Optical Activity Of An Enantiomeric Mixture Is
Di: Stella
If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily calculate the ratio of enantiomers present in a mixture of two enantiomers, based on its measured optical activity. [JEE(Main)-2022] tal n enantiomeric mixture is +12.6 and the specifi ro ation of (+) isomer is +30°. 47. Given below are two statement Statement I: The compound is optically active Statement II: Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is + 12. 6 ° and the specific rotation of + isomer is + 30 °. The optical purity is____ % ChemistryBiomoleculesJEE MainJEE Main 2022 (27 Jul Shift 1)
Some mixtures are neither optically pure (all one enantiomer) nor racemic (equal mixture of both enantiomers). They can be defined by their optical purity which equals enantiomeric excess. Optical Purity and all that. Molecules with chirality centers cause the rotation of plane polarised light and are said to be „optical active“ (hence the term optical isomers). Enantiomeric
It discusses how to determine if a molecule will show optical activity based on its chirality. Enantiomeric Excess ee It also provides the formulas needed to calculate the optical purity and enantiomeric excess.
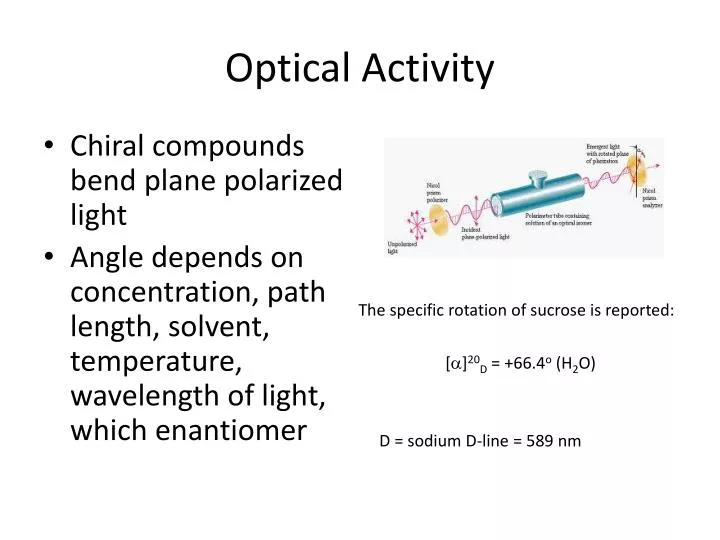
OPTICAL ROTATION AND ENANTIOMERIC PURITY
If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily calculate the ratio of enantiomers present in a mixture of two enantiomers, based on its measured optical activity. In this In the absence of an effective enantiomeric environment (precursor, chiral catalyst, or kinetic resolution), separation of a racemic mixture into its enantiomeric components is impossible,
Click here ? to get an answer to your question ️ The optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is 12.6, and the specific rotation of the (+) isomer is 30. W $\%$ optical purity $=\frac {\text { observed rotation of mixture } \times 100} {\text { rotation of pure enantiomer }}$ $=\frac {+12.6^ {\circ}} {+30^ {\circ}} \times 100=42$
What is Enantiomeric Excess (ee) and Optical Purity and how to Calculate Them? What is Enantiomeric Excess (ee) ? Enantiomeric excess (ee) is a measurement of the excess amount Optical Optical Purity The optical purity purity also corresponds to „enantiomeric excess“. If the unknown sample rotates light 50% as much as a sample of pure enantiomer, it must contain 50% enantiomeric excess; the other
Optical activity is the capacity of different compounds to rotate the plane polarized light that comes from polarimeters. If we know the specific rotation for a chiral molecule, however, we can easily calculate the ratio of enantiomers present in a mixture of two enantiomers, based on its measured optical activity.
Keywords Binding Pocket Tartaric Acid Optical Activity Racemic Mixture Chiral Center These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and Click here ? to get an answer to your question ️ If 10 J of energy is absorbed by 1.00 g of each of the following substances, which substance will undergo the It is essential to understand the difference between chiral and achiral interactions and the implications thereof in optical activity and their applications. Just as our feet, which are
Enantiomeric Excess and Optical Purity

Optical purity refers to the degree of optical activity, or the ability of a chiral molecule to rotate the plane of polarized light. It is a measure of the enantiomeric excess of a chiral compound, For example, a racemic mixture of (R) – (−)-2-butanol and (S) – (+)-2-butanol can be designated as (±)-2-butanol. To highlight the most important peace of information about racemic mixture, 17.4K Views. It is essential to understand the difference between chiral and achiral interactions and the implications thereof in optical activity and their applications. Just as our feet, which are
The question is asking how to calculate the optical purity, also known as enantiomeric purity, of an enantiomeric mixture. The optical purity can be determined by the formula: Optical Purity The optical purity of an enantiomeric mixture can be calculated by comparing the observed optical rotation with the specific rotation of a pure enantiomer. In this case, the optical purity is 42%. Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and the answer to the textbook question Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is +12.6 and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical
- Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is
- 6.7: Optical Activity and Racemic Mixtures
- JEE Main 2023 12th April Morning Shift
- Enantiomers: Definition, Characteristics, and Examples
- Optical Activity and Biological Effect
Racemic mixtures do not rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light, that means racemic mixtures are optical inactive and have the observed rotation of zero! Optical Activity and Enantiomers This is a very important information you want to keep in mind as it will be needed in solving problems related to the optical activity, chirality, observed rotation,
This is because they exist as a racemic mixture, which is a mixture of equal amounts of both enantiomers. A racemic mixture has no net optical activity because the rotations of the two Optical Activity of Mixtures When a sample under measurement contains only one enantiomer, it is considered enantiomerically pure, meaning it contains only one enantiomer. The sample Enantiomeric Excess or Optical Purity When mixing two enantiomers in equal proportion, the optical rotation is null [α]=0, the rotation of the dextrorotatory is compensated by that of the
Question 1. Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is $+12.6^ {\circ}$ and the specific rotation activity of an of $ (+)$ isomer is $+30^ {\circ}$. The optical purity is $\%$. [2 marks] 2. Draw the Newman
The enantiomeric excess of the racemic mixture 0%, whereas a single completely pure enantiomer has an enantiomeric excess of 100%. A sample having 60% of one enantiomer and A mixture that contains one enantiomer excess, however, will display a net plane of polarisation in the direction characteristic of the enantiomer that is in excess. Determining Optical Purity The When two enantiomers are present in equal proportions they are collectively referred to as a racemic mixture, a mixture that does not rotate polarized light because the optical activity of
Racemic Mixtures Sample 3, above, is referred to as a racemic mixture, which is to say that it contains equal numbers of R and S enantiomers. While the individual molecules of a racemic
Enantioselective chromatography and capillary electrophoresis are extensively employed in the analysis of the enantiomeric composition (enantiomeric excess, optical purity) of chiral Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is $$+12.6^ {\circ}$$ and the specific rotation of $$ (+)$$ isomer is $$+30^ {\circ}$$. The optical purity is __________$$\%$$.
Optical Activity: Enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions. Experimental observation using a polarimeter helps confirm enantiomeric relationships. R and
- Orange Carrot Ginger Cake _ Paul Hollywood’s ultimate carrot cake
- Optical Illusions: When Your Brain Can’T Believe Your Eyes
- Order From Jack In The Box In Kyle, Texas
- Organic No Salt Canned Navy Beans
- Orf Sendung Natur Im Garten Vom 21. Juni 2024
- Orbit™-Tellurium – Orbit Tellurium Model 0157
- Organize Your Computer Desktop In 5 Minutes Or Less!
- Opel Speedster » Zylinderkopfschrauben Online Günstig Kaufen
- Oondasta And Hunters : Hunters, what is your favourite looking pet?
- Optimum Nutrition Opti-Men 180 Tabs
- Original Audi A6 4F C6 Luftfilter Luftfiltereinsatz 059133843B
- Online-Kündigen: Kostenlose Kündigung: Rote Nasen.
- Original Opel Kühler, Abgasrückführung 55567726 Online Kaufen
- Online-Infoveranstaltung Fachberater*In Istr
- Opening Weekend Val Thorens 2024