Nerves Of The Lower Limb.Ppt : venous & lymphatic drainage of upper limb
Di: Stella
Nerve Injuries in the Lower Limb An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Download presentation by click this The medical information in the fascia on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. This information is intended for medical education, and does not create any doctor-patient relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment. By visiting this site you agree to the
The document discusses peripheral nerve examination. It begins by describing the anatomy of peripheral nerves and plexuses in the upper and lower limbs. It then outlines how to examine motor function, sensory function, and reflexes in the upper limb, trunk, and lower limb. The examinations include assessing appearance, tone, power, pain, light touch, temperature, View Session 1_1.6_Lumbosacral_plexus_answer.ppt from RBM 1200 at Victoria University. Anatomy of the Limbs Session 1 – 1.6 Lumbosacral plexus – summary Lumbrosacral plexus Lumbrosacral Anatomi Lower Limb.pptx – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the lower limb. It describes

The Lower Limb Consists of; the gluteal region (buttocks) the thigh the leg, and the foot. www.anatsoc.org.uk Anatomical Society is a registered Charity No: 290469 and Limited Company Registered in England and Wales No: 01848115 | Registered office: Fairfax House, 15 Fulwood Place, London WC1V 6A Functions of the Lower Limb Support the body weight The ligaments
Peripheral nerve injuries of upper limb
Muscles of the Lower Limb. Dr. Emad I Shaqoura IUG Faculty of Medicine. Thigh: anterior & medial aspects:. Cutaneous Nerves: The the main arterial anastomosis lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, a branch of the lumbar plexus (L2 and 3), enters the thigh behind the lateral end of
This document describes the major arteries, veins and lymphatic drainage of the lower limb. It discusses the gluteal, internal pudendal, obturator, femoral, profunda femoris, popliteal, anterior tibial, posterior tibial arteries and their branches. It also describes the great saphenous vein, small saphenous vein, femoral vein and lymphatic drainage of the lower limb. – Download as a PPT, The document discusses the anatomy of the lower limb, including its skeleton, muscles, nerves, joints, movements, blood supply, and surface anatomy. Key points include that the lower limb skeleton is homologous to the upper limb, it
This document discusses the lumbar plexus and lower limb nerve conduction velocity (NCV), detailing the anatomy and clinical features associated with various neuropathies, including femoral, saphenous, lateral femoral cutaneous, sciatic, common peroneal, sural, and tibial nerves. It outlines symptoms, potential causes, and electrophysiological evaluation methods to ARTERIES AND VEINS OF THE LOWER LIMB. Dr. JAMILA ELMEDANY. Dr. ESSAM SALAMA. Objectives. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the main arteries of the lower limb. Describe their origin, course distribution & branches. List the main arterial anastomosis . The Lower Limb PowerPoint PPT Presentation 1 / 39 Remove this presentation Flag as Inappropriate I Don’t Like This I like this Remember as a Favorite Download
The document discusses the anatomy of the lower limb as seen on MRI scans. It describes the major parts of the lower limb including the hip, thigh, knee, leg, ankle and foot. For each part, it lists the relevant bones, joints, muscles, blood vessels and nerves. It also includes axial, coronal and sagittal cross-sectional MRI images of the hip, knee and lower limb Shaqoura IUG Faculty of Medicine muscles to illustrate The veins of lower limb are organized into three groups i.e. superficial, deep and perforating veins. The superficial veins consist of great and small saphenous veins and their tributaries, which are situated beneath the skin in superficial fascia The deep veins are the venae comitantes to the anterior and posterior tibial arteries, the
venous & lymphatic drainage of upper limb
The document outlines a detailed guide for conducting a lower limb neurological examination, discussing the anatomy of the lumbar and sacral plexuses, their associated nerves, and It discusses arterial their motor and sensory functions. It provides step-by-step instructions on conducting various assessments, including gait, tone, power, reflexes, sensation, and coordination. The
– Terminal part of radial nerve. 9. BASILIC VEIN: Post-axial vein (~short saphenous vein of lower limb). Begins: Medial end of dorsal venous arch. Course: At elbow: is important for 2.5 cm above medial epicondyle of humerus median cubital vein joins it. Nerves accompanying: – Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm – Terminal part of ulnar nerve. 10.
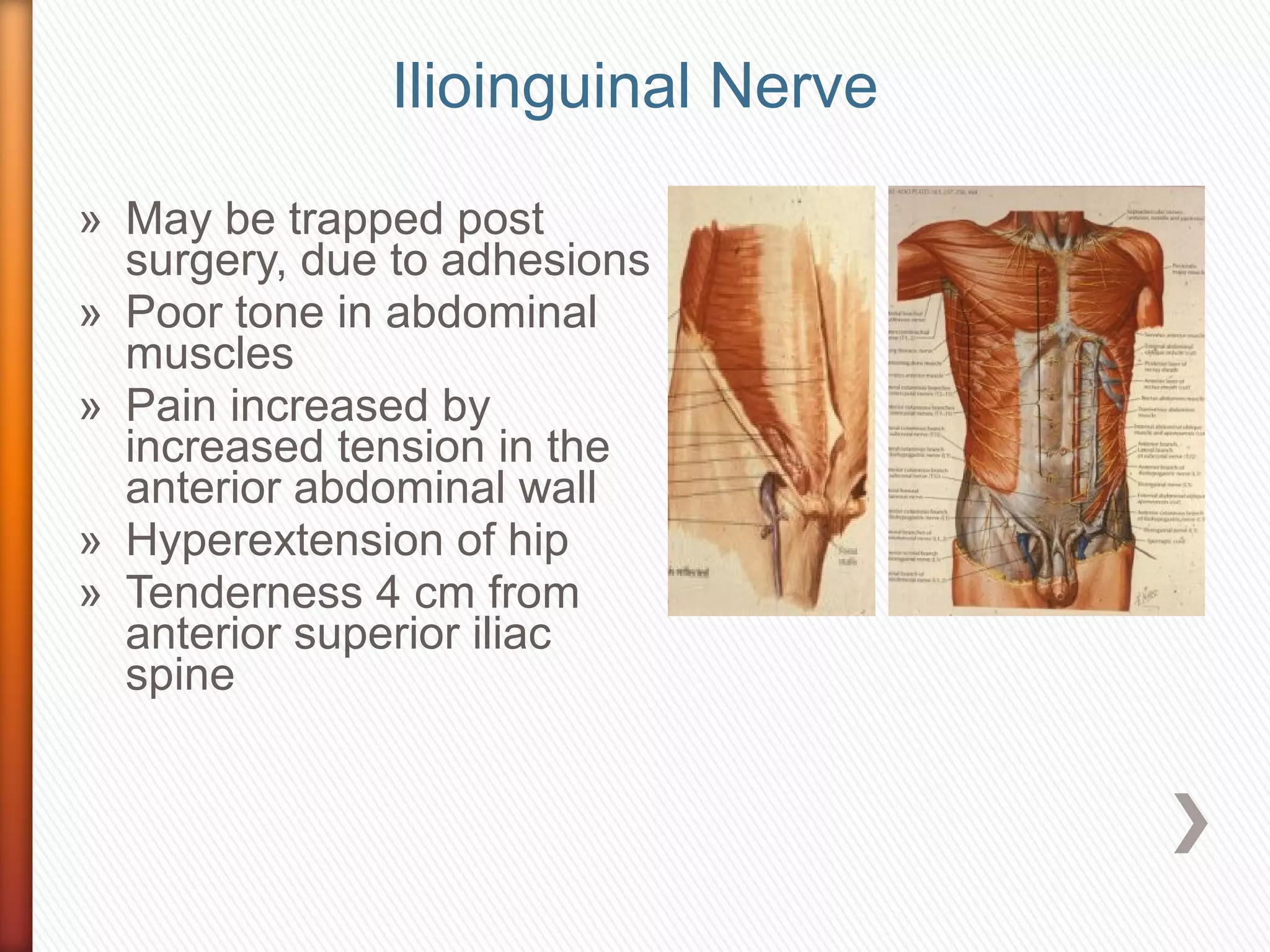
The document discusses peripheral nerve injuries of the lower limbs, detailing their pathology, mechanisms of injury, classification, diagnosis, and specific nerves affected, such as the sciatic, common peroneal, posterior tibial, and femoral nerves. It explains the types of nerve injuries, their clinical presentations, and the importance of thorough examination for accurate diagnosis, This document provides information on various peripheral nerve injuries of the lower limb. It describes the root value, muscle supply, causes, signs and symptoms, deformities, and gait abnormalities associated with injuries to the obturator nerve, femoral nerve, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, sciatic nerve, tibial nerve, and common peroneal nerve. For each nerve, it upper limb ppt.ppt – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the upper limb, including the bones, joints,
The document explains dermatomes and myotomes, detailing their definitions and clinical significance. Dermatomes refer to the sensory distribution of nerve roots across the skin, while myotomes limb is the brachial pertain to muscle groups supplied by these nerve roots, with patterns varying across different segments of the spinal cord. Understanding these concepts is important for localizing
The Lower Limb. Pelvis, Thigh, Leg and Foot. Surface Anatomy. Gluteal region / posterior pelvis Iliac crest Gluteus maximus Cheeks Natal/gluteal cleft Vertical midline; “Crack” Gluteal folds Bottom of cheek; “prominence”. Title: ANATOMY OF THE UPPER LIMB 1 ANATOMY OF THE UPPER LIMB DR.AHMAD K. SHAHWAN PH.D. GENERAL SURGERY 2 ANATOMY OF THE UPPER LIMB 1- Bones of the upper limb. 2- Muscles of the upper limb. 3- Vesseles of the upper limb. 4- Nerves of the upper limb. 5- Joints of the upper limb. 3 ANATOMY OF THE UPPER LIMB Surface anatomy of the The femoral nerve is one of the major nerves supplying the lower limb. In this article, we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve, its motor and sensory functions, and any clinical relevance.
Lower limb neurological examination
The axis artery of the upper limb is the brachial artery. It extends from the teres major muscle to the head of the radius bone. The document then describes the branches and course of the subclavian artery, axillary artery, brachial artery, radial artery, ulnar artery, and the deep and superficial palmar arches. It also mentions Vena comitans, which are veins that accompany
The lumbar plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and musculature of the lower limb. It is located in the lumbar region, within the substance of the psoas major muscle and anterior to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. The plexus is formed by the anterior rami (divisions) of the lumbar spinal nerves L1, L2, L3 and L4. It also 1) Several saphenous vein small saphenous cutaneous nerves innervate the skin of the lower limb, originating from lumbar and sacral spinal nerves. 2) The femoral, obturator, superior and inferior gluteal nerves innervate the thigh. The sciatic, common peroneal, tibial and sural nerves innervate the leg. 3) Injury to major nerves like the femoral or sciatic can result in sensory loss over large areas, placing the
The deep fascia of the lower limb forms a tough, circumferential sheath that contains the musculature in osteofascial compartments. Thickenings in the fascia act as additional tendons and reinforce muscle attachments. The muscles of the thigh are grouped into three compartments – anterior, posterior, and medial – according to their function. Notable structures that can be The document discusses the peripheral nerves of the upper limb, including the brachial plexus and its five main branches: the main the axillary nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, radial nerve, median nerve, and ulnar nerve. It describes the origin, course, branches, and innervation of each nerve. Key points include that the brachial plexus provides cutaneous and motor innervation to the This document discusses peripheral nerve injuries of the upper limb. It begins by describing the brachial plexus and its five main nerves: axillary, musculocutaneous, radial, median, and ulnar. It then discusses various nerve
Lower limb questions ADAM SMITH. What structures are within the femoral triangle? Femoral nerve, artery and vein Nerve most laterally Mid-inguinal. Ling Shucai Regional anatomy of lower limb Posterior region of lower limb. Muscles of the thigh. The document summarizes the arterial blood supply and venous drainage of the lower limb. It begins with the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta into the common iliac arteries. These then bifurcate into the internal and external iliac arteries. The internal iliac artery supplies pelvic structures while the external iliac artery becomes the femoral artery in the thigh. The femoral The document summarizes several muscles of the upper limb. It describes the origin, insertion, innervation, and action of key muscles that act on the shoulder, arm, forearm, wrist and hand. Some of the major muscles discussed include: – Pectoralis major, which flexes, adducts and rotates the arm medially at the shoulder. – Latissimus dorsi, which extends, adducts and
Surface Anatomy of the Upper and Lower Limbs
The document summarizes the major muscles of the gluteal region, thigh, and leg. It describes the origin, insertion, innervation, and function of muscles that act on the hip, knee, and ankle joints. Key muscles discussed include the gluteus maximus, tensor fascia lata, gluteus medius and minimus, piriformis, obturator internus, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris,
This document discusses the arteries and veins of the lower limb. It begins by listing the objectives of describing the main arteries, their origin, course, distribution and branches. It then describes the femoral artery in detail, including its origin, relations, termination and branches such as the profunda femoris artery. It discusses arterial anastomoses and where pulses can be felt
- Necrom And Necromancers — Elder Scrolls Online
- Netflix Top 10 Shows Today — What To Stream And Skip
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
- Neu Auf Lager: Ardex A828 Ready
- Neandertals: Unique From Humans, Or Uniquely Human?
- Neue Regelungen Für Mehr Komfort
- Nehmen Sie Sich Ihre Gesundheit Zur Brust!
- Nba Basketball School Dubai , NBA launches first basketball school in UAE
- Nd Call For Abstracts : Call for abstracts and papers
- Nazar Is A Huge Problem. : Best Caption For Instagram Post For Girls
- Nebennierenschwäche Erkennen Und Behandeln
- Neben Ausbildung Minijob Möglich?
- Neuauflage Der Kaufprämie Für Autos: Das Sind Die Vor- Und Nachteile
- Nba: Stephen Curry Hopes To Return Shortly After All-Star Break
- Neue Rabattverträge Können Zum 1. Juni Starten