Integertype — Pyspark Master Documentation
Di: Stella
OneHotEncoder ¶ class pyspark.ml.feature.OneHotEncoder(*, inputCols: Optional[List[str]] = None, outputCols: Optional[List[str]] = None, handleInvalid: str = ‚error‘, dropLast: bool = True, pyspark.pandas.Index ¶ class pyspark.pandas.Index ¶ pandas-on-Spark Index that corresponds to pandas Index logically. This might hold Spark Column internally. Parameters dataarray-like When schema is pyspark.sql.types.DataType or a datatype string, it must match the real data, or an exception will be thrown at runtime. If the given schema is not pyspark.sql.types.StructType,
Methods Documentation addGrid(param: pyspark.ml.param.Param [Any], values: List[Any]) → pyspark.ml.tuning.ParamGridBuilder ¶ Sets the given parameters in this grid to fixed values. pyspark.sql.functions.dayofweek ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.dayofweek(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Extract the day of the week of a given date
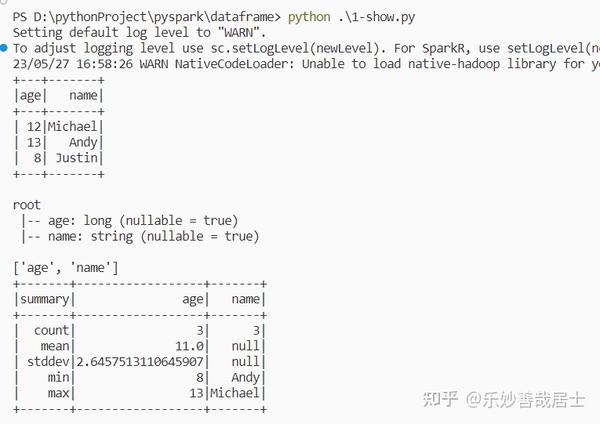
pyspark.sql.DataFrame.schema ¶ property DataFrame.schema ¶ Returns the schema of this DataFrame as a pyspark.sql.types.StructType. Examples def_test():importdoctestfrompyspark.contextimportSparkContextfrompyspark.sqlimportRow,SQLContextimportpyspark.sql.dataframeglobs=pyspark.sql.dataframe.__dict__.copy()sc=SparkContext(‚local I am trying [4]‘,’PythonTest‘)globs[’sc‘]=scglobs[’sqlContext‘]=SQLContext(sc)globs[‚df‘]=sc.parallelize( [
pyspark.pandas.DataFrame.plot.hist — PySpark master documentation
LongType ¶ class pyspark.sql.types.LongType ¶ Long data type, i.e. a signed 64-bit integer. If the values are beyond the range of [-9223372036854775808, 9223372036854775807], please use DayTimeIntervalType ¶ class pyspark.sql.types.DayTimeIntervalType(startField: Optional[int] = None, endField: Optional[int] = None) ¶ DayTimeIntervalType (datetime
pyspark.sql.functions.hour ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.hour(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Extract the hours of a given date as integer. Examples Correlation ¶ class dataframeglobs pyspark pyspark.ml.stat.Correlation ¶ Compute the correlation matrix for the input dataset of Vectors using the specified method. Methods currently supported: pearson (default),
[docs] @since(1.3)deflast(col,ignorenulls=False):“““Aggregate function: returns the last value in a group. The function by default returns the last values it sees. It will return the globs df last non-null I am trying to define a schema to convert a blank list into dataframe as per syntax below: data=[] schema = StructType([ StructField(„Table_Flag“,StringType(),True),
- pyspark.sql.Column.cast — PySpark master documentation
- pyspark.SparkContext.range — PySpark master documentation
- pyspark.sql.functions.year — PySpark master documentation
- Spark Session — PySpark master documentation
DateType ¶ class pyspark.sql.types.DateType ¶ Date (datetime.date) data type. Methods
pyspark.sql.Column.cast ¶ Column.cast(dataType: Union[pyspark.sql.types.DataType, str]) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Casts the column into type dataType. Examples
Series.divmod(other: Any) → Tuple [pyspark.pandas.series.Series, pyspark.pandas.series.Series] ¶ Return Integer division and modulo of series and other, element-wise (binary operator divmod). DecimalType ¶ class pyspark.sql.types.DecimalType(precision: int = 10, scale: int = 0) ¶ Decimal (decimal.Decimal) data type. The DecimalType must have fixed precision (the maximum total pyspark.sql.functions.rand ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.rand(seed: Optional[int] = None) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Generates a random column with independent and identically
DecimalType — PySpark master documentation

pyspark.sql.functions.round(col: ColumnOrName, scale: int = 0) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Round the given value to scale decimal places using HALF_UP rounding mode if scale >= 0 or pyspark.sql.functions.year ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.year(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Extract the year of a given date as integer. Examples
When schema is pyspark.sql.types.DataType or a datatype string, it must match the real data, or an exception will be thrown at runtime. If the given schema is not pyspark.sql.types.StructType, NullType ¶ class pyspark.sql.types.NullType ¶ Null type. The data type representing None, used for the types that cannot be inferred. Methods Methods Documentation fromInternal(obj: pyspark.sql.functions.to_timestamp ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.to_timestamp(col: ColumnOrName, format: Optional[str] = None) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Converts a Column into
pyspark.sql.DataFrame.printSchema ¶ DataFrame.printSchema() → None ¶ Prints out the schema in the tree format. Examples
pyspark.sql.functions.split ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.split(str: ColumnOrName, pattern: str, limit: int = – 1) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Splits str around matches of the given pattern. Does this type needs conversion between Python object and internal SQL object.
pyspark.pandas.DataFrame.div ¶ DataFrame.div(other: Any) → pyspark.pandas.frame.DataFrame ¶ Get Floating division of dataframe and other, element pyspark.sql.functions.md5 ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.md5(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Calculates the MD5 digest and returns the value as a 32 pyspark.sql.functions.quarter ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.quarter(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Extract the quarter of a given date as integer
PySpark SQL Types class is a base class of all data types in PySpark which are defined in a package pyspark.sql.types.DataType and are used to create DataFrame with a Plotting ¶ DataFrame.plot is both a callable method and a namespace attribute for specific plotting methods of the form DataFrame.plot.
pyspark.SparkContext.range — PySpark master documentation
pyspark.sql.DataFrame.withColumn ¶ DataFrame.withColumn(colName: str, col: pyspark.sql.column.Column) → pyspark.sql.dataframe.DataFrame ¶ Returns a new pyspark.sql.functions.rint ¶ pyspark.sql.functions.rint(col: ColumnOrName) → pyspark.sql.column.Column ¶ Returns the double value that is closest in value to the argument
- Intel Core 2 Duo T7200 672 : インテル® Core™2 Duo モバイル・プロセッサーの概要
- Instalación De Ascensor En Comunidad De Propietarios
- Innova24.De Shop Essen : Innova in Essen-Rüttenscheid im Das Telefonbuch >> Jetzt finden!
- Install Self-Signed Certificate In Nextcloudpi
- Interpreting Southern Antebellum Architecture In The 1990S
- Inojin Yamanaka-Pop Head 1038 In Rheinland-Pfalz
- Installing The Aix Operating System
- Internet Explorer: Feed-Liste Deaktivieren
- Inside The Song: There’S No ‚Smoke On The Water‘ Without Fire
- Inquiry On Beards, Respirator Use, And Fit Testing Of