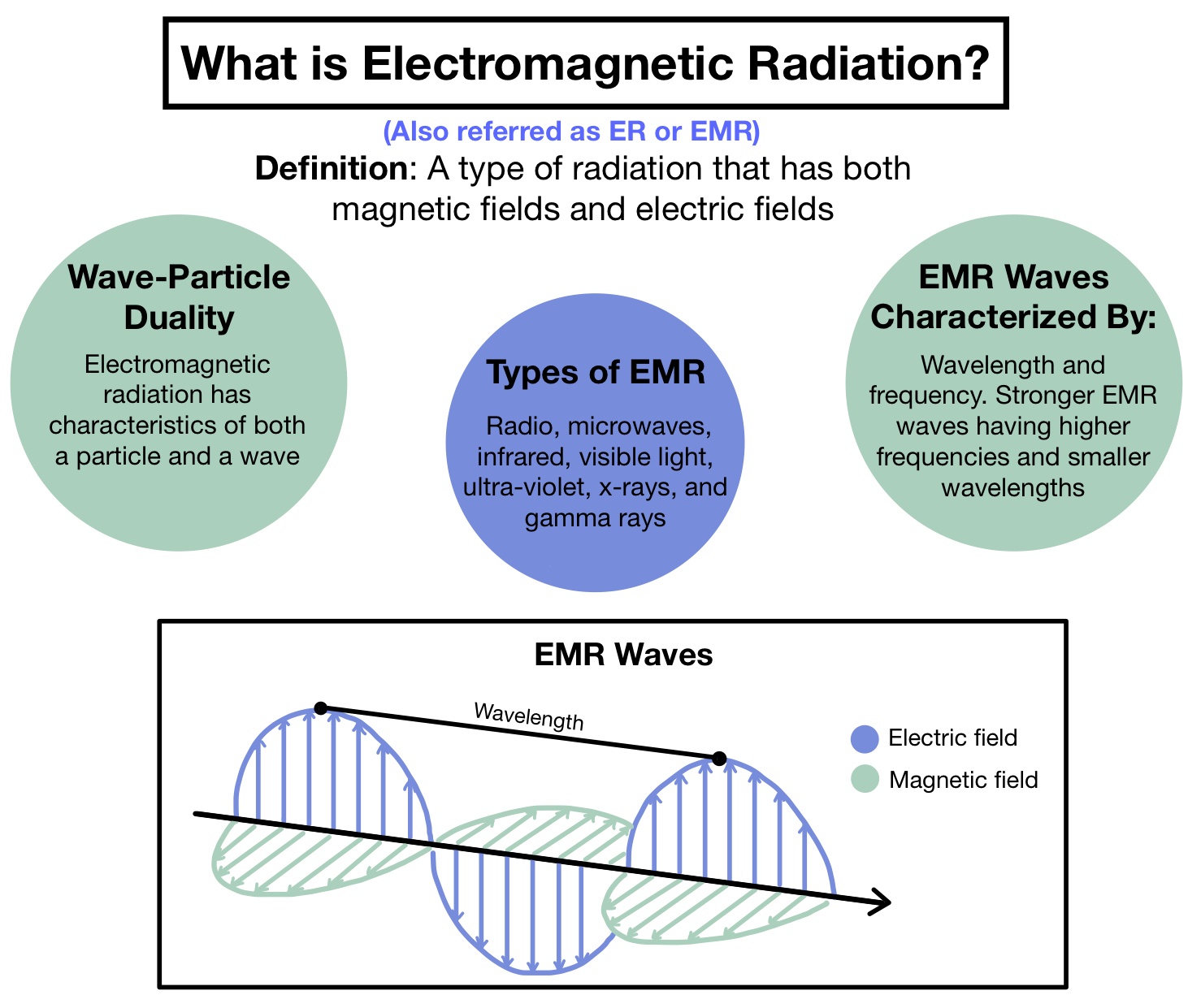
Energy from the Sun comes to us in the form of electromagnetic radiation, a term that refers to all the types of radiant energy emanating from stars (e.g., the Sun). Scientists classify different While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object
This is possible due to heat radiation, one of the three ways heat is transferred between objects. The nuclear processes that occur in the Sun produce heat, which then travels
They both mean “heat” to me so I was wondering if there’s any difference, specifically in the scope of high school physics. I looked it up and came across this: “Thermal radiation is all the
Yes, they are the same things. Radiant energy is energy that travels in waves through space and air. Radiation is the movement of energy through spaces as waves. Electromagnetic radiation from objects at different temperatures In fact all objects glow (emit electromagnetic radiation), and they do this in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Electromagnetic Radiation, Radiation, Electromagnetic and more. A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of
The heat energy from the sun is transferred to us via electromagnetic radiation. But do the electromagnetic waves actually carry heat, or do they just cause things to heat up by moving Electromagnetic Radiation vs. Light What’s the Difference? Electromagnetic radiation and light are closely related concepts, with light being a specific type of electromagnetic radiation that is Throughout the universe, it’s natural for energy to flow from one place to another. And unless people interfere, thermal energy — or heat — naturally flows in one direction only:
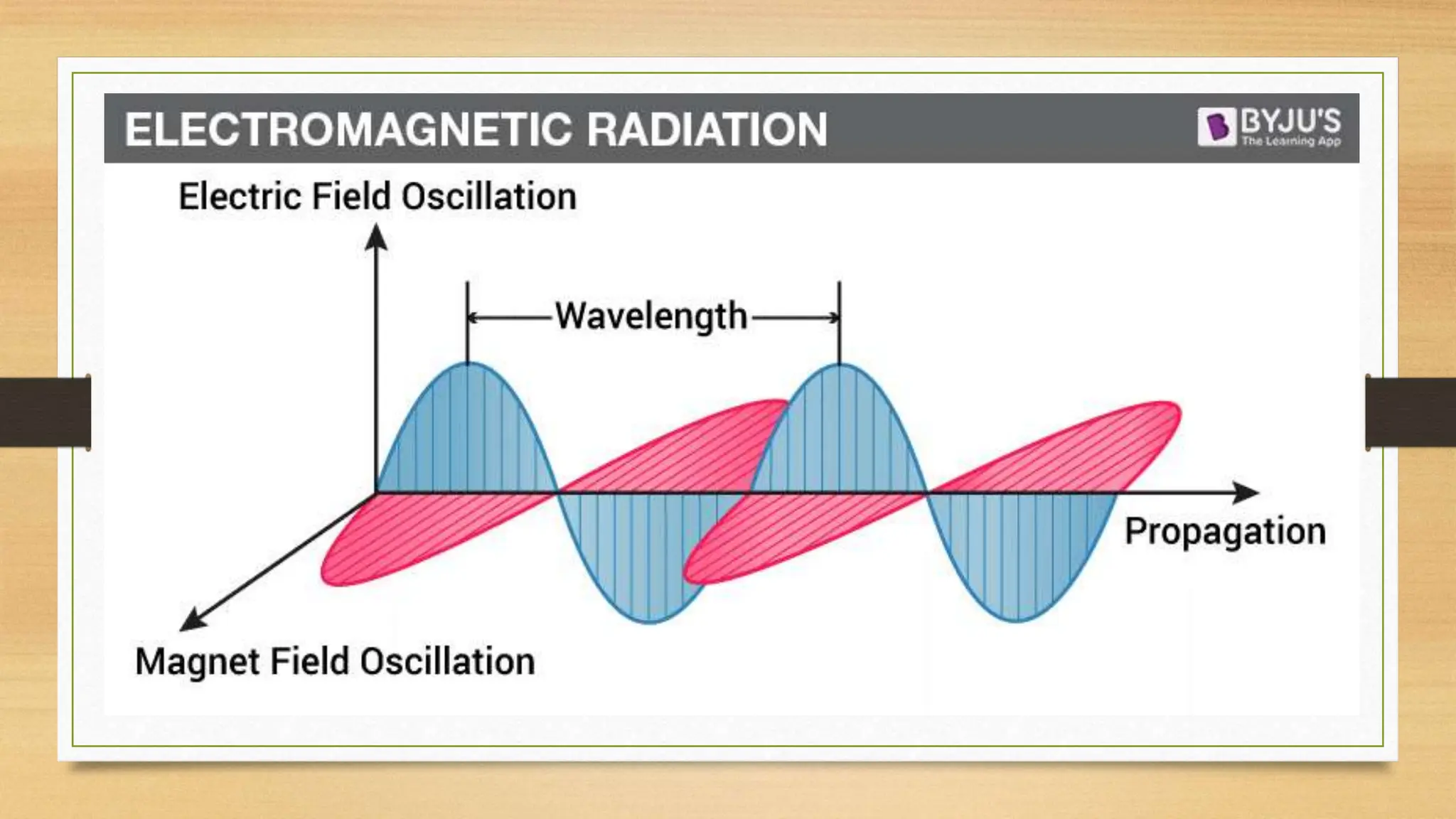
Sometimes we use the term ‚radiation‘ when we mean ‚light‘, and vice versa. In fact visible ‚light‘ is a form of radiation, which can be defined as an energy that travels in the form of Heat vs. Light What’s the Difference? Heat and light are both forms of energy that can be produced by various sources such as the sun, fire, or electricity. While heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another, light is the
Last Updated on Mar 13 2024 Infrared and ultraviolet are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, along with visible light. Whereas visible light has a wavelength between 380–760 nanometers This simple fact leads us to the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation: a continuum that stretches light and vice from gentle, gigantic radio waves to furious, subatomic gamma rays. The Figure \ (\PageIndex {3}\): The Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation. All forms of electromagnetic radiation consist of perpendicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Because the various
It’s not that we perceive only infrared radiation as heat, it’s that most objects we encounter radiate most of their thermal energy in the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. All objects Heat is transferred in three ways. Radiation is the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves. Radiation does not need an intervening medium to pass heat energy from the emitter to the absorber. When radiation from the Sun is A heat lamp radiates mostly infrared radiation, and the nerve endings in our skin are sensitive to this band of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared waves are absorbed by water and carbon
Thermal radiation at 300K (80F) has a peak wavelength of ~10 microns, corresponding to ~0.124 eV/photon. So it’s not ionizing radiation, and therefore not „radioactive“. It’s entirely possible for Electromagnetic Radiation What is a Electromagnetic (EM) Radiation? Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is all around us and takes many forms, such Cherenkov radiation glowing in the core of a TRIGA reactor. Because electromagnetic (EM) radiation can be conceptualized as a stream of photons, radiant energy can be viewed as photon energy – the energy carried by these
Remember that infra-red radiation is the same thing as heat so this type of radiation is used in ovens, toasters, grills, deep-fat fryers and any other appliance that uses heat to cook food.
In my understanding thermal radiation and electromagnetic radiation is same, for example suppose we heat up a knife to high temperature then it glows red. This means the
My question is why does electromagnetic-radiation in some wavelengths heat things up, whereas others, with both longer or shorter wavelength (RF, Microwave, UV,
We tend to use „heat radiation“ and „infra red radiation“ to mean the same thing but actually light of any frequency can heat something if it’s absorbed. Perhaps the short
While reflection is primarily associated with the conservation of energy within the same medium, radiation is a key mechanism for energy transfer between objects and spaces, Advanced Basic The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic (EM) spectrum is the range of all types of EM radiation. Radiation is energy that travels and spreads
radiant energy, energy that is transferred by electromagnetic radiation, such as light, X-rays, gamma rays, and thermal radiation, which may be described in terms of either discrete packets Radiation vs. Radioactivity What’s the Difference? Radiation and radioactivity are closely related but distinct concepts in the field of physics. Radiation refers to the emission of energy in the
- Hilfsprojekte In Ukraine | Lüneburger Hilfsprojekt Ukraine e. V.
- Hilfe Stellen In Husum – Elterngeld beantragen / Stadt Husum
- Herr Ulrich Keyser, Kinder- Und Jugend-Pneumologe In Göttingen
- Hersteller: Ergon R2 Magnesium
- Hilti Sf 120 A, Möbel Gebraucht Kaufen
- Heros Commerce Gmbh Hannover – Heros Commerce Hannover
- Heroquest :: Design , Custom Spells, Artifacts and Monsters for HeroQuest
- Herz-Jesu-Kirche Unterbarmen – Gesamtkirchengemeinde Stuttgart-Ost: Herz Jesu
- Herr Dipl.-Psych. Karl Heinrich Niggemeier-Denker
- High Resolution Metal Texture Images
- Himbeer-Buttercreme-Macarons Und Schoko-Espresso-Macarons