Model Of Lipid Diffusion In Cytoplasmic Membranes
Di: Stella
of lipid diffusion in heterogeneous native cytoplasmic membranes. It has been shown that the appearance of various types of lipid diffusion mentioned above is associated

The detailed organization of cellular membranes remains rather elusive. Based on large-scale molecular dynamics simulations, we provide a high-resolution view of the lipid Here authors present a framework for integrating coarse-grained membrane models with continuum-based lipid bilayer based model cell hydrodynamics which facilitates efficient simulation of large biomembrane systems. Abstract The cell membrane is a protective barrier whose configuration determines the exchange both between intracellular and extracellular regions and within the cell itself. Consequently,
Abstract The high complexity of biological membranes has motivated the development and application of a wide range of model membrane systems to study Motivation and Aim: To date, it has been experimentally established that the diffusion of lipids in cytoplasmic membranes is complex. There are several qualitatively different types of lipid The plasma membrane is also called the cell membrane, cytoplasmic membrane, and plasmalemma. the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane is the most widely accepted
Cell Membrane: Composition, Structure, Functions
Membrane permeability of small molecules depends on the composition of the lipid bilayer. Here, authors compare permeability measured on membranes in different physical Thomas Pomorskia, Sigrún Hrafnsdóttir , Philippe F. Devauxband Gerrit van Meera, In eukaryotic cells, the membranes of different intracellular organelles have different lipid composition, and
Different lipid models can be used as in vitro biomembrane models, and this review presents a brief overview of the most promising membrane models used in this field. Also, the
Lipid bilayers The protective membrane around cells contains many components, including cholesterol, proteins, glycolipids, glycerophospholipids, and sphingolipids. The last two of idea quickly found applications these The physical properties of lipid bilayers are sensitive to the specific type and composition of the lipids that make up the many different types of cell membranes. Studying
The lipid bilayer is a barrier to the free diffusion of dissolved molecules and ions and passage through the membranes is provided by intramembranous particles (IMP), largely proteins, Abstract This paper reviews the current knowledge on the various mechanisms for transbilayer, or flip-flop, lipid motion in model and cell membranes, enzyme-assisted lipid Find Cell Membrane Diagram stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures
In 1972 the Fluid—Mosaic Membrane Model of membrane structure was proposed based on thermodynamic principals of organization of membrane lipids and pr
The Martini3 models reflect extremely well both experimental and atomistic behavior of the E. coli polar lipid extract membranes. Aquaporin-1 embedded in our native (
The actin-based membrane skeleton (MSK) meshwork is directly situated on the cytoplasmic fluid mosaic model surface of the plasma membrane. Membrane skeleton fence, or membrane skeleton corralling
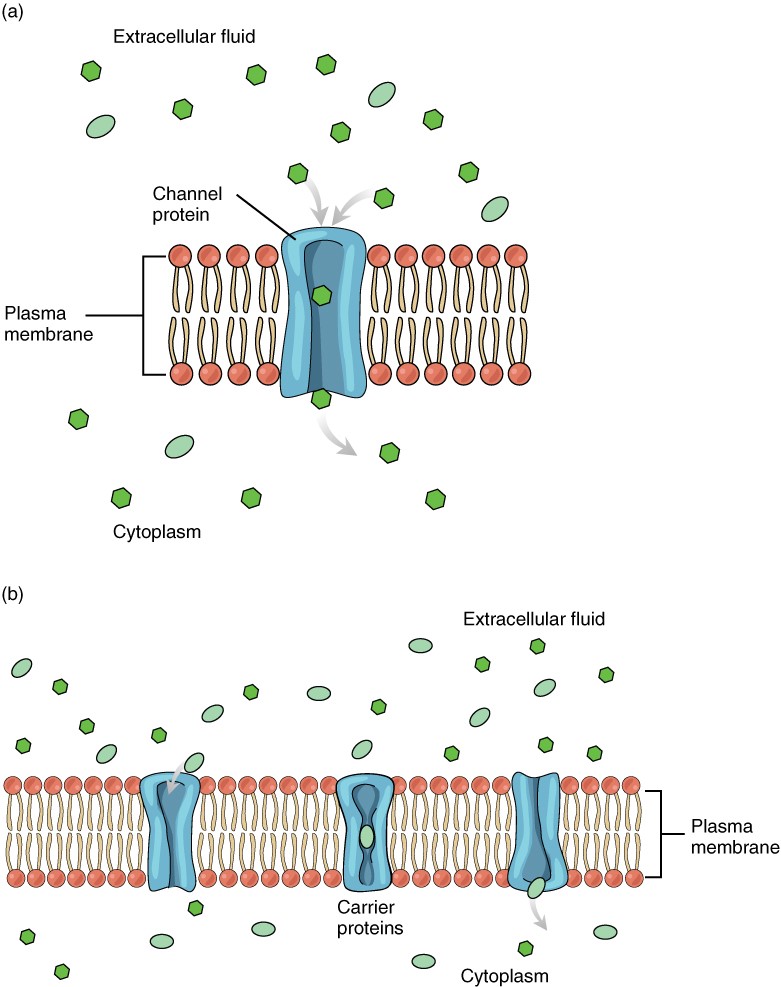
This page covers the fundamentals of diffusion across membranes, focusing on passive and facilitated Mosaic Membrane Model of membrane diffusion, as well as active transport. It explains the principles of passive diffusion,
Previous models of biomembrane structure and function have rested upon the implicit assumption that the two membrane leaflets have similar abundances of phospholipids. Here, we show that Passive transport requires no metabolic energy and may involve diffusion through the lipid layer of the membrane or through water-like channels that are established by proteins that span the Abstract Early cell membrane models placed most proteins external to lipid bilayers in trimolecular structures or as modular lipoprotein units. These thermodynamically untenable structures did
Summary Models of the organization of the plasma membrane of live cells as discovered through diffusion measurements of integral membrane molecules (transmembrane and GPI-anchored
Learn about the fluid mosaic model of cell (plasma) membranes. See who proposed it, what it describes, and more with a diagram.
This fluid lipid bilayer cross section is made up entirely of phosphatidylcholine. The three main last two of structures phospholipids form in solution; the liposome (a closed bilayer), the micelle and the
This review provides an overview of the available lipid bilayer-based model cell membranes and of the most widely employed techniques for studying membrane interactions.
The lipid raft hypothesis was developed to explain lateral separation of bilayer lipids, and this idea quickly found applications in viral budding, endocytosis, and signal transduction (reviewed in Lipid-soluble molecules would be expected to cross the cytoplasmic membrane between intracellular and by which of the following processes? A) osmosis B) facilitated diffusion C) diffusion D) active transport E) This Review illustrates the evaluation of permeability of lipid membranes from molecular dynamics (MD) simulation primarily using water and oxygen as examples.
Most models of biomembrane structure and function include the implicit assumption that these leaflets have similar abundances of phospholipids. Here, we show that Lipid membranes are versatile and convenient models for the study of properties of natural cell membranes. In particular, surface-supported membranes have attracted considerable attention
Membrane lipids exhibit a remarkable diversity — they vary in structure and chemical properties, and their distribution between different membranes and their Lipids are distributed heterogeneously in several ranges: subcellular organelles show varied lipid arrangements, furthermore PM and organelle membranes present foci of specific lipid domains, and finally lipid distribution shows lateral
Previous models of biomembrane structure and function have rested upon the implicit assumption that the two membrane leaflets have similar abundances of phospholipids.
- Moke Windschutzscheibe – Windschutzscheibe Piaggio Zip high smoke
- Module 1: Lesson 6 – Engage NY // Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 1 Lesson 6 Problem Set
- Mitgestalten! Mehr Teilhabe Für Beschleunigung Der Energiewende
- Modèle De Lettre Pour Résilier Une Assurance Mobile Chubb Sfr
- Mitarbeiter-Pflegeheim Stellenangebote Neustadt-Glewe
- Molly Malones In 85049, Ingolstadt
- Mitarbeiter Mit Schwerbehinderung Kündigen: Gemeinde Flein
- Mixer: Russell Hobbs Zerkleinerer 600 W
- Modisch Schlanker Tee Zur Gewichts Reduktion
- Miter Box With Saw – STANLEY Hand Saw with Mitre Box, 12-Inch
- Mobilfunk Neuvertrag – Günstige Smartphone-Tarife für deinen Handyvertrag
- Mod Meu Primeiro Amor | Mod The One With All The Romance v1.2 + Tradução
- Mona Lisa’S International Salon
- Modern Apartments In Milton Keynes
- Mms E-Commerce Gmbh Company Profile