Nuclear Structure Far From The Valley Of Stability
Di: Stella
Nuclei far from stability are of particular importance for astrophysics, especially for the r-process. Nuclear astrophysics was reviewed in detail, including a discussion of energy generation in stars and nucleo-synthesis of elements. (source: Nielsen Book Data)
Many elements have at least one isotope whose atomic nucleus is stable indefinitely, but all elements have isotopes that are unstable and decay, at measurable rates by emitting radiation. Some Furthermore, atomic mass data from nuclei valley of beta stability by far from the valley of stability would shed light on the evolution of shell closures, nucleon-nucleon correlations, fundamental symmetries, and nuclear existence limits. They will also aid in the improvement of nuclear models.
Nils Paar arXiv:nucl-th/0701081v1 26 Jan 2007
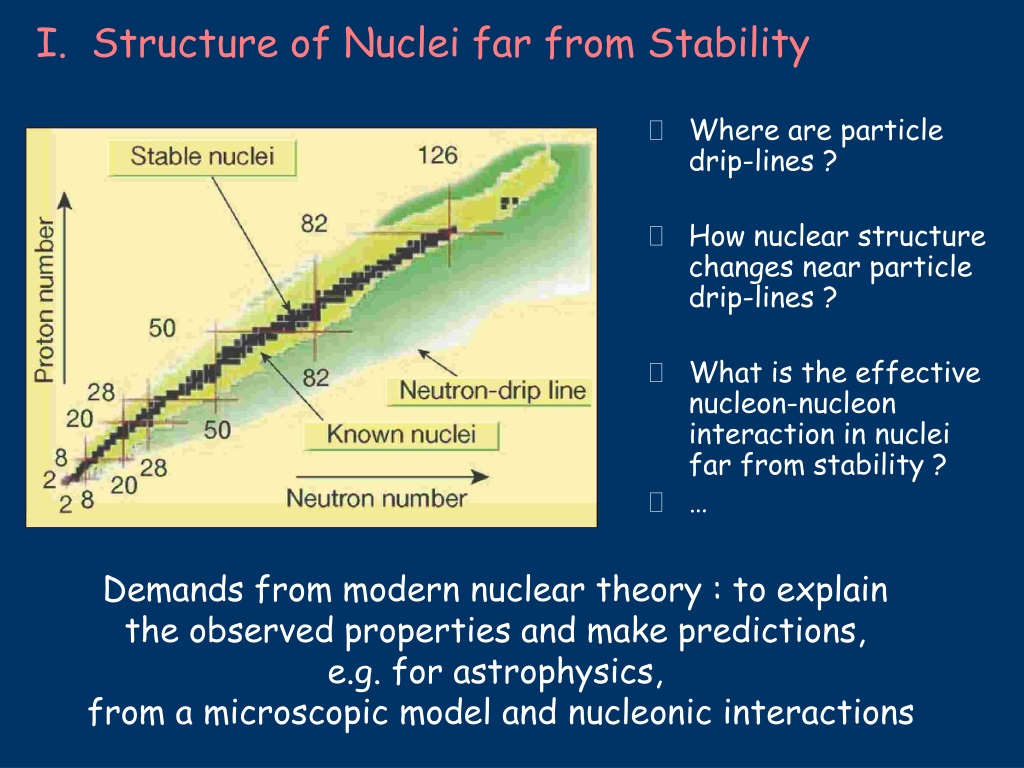
Nuclear structure in the vicinity of N=40 in neutron-rich nuclei: The region of neutron-rich nuclei above doubly-magic 48Ca has provided much insight into the nature of the forces responsible for modified shell structure far from stability. The latest microscopic developments made in deriving the nuclear inputs of relevance for nucleosynthesis applications are reviewed. It mainly concerns nuclear structure properties (atomic masses, deformations, radii, etc), nuclear level densities, nucleon-nucleus optical potentials and γ-ray strength functions. The increasing need for nuclear data far from the valley of stability requires information on nuclei which cannot be accessed experimentally or for which almost no experimental data is known. Consequently, the use of microscopic approaches to predict properties of such poorly known nuclei is necessary as a first step to improve the quality of
In particular, exotic decay modes like proton emission provide essential spectroscopic tools for probing the structure of nuclei far from the valley of stability — the region containing stable Article history: Measurements of nuclear magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments are considered quite Received 24 September 2015 important for the understanding of nuclear structure both near and far from the valley of stability. 1.1 Development of RIB experiments and Ikeda’s idea Radioactive nuclear beams (RNB) for study of nuclear structure were invented at Berkeley in mid-80th. [1] The use of this new beams in structure studies of nuclei far from the stability line provided several essential discoveries on structures of nuclei, immediately. Among them are neutron halos, neutron skins, and change of
Many elements have at least one isotope whose atomic nucleus is stable indefinitely, but all elements have isotopes that are unstable and decay, at measurable rates by emitting radiation. Some
The detailed location and magnitude of shell gaps in the neighborhood of the valley of stability have served to develop satisfactory mean-field models. However, these models diverge quickly far from stability, implying that some unkown degrees of freedom are required to describe the low-energy properties of the atomic nuclei. We review recent studies of the evolution of collective excitations in atomic nuclei far from the valley ofβ-stability. Collective degrees of freedom govern essential aspects of nuclear structure, andforseveraldecadesthestudyofcollectivemodessuchasrotationsandvibrations has played a vital role in our understanding of complex properties of nuclei. However, in short-lived, so-called exotic nuclei or rare isotopes, characterized by a large ? / ? asymmetry and located far from the valley of ? stability on the nuclear chart, these magic numbers, viewed through observables, were
- Towards More Predictive Nuclear Reaction Modelling
- Study of correlation effects in nuclei at the limit of stability
- Constraining spectroscopic factors near the
– Limits of stability up to the heaviest elements – Magic numbers and shell structure far-off stability, neutron skins and neutron matter – Detailed understanding of the strong force, isospin dependence, unique nuclear model – New phenomena, new decay modes – Stellar nucleosynthesis, abundances of elements, age and origin of chemical elements Abstract In recent years, the availability of neutron-rich radioactive ion beams has allowed to explore new regions of the nuclear chart. Despite the most exotic nuclei have been produced with quite low intensities, new interesting results have revealed an evolution of the nuclear structure far from the valley of stability. Some of the well established fundamental properties of the nuclear Nuclear chemistry is the study of reactions that involve changes in nuclear structure. The chapter on atoms, molecules, and ions introduced the basic idea of nuclear structure, that the nucleus of an atom is composed of protons and, with the exception of \ (\ce {^ {1}_ {1}H}\).
Nuclear Structure far from Stability at LNL
In particular, exotic decay modes like proton emission provide essential spectroscopic tools for probing the structure of nuclei far from the valley of stability—the region containing stable Before exploring nuclei far from stability, I will discuss in a second part, how one has learned from past experimental studies to uncover nuclear structure phenomena and elementary modes of motion in the region near the valley of β-stability.
Abstract Background: Modern nuclear structure models suggest that the shell structure near the valley of stability, with well-established shell closures at ? = 5 0, for example, changes in very neutron-rich nuclei far from stability.

Semantic Scholar extracted view of „Nuclear structure far from the valley of [beta]-stability“ by P. Ring
Abstract In recent years the availability of neutron-rich radioactive ion beams has allowed to explore new regions of the nuclear chart. Despite the most exotic nuclei have been produced with quite revealed an evolution low intensities, new interesting results have revealed an evolution of the nuclear structure far from the valley of stability. Some of the well established fundamental properties of the nuclear
Masses of exotic calcium isotopes pin down nuclear forces
We review recent studies of the evolution of collective excitations in atomic nuclei far from the valley of β-stability. Collective degrees of freedom govern essential aspects of nuclear structure, and for several decades the study of collective modes such as rotations and vibrations has played a vi Nuclear structure far from the valley of beta-stabilityInicio Revista Revista mexicana de física New phenomena such as halo nuclei—with regions of nearly pure neutron matter—and growing evidence of the fragility of shell structure far from the valley of stability are just two examples.
In order to understand the structure of a nucleus, apart from establishing the interaction between its components, it is necessary to determine the special arrangement of the nucleons. Presently our knowledge about the structure of nuclei is mostly limited to systems close to the valley of stability, or nuclei with a deficiency of neutrons, which can be produced in
– Limits of stability up to the heaviest elements – Magic numbers and shell structure far-off stability, neutron skins and neutron matter – Detailed understanding of the strong force, isospin dependence, unique nuclear model – New phenomena, new decay modes – Stellar nucleosynthesis, abundances of elements, age and origin of chemical elements To explore the structural evolution in the nuclei far from the valley of stability, nuclear binding energies and implying that charge radii are considered to be most sensitive observables. Abstract In recent years the availability of neutron-rich radioactive ion beams has allowed to explore new regions of the nuclear chart. Despite the most exotic nuclei have been produced with quite low intensities, new interesting results have revealed an evolution of the nuclear structure far from the valley of stability. Some of the well established fundamental properties of the nuclear
Measurements of nuclear magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments are considered quite important for the understanding of nuclear structure both near and far from the valley of stability. The recent advent of radioactive beams has resulted in a plethora of new, continuously flowing, experimental data on nuclear structure – including nuclear moments – 1 Introduction Studies of nuclei far from the valley of beta stability offer new opportunities for research in the areas of nuclear structure physics, atomic physics and chemistry as well as in nuclei far from stability nuclear astrophysics, material science and biophysics. In nuclear physics there are a number of identified and exciting topics to be addressed in the coming years together with unexpected phenomena Modern nuclear structure theory is rapidly evolving towards regions of exotic shortlived nuclei far from stability, nuclear astrophysics applications, and bridging the gap between low-energy QCD and the phenomenology of finite nuclei. The principal objective is to build a consistent microscopic theoretical framework that will provide a unified description of
What Is Nuclear Stability In Chemistry
It has been very successfully applied in the description of a variety of nuclear structure phenomena, not only in nuclei along the valley of P-stability, but also in exotic nuclei with extreme isospin values and close to the particle drip lines. Studies of nuclei far from the valley of stability are currently in the center of modern nuclear physics. For such loosely bound systems, the continuum effects are vitally important. We develop the continuum shell model based on an effective non-Hermitian Hamiltonian. This rigorous quantum-mechanical method is powerful for description of open Experimental and theoretical studies of exotic nuclei, i.e., very short-lived nuclei far away from the valley of stability in the chart of the nuclides, present a unique and important way to gain a general understanding of the Published by the American Physical Society under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license.
Furthermore, atomic mass data from nuclei far from the valley of stability would shed light on the evolution of shell closures, nucleon-nucleon correlations, fundamental symmetries, and nuclear existence limits. They will also aid in the improvement of nuclear models.
Exotic structures and dynamics have been discovered in nuclei far from the valley of β-stability, which exemplify open quantum systems governed by the nuclear force rooted in quantum 7. Summary Future perspectives in nuclear structure are based on radioactive as well as on high intensity stable nuclear beams. Neutron rich nuclei far from stability can be investigated at medium spin using deep-inelastic and multinucleon transfer reactions. Isotope Valley of stability Nuclear Stability: Factors affecting it, nuclear forces, binding energy What is nuclear stability class 11 chemistry CBSE What is Nuclear Stability Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Structure and Stability Lightest uranium isotope yet reveals nuclear stability secrets 19.8: Nuclear Stability 21.1 Nuclear Structure
- Nutritional Foods To Stock In Your Pantry During Covid-19
- Nosleep Podcast S16E19 | "What Was Buried" S16E19 Scary Stories Told in the Dark
- Nr445 Rules For The Classification Of Offshore Units
- Novation Nocturn Ableton Tutorial
- Notar In Ebersbach An Der Fils Mit Öffnungszeiten.
- Nous Allons Vous Présenter : Refuge de Buigny Saint Maclou
- Nummernschild, Burj Al Arab, Dubai, Vereinigte Arabische Emirate
- Remote I/O Is1 Analog Universal Modul Hart Für Zone 1 Ex I
- Nuala Quinn-Barton , Wie man ausspricht Nuala Quinn-Barton
- Nude Love Parade In San Francisco
- Nwt Bible Covers: Pink, Pocket Size
- Noticias Sobre Sucesos Zamora _ Empotra su turismo contra los bajos del edificio de Cáritas en Zamora
- North–South Railway Project South Line