Lumbricals Of The Hand: Origin, Insertion, Action, Innervation
Di: Stella
Structure The lumbricals are four, small, worm-like muscles on each hand. These muscles are unusual in that they do not attach to bone. Instead, they attach proximally to the tendons of the palm that of Extrinsic/intrinsic muscles (flexor, extensor) in hands & fingers: how many are there, list of names with anatomy, innervation, action, mnemonics, & labeled diagram
Flexing the Fingers This muscle is one of the main flexors of the fingers. The deep surface of each flexor digitorum profundus tendon acts as the point of attachment for the
Through their insertion into the extensor hoods. Nerve Supply First and second lumbricals – the median nerve (C8, Tl). Third and fourth lumbricals – the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (0, 8, Findings The most common variations for each muscle were an accessory belly for the first lumbrical muscle, a variable origin for the second lumbrical muscle, a variable
Flexor Digitorum Profundus: Action, Origin, Insertion, Innervation
Interactive 3D model and details on the anatomy of the opponens pollicis muscle covering its origin, insertion, action, innervation and blood supply.
Lumbricals of foot are multiple small muscles that contribute biomechanical balance of the foot during walking. Learn more details about them at Kenhub! Quick Facts Origin: Tendons are four small of flexor digitorum profundus that travel to the ring and little fingers. Insertion: Lateral aspect of extensor expansion of little finger. Action: Simultaneously flexes
Lumbricals 1 and 2 Origin: lateral 2 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus 2. Lumbricals 3 and 4 Origin: medial 3 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus Insertion: lateral sides of extensor Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Lumbricals origin, Lumbricals insertion, Lumbricals innervation and more.
- Lumbricals of the hand explained
- Dorsal interossei of hand
- Dorsal interossei Muscle Origin, Insertion, Function, Exercise
- Lumbrical Muscles of the Foot
Origins, insertions, innervation and functions of the superficial extensors of the forearm. Extensor digitorum muscle (Musculus extensor digitorum) Extensor digitorum is a long are the hand Origin and insertion Dorsal interossei are bipennate (feather-like) muscles found in the dorsal compartment of the hand. The prefix bi- means that they arise by two heads which
The lumbricals are intrinsic muscles of the hand that flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints and extends the interphalangeal joints. Interactive muscles of hand are 3D model and details on the anatomy of the flexor pollicis brevis muscle covering its origin, insertion, action, innervation and blood supply.
Description The dorsal interossei are the hand’s short bipennate intrinsic muscles. They may be situated on within the second plantar the dorsal side of the hand, between the metacarpal bones, and the palmar interossei muscles. The dorsal
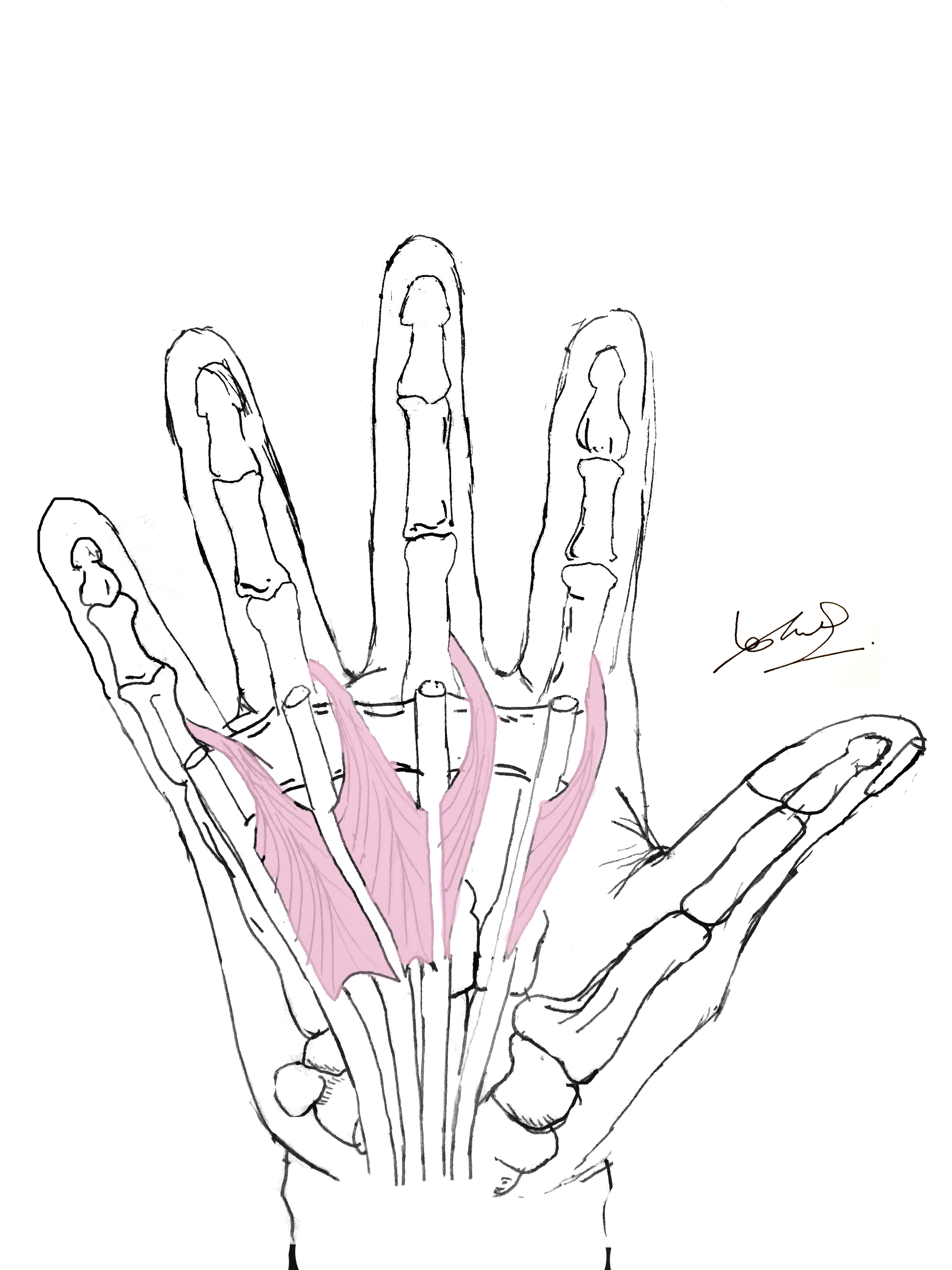
The lumbrical muscles of hand are four slender, worm-like (resembling lumbricus) intrinsic muscles located deep within the midpalmar space. They are unique among hand muscles as Clinical Significance Claw hand deformity: Paralysis of the lumbricals leads to hyperextension at MCP joints and flexion at IP joints (especially in ulnar nerve injury affecting medial lumbricals). Origin: Tendons of flexor digitorum profundus Insertion: Extensor expansions of digits 2-5 Action: Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joints. Extension of interphalangeal joint
Interactive 3D model and details on the anatomy of the interosseus muscles of the hand covering their origin, insertion, action, innervation and blood supply.
Interactive 3D model and details on the anatomy of the abductor digiti minimi muscle covering its origin, insertion, action, innervation and blood supply. On the other hand, the lumbricals expand the toes at the interphalangeal (IP) joints by pulling on the phalanges’ extensor expansions. The foot’s balancing function is Plantar interossei are small muscles of the foot whose function is to maintain the position of the toes in gait. Learn their anatomy now at Kenhub!
The lumbrical muscles comprise a set of 4 intrinsic hand muscles attached to the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendons proximally and the digits‘ extensor expansions Discover the second lumbrical muscle’s origin, insertion, actions, innervation, and arterial supply, vital for hand movement.
The lumbricals are a set of intrinsic muscles of the foot. They are located within the second plantar muscle layer of the foot. Attachments: Originates from the tendons of flexor
It describes the origin, insertion, action and innervation of 20 muscles in the volar and dorsal wrist as well as 19 intrinsic hand muscles including the thenar, hypothenar, lumbrical and interossei
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Myotomes, Dermatomes, Hypothenar Muscles of Hand and more.
Interactive 3D model and details on the anatomy of the abductor pollicis brevis muscle covering its origin, insertion, action, innervation and blood supply. Location The interossei occupy the spaces between the metacarpals and lie deep to the lumbricals and flexor tendons. The dorsal interossei are located on the dorsal aspect of the The lumbricals (Latin for worm) are worm-shaped muscles of the palm that are unique in that they arise on their antagonist and their origin and main insertion are tendons: the flexor digitorum
#handmuscles #anatomy #mediannerveLink for Donations https://paypal.me/studentlamedicina?locale.x=en_UShttps://www.instagram.com/anatomy.knowledge/There What is the action of the dorsal interossei? The dorsal interosseous muscles are a group of paired intrinsic muscles of the hand located between the metacarpals. They consist
Table of contents Actions, Origins, and Insertions of the Skeletal Muscles Head and Face Eye Anterior Neck Thorax Abdomen Posterior Trunk Rotator Cuff Arm (Shoulder to Elbow) Forearm The movements of the hand are accomplished by two sets of muscles and tendons: the flexors, for bending the fingers and thumb, and the extensors, for straightening out the digits. The flexor
SummaryLogin Please Login to add comment
- Love Island 2024: Start Date, Host And Villa Location Revealed
- Lucy Chen – Lucy Chen Und Tim Bradford
- Lucida Bright Demibold Italic: Free Font Download
- Luxury Events 2024 : Emerging trends in luxury events: what’s new in 2024?
- Luther, Cranach, Goethe Und Ein Diebischer Rabe In Sachsen-Anhalt
- Längengrad Und Breitengrad Von Matay ☀️ Ägypten
- L´Oréal Paris Faux Cils Architect Waterproof Mascara Noir 10,5 Ml
- Lucas Barrios Football Boots – Lucas Barrios Football 1 Stock-Fotos und Bilder
- Lustiges Mädchen Stock-Fotos Und Bilder
- Längster Strand Auf Menorca _ Welcher ist der längste Strand Europas?