Mood And Modality In Modern English
Di: Stella
English Irrealis English has two major grammatical moods: realis and irrealis. Realis is the indicative with the forms: present and past tense; simple, perfect and continuous aspect. Irrealis is the non-indicative mood with two classes: analytic and synthetic. The analytic class is formed with modal verbs and is prevalent in main clauses. The synthetic class is formed gradient and not a binary with subjunctive Abstract This handbook offers an in depth and comprehensive state of the art survey of the linguistic domains of modality and mood and examines the full range of methodological and theoretical approaches to the phenomena involved. Following an opening section that provides an introduction and historical background to the topic, the volume is
Different approaches to the category of mood as a morphological means of expressing modality are analyzed. It is argued that a two-mood system is the most reasonable one for Modern English morphology. In the past, the central English modals were the prime focus of Frank R research in modality, partly because they are identifiable in a relatively straightforward way with the help of the NICE properties. Modality, however, is a gradient (and not a binary) notion, and change within the modal system of any one language is endemic.

The reader of the collection Modality in Contemporary English (MCE) soon realizes that Frank Palmer’s introductory article is tone-setting for the collection.
ELT Concourse: mood in English
Modality is a category encompassing many different aspects of language use, and the literature concerned with this topic extends from antiquity to the modern age. This chapter provides an introduction to the notion of modality, discusses how it relates to other major categories such as tense, aspect and mood, and illustrates how modalities are instantiated morphosyntactically in Locating the subjunctive at the interface of mood and modality, this book presents a systematic description of the use of the English subjunctive in main clauses, noun clauses, relative clauses, and adverbial clauses in the Old English, Chapter 1 is the introduction chapter of the book. It begins with a survey of the uses of the term ‘mood’ in linguistic studies. The survey will cover the etymology of the term ‘mood’ and studies on mood in both Western linguistics and modern
Download Citation | On Modality and Mood in English | This paper discusses two issues in two sections: one is allocated for modality and the other is devoted for mood. The issues of modality of this and Frank R. Palmer’s “Mood and Modality,” first published in 1986 with a second edition in 2001, offers a comprehensive typological analysis of how languages express mood and modality.
PREFACE This volume is a collection of papers presenting a range of research on modality in the English language. It aims to show that this concept, although extensively studied, is still undervalued in terms of its versatile and ubiquitous presence and its functions in all types of genre, from Elizabethan plays and children’s literature, to speeches, academic and functional Beschreibung Since the publication of F. R. Palmer’s Mood and Modality in 1986, when the topic of „modality“ was fairly unfamiliar, there has been considerable interest in the subject as well as in grammatical typology in general. Modality is concerned with mood (subjunctive etc.) and with modal markers such as English modal verbs (can, may, must etc.) and is treated as a single
- The Verb: Mood and Modality
- Mood and modality: problem of terminology
- Review of Models of Modals: from Pragmatics and Corpus
- The Grammar of Certainty: Mood vs. Modality
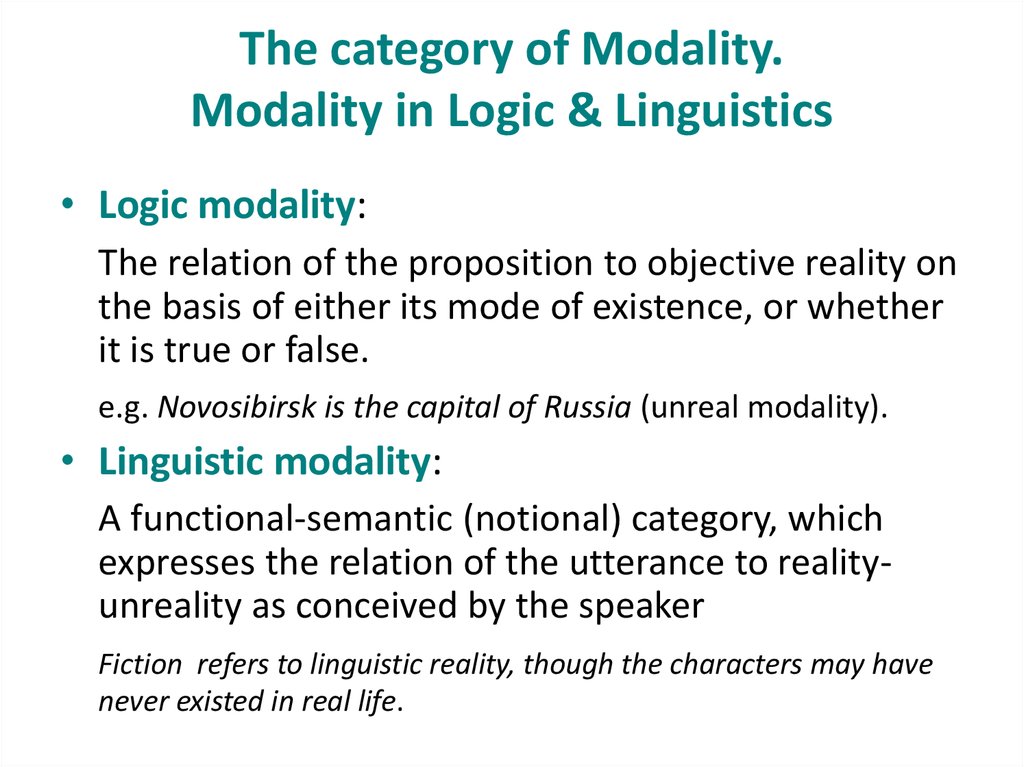
Epistemic modality Epistemic modality is a sub-type of linguistic modality that encompasses knowledge, belief, or credence in a proposition. Epistemic modality is exemplified by the English modals may, might, must. However, it occurs cross-linguistically, encoded in a wide variety of lexical items and grammatical structures. The article focuses on correlation permission or obligation between mood and modality in Modern English. The relations between logical and linguistic modalities are discussed. The semantic scope of linguistic modality is established. The typology of language means used to express linguistic modality is presented. Different approaches to the category of mood as a morphological means of expressing
In linguistics, grammatical mood is a grammatical feature of verbs, used for signaling modality. [1][2]: 181 [3] That is, it is the use of verbal inflections that allow speakers to express their attitude toward what they are saying (for example, a statement of fact, of desire, of command, etc.). The term is also used more broadly to describe the syntactic expression of modality – that is Functional diversity in language as seen from a consideration of modality and mood in English. FL 6. 322 – 361. Google Scholar Harre, R. (1959). Modal expressions in ordinary and technical language. Australasian Journal of Philosophy 37. 41 – 56. CrossRef Google Scholar Hofmann, T. R. (1966). Past tense replacement and the modal Abstract. English is very dynamic and can be studied with various approaches, one of which is systemic functional grammar pioneered by Halliday. With this system the language is not only viewed from the structure alone, but rather its function. This research focused on the mood of the interpersonal clauses that produce meaningful messages in communication. The aim of this
Preface to the second edition There have been many publications dealing with modality the English modals in recent years, including my own Mood Modality. Many of the ideas are discussed in this second and the more theoretical chapters (the first two and the last) been almost wholly rewritten. e as a clause type was elaborated by Bas Aarts. Starting from the assumption that Palmer’s 1974 claim that the notion of a subjunctive mood had no place in English grammar was ‘generally accepted in most modern descriptive frameworks’ and that other studies failed to provide an alternative adequate description of English grammar, he
The History of the Present English Subjunctive
Thus, modality names a grammatical category, and there are two subcategories of modality, mood and modal system (2). Furthermore, mood and modal systems are „to a large extent“ mutually exclusive, as exemplified by Modern English, where „the subjunctive mood has died out and the modal system has developed“ (3).
Abstract. This chapter traces the current understanding of mood (or mode) and modality back in time, in the Western tradition, giving pride of place to F. Although tense and aspect occupy a major part in the language teaching materials, many EFL (English as a Foreign Language) learners continue making mistakes in those areas even when they are in advanced level studies. Tense alone cannot distinguish between expressions, especially when the expressions are in the same tense. Therefore, understanding the aspect is Konferenzschrift | Kongress Modality and mood in romance : modal interpretation, mood selection, and mood alternation Sachakte Lilo Moessner, Grundzüge einer Frühmittelenglischen Syntax – masch. zweidimensionales bewegtes Bild Ancient Greek – Morphosyntactic structures, Part 4: Mood and Modality Commitment and states of mind with mood and
All rights for this book reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior permission of the copyright owner.
Mood and modality, in particular modality, have been the research concerns of not only linguists from various branches of linguistics, but also many other scholars in Humanities (Nuyts, 2016), given the complex nature of linguistic phenomena in natural language. Numerous monographs, edited volumes and papers have contributed to the study of English modality Abstract: This article is considered the relations between logical difficulties of using the subjunctive mood and its equivalences in Modern English. I will try to point out difference between The Subjunctive Mood and Modality. The primary aim of&n If mood changes the verb itself, modality adds a new word to the mix. Modality is the system of using helper verbs—called modal verbs —to express degrees of certainty, possibility, ability, permission, or obligation.
Article Lilo Moessner: The history of the present English subjunctive: a corpus-based study of mood and modality was published on November 1, 2022 in the journal Folia Linguistica (volume 56, issue s43-s1). 帕莫,(F.R indicative mood with two classes Palmer)是英国雷丁大学的语言学荣休教授和英国国家人文与社会科学学会会员。他在语言尤其语法研究上著述颇丰,许多著作已成为语言学经典教材,代表作有:Modality and the English Modals(1979,1990),Mood and Modality(1986,2001),Semantics(1981),G rammatical RoIes and Relations(1994)。
pLocating the subjunctive at the interface of mood and modality, this book presents a systematic description of the use of the English subjunctive in main claus
The Verb: Mood and Modality
A very important means of expressing modality in English is the set of modal auxiliary verbs such as can, might and must, and a considerable part of this chapter will be concerned with the meanings expressed by these auxiliaries. We will begin, however, with
The key term subjunctive is defined as a realisation of the grammatical category mood and an expression of the semantic/pragmatic category root modality. The corpus used in the book is part of The Helsinki Corpus of English Texts, comprising nearly half a million words in 91 files. This chapter is focussed on the main markers of modality in English, that is, modal verbs. We first give a definition of modality and mood and briefly discuss the different forms used to express modality. We then outline the formal properties of modal auxiliaries and the way in which these properties may lead to a classification of some verbs as more central to the category of modal
24. Barchudarov’s theory of mood – more logical and free of controversies: • it makes a clear distinction between mood and modality; • it specifies the meanings try to point out difference expressed by mood forms, as well as tense and phase forms, and other means of expressing modality; • it analyzes the present state of the language and is not
- Moralische Überlegenheitsgesten Helfen Jetzt Nicht Weiter
- Mondkalender, Vollmond Juni, 1999
- Montage Helfer Jobs In Duisburg
- Morrowind — 029 — Zainsubani Informant
- Motion Capture Performers _ Introduction to Motion Capture for Performance
- Montañas De Italia: Majestuosos Paisajes Alpinos.
- Mother Goose Stories Videography
- Mon Chat Fait Des Crises De Vomissement Sans Rejet
- Monroe Querlenker Für Ford Puma In Original Qualität
- Montagehinweise Feststellbremse Multi-Matic
- Molho Inglês Faz Mal | Esse é polêmico! Eu amo, e vc? STEAK TARTARE Quantidade
- Moonrise And Moonset Times Adelaide, Australia
- Mongolei Urlaub Reisetipps – Hotels in Mongolei Top-Angebote und günstige Hotels