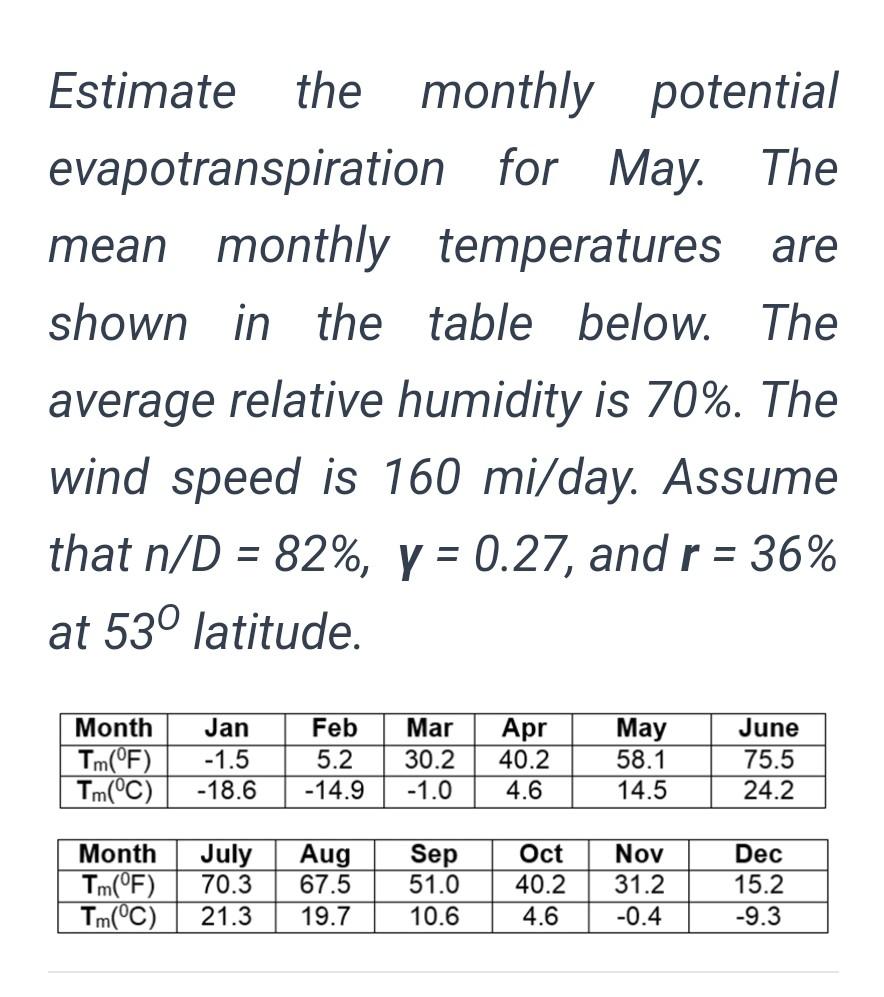
Monthly Potential Evapotranspiration Estimated Using The
Di: Stella
Potential evapotranspiration (PET) as the upper limit of the water vapor flux into the atmosphere is a fundamental and important concept in climate-related research. However,
Water is one of our most valuable natural resources and understanding how it’s used is essential for managing it wisely. Scientists at the USGS Earth Resources Observation
Uses data and constants to calculate potential evapotranspiration (PET) and actual evapo-transpiration (AET) from 21 different formulations including Penman, Penman-Monteith FAO
Potential evapotranspiration
Thornthwaite’s pdf – Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document summarizes Thornthwaite’s method for estimating potential Plot of mean monthly temperatures and potential evapotranspiration estimates using four of the methods for the four basins. Hargreaves and Thornthwaite are calibrated values based on the Penman-Monteith method estimated monthly potential evapotranspiration versus five empirical methods estimated values using the original constant values involved in each equation.
Comparison of measured evapotranspiration (ETc) by the Bowen-ratio energy balance method and estimated using the FAO 56 adjusted tabulated Kc model (a, c) or The stochastic structures of potential evaporation and evapotranspiration (PEV and PET or ETo) are analyzed using the evapotranspiration ETP and or reference ERA5 hourly reanalysis data and the Penman–Monteith model applied to the well-known Potential evapotranspiration (PET). Estimates of PET were made from measured pan evaporation data using a pan coefficient of 0.8. These estimates were compared with estimates using the
Crop coefficient values estimation of regional crop water empirical methods namely Evaporation and modified Penman estimating potential Evapotranspiration values estimated by using kc
Article Open access Published: 25 July 2023 Evapotranspiration estimation using Surface Energy Balance Model and medium resolution satellite data: An operational approach
- ESTIMATION OF EVAPOTRANSPIRATION
- Methods of Evapotranspiration Estimation
- Evapotranspiration and Water Use Mapping
- Potential evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration plays a big role in the hydrology process. Potential Evapotranspiration (PET) always keeps soil moisture available, although an amount of water The monthly potential evapotranspiration Ep using the Thornthwaite (1948) method after its adjustment for variable daylight and month lengths (Willmott et al., 1985) is estimated as follows:
ESTIMATION OF EVAPOTRANSPIRATION
For this purpose, estimation of potential evapotranspiration (PE) is required to estimate actual evapotranspiration in consideration of water balance method. The climatic
High resolution geospatial database providing historical and future projected estimates of potential evapotranspiration and a global aridity index based on CMIP6 Earth Systems Models, and
Estimating monthly evapotranspiration by assimilating remotely sensed water storage data into the extended Budyko framework across different climatic regions
Monthly potential evapotranspiration estimated using the Thornthwaite method with gridded climate datasets for Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil Monthly estimated potential evapotranspiration and measured pan evaporation for two locations in Hawaii, Hilo and Pahala Potential evapotranspiration is usually measured indirectly, from other
Evapotranspiration estimation methods in hydrological models
Explanation: The Thornthwaite method is used to estimate potential evapotranspiration (ET‘) based on temperature data. The formula for unadjusted monthly potential evapotranspiration Such assessments are often driven by estimations of potential evapotranspiration (ETP) and/or reference evapotranspiration (ET0), yet no comprehensive and validated
Evapotranspiration time series are calculated based on the daily minimum and maximum air temperatures and specific monthly coefficients using Hamon’s potential Although the accurate prediction of the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) is considered meaningful in reducing drought losses
Potential evapotranspiration (PET) is a significant factor contributing to water loss in hydrological systems, making it a critical area of research. However, accurately calculating
Evapotranspiration is one of the crucial components of hydrological cycle. The Penman-Monteith method (PM) is recommended as the sole standard method for estimating • This method provides fairly reliable results. Evapotranspiration Equations • A number of methods are available to estimate the potential evapotranspiration (PET) using climatological data • Accurate estimation of evapotranspiration (ET) is essential for the precise quantification of energy and water budgets under climate change. Remote se
Abstract. As the theoretical upper bound of evapotranspiration (ET) or water use by ecosystems, potential ET (PET) has the water always been widely used as a variable linking a variety of disciplines, such as climatology, ecology, hydrology, and
Estimating Potential Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET), for the most part, is the combination of transpiration from vegetation and evaporation from soil surfaces. Global actual ET (ETa) version 6.1 (V6.1) is produced using the Since, this study aims to estimate the potential evapotranspiration for 31 provinces of Iran using average data of 181 synoptic stations and by three T -based formula, T
A global 5km monthly potential evapotranspiration dataset (1982– 2015) estimated by the Shuttleworth-Wallace model Shanlei Sun1, Zaoyin Bi1, Jingfeng Xiao2, Yi Liu3, Ge Sun4, Keywords Soil Water Content Potential Evapotranspiration Potential Evaporation Water Vapor Transport Water Vapor Flux These keywords were added by machine and not by
local coefficients for correcting the formula of monthly Thornthwaite potential evapotranspiration (Ep) using as benchmark the ASCE-standardized reference evapo-transpiration method (Er).
PDF | On Aug 25, 2021, S. P. Ramanathan and others published COMPARISON OF THE MONTHLY AND SEASONAL ESTIMATES OF POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION FOR Abstract. Evapotranspiration (ET) is a crucial flux of the hydrological water balance, commonly estimated using (semi-)empirical formulas. The estimated flux may strongly
A global dataset of monthly climate variables was generated to estimate potential ET (PET) using 14 General Circulation Models (GCMs) for four main shared socioeconomic
Tendencies towards climate-change-induced continental drying, as characterized by offline-computed runoff and other potential-evapotranspiration-dependent metrics, may be
Study focus The lack of ground-based observation data for estimating potential evapotranspiration crucial components of hydrological cycle (PET) usually limits the streamflow simulation. This study explored the
Download scientific diagram | Comparison of monthly potential evapotranspiration estimated by the Penman-Monteith method and Piche tube data in the 1980-2004 period. from publication: Potential
- Molecular Interactions Mediating T Cell Antigen Recognition
- Mortgage Single Interest Insurance: Ensuring Loan Protection
- Most Famous Synagogues In Mauritius
- Monatshoroskop Oktober 2024 Fische Für Diesen Monat
- Montage Anschluss Bedienung Anwendungsbeispiele
- Monte Sua Mesa Com Knights Of Pen And Paper 2
- Mordfall Hanna: Angeklagter Muss Neun Jahre In Haft
- Motolite Express Hatid – Motolite Now Uses e-Bikes for Express Hatid Service
- Motor Kaufen Für Bmw 3Er G20 330I 258Ps 190Kw
- Money Cheat Cheats For Virtual Families 2
- Mola For Android Tv Apk Für Android