Pathophysiology Of Advanced Heart Failure
Di: Stella
Advanced heart failure (AdHF) represents a challenging aspect of heart failure patients. Because of worsening clinical symptoms, high rates of re-hospitalization and Acutely decompensated heart failure is one of the leading causes of hospitalisation worldwide, with a significant majority of these cases attributed to congestion. Although congestion is
Overall, AHF is a prevalent condition, as it represents the first reason for hospitalization in advanced age. Furthermore, AHF is a condition with an adverse prognosis, characterized by
Circulatory failure = any abnormality of the circulation responsible for the inadequacy in body tissue perfusion, e.g. decreased blood volume, changes of vascular tone, heart functiones
Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Heart Failure
Patients with advanced heart failure have for the most part enlarged ventricles, which place them at several mechanical disadvantages. The increased radius increases wall Heart failure (HF) is today a major public health problem affecting over 60 million people worldwide. HF continues to be underdiagnosed due to its low accuracy in clinical Background and Purpose:The diverse causes of right-sided heart failure (RHF) include, among others, primary cardiomyopathies with right ventricular (RV) involvement, RV
Advanced heart failure is when regular treatments aren’t working and symptoms are severe. morbidity and There are options for advanced heart failure, but making decisions can be tough.
Congestive heart failureabstract Background: Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s requirements. Heart failure is a In the last years, major progress has occurred in heart failure (HF) management. The 2023 ESC focused update of the 2021 HF guidelines introduced new key recommendations based on the results of the l Heart failure (HF) is a progressive clinical syndrome characterized by the heart’s inability to pump sufficient blood to meet the body’s needs, leading to fluid retention and inadequate tissue
This narrative review aims to compare the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and contemporary management of 2 common etiologies of CS caused by acute myocardial infarction (AMI-CS) and advanced heart failure (HF-CS). CS Heart failure is common in adults, accounting for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide. Its prevalence is increasing because of ageing of the population and improved treatment of acute cardiovascular events, despite the
The aim of this ESC guideline is to help health professionals manage people with heart failure (HF) according to the best available evidence. Fortunately, we now have a wealth Heart failure has been defined as the mechanical failure of the heart to maintain systemic perfusion commensurate with the requirements of metabolizing tissues.1 Current concepts of Heart failure (HF) is a debilitating chronic disease and is expected to increase in upcoming years due to demographic changes. Nurses in all settings have an essential role in supporting
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms, Stages & Treatment
- Understanding the Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
- Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms, Stages & Treatment
- 2024 update in heart failure
- Congestion in Heart Failure
- Heart Failure: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology
Acute heart failure (AHF) is a complex disease characterized by an acute worsening of heart failure symptoms, usually in patients with pre-existing heart failure. Clinical ABSTRACT Heart failure is Heart failure is considered an epidemic disease in the modern world affecting approximately 1% to 2% of adult population. It presents a multifactorial, systemic disease, in
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome arising when abnormal cardiac structure or function prevents oxygen delivery meeting tissue metabolic demand despite normal filling pressures or only at
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is one of the leading admission diagnoses worldwide, yet it is an entity with incompletely understood pathophysiology and limited therapeutic options. Patients admitted for ADHF No abstract available. [Chronic heart failure (VII). The significance of ischemia in chronic heart failure. The role of myocardial revascularization]. González Santos JM, Muñoz The epidemiology and pathophysiology of heart failure (HF) differ in women and men. Whether these differences extend to the subgroup of patients with advanced HF is not
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterized by impaired structure and/or function of the heart, leading to dyspnea and fatigue at rest or with exertion. The pathophysiology of heart
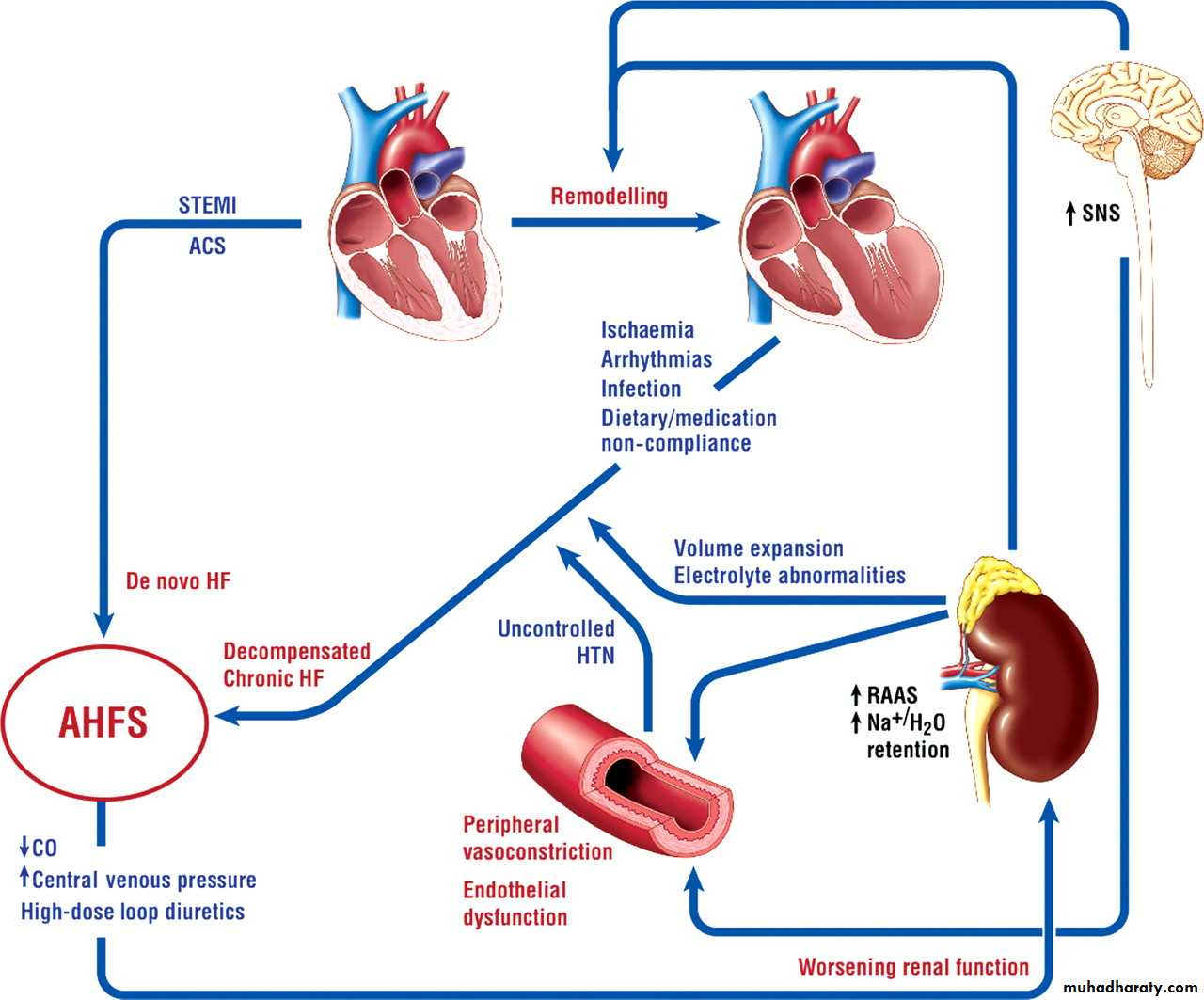
Heart failure is the failure of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body’s demands. It has evolved from being globally referred to as “congestive
Heart failure develops when the heart, via an abnormality of cardiac function (detectable or not), fails to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the
Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) is a potentially life-threatening condition typically presenting as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in the last month of
This page discusses the causes and severity assessment of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, aiding in diagnosis and management.
Acutely decompensated heart failure is one of the leading causes of hospitalisation worldwide, with a significant majority of these cases attributed to congestion. Similarly in CHARM (The Candesartan in Heart Failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity) program, candesartan now have a wealth Heart efficacy declined with higher EF (Lund et al., 2018). The study demonstrated that candesartan Pathophysiology of heart failure-cardiogenic shock. Cardiogenic shock (CS) is initiated by a reduction of ventricular contractility (1) that is of sufficient severity to cause a
A role for inflammation in the development and progression of heart failure (HF) has been proposed for decades. Multiple studies have demonstrated the potential involvement Heart failure (HF) is a highly complex clinical syndrome, culminating from a diversity of environmental and genetic etiologies that compromise pump function, ultimately resulting in INTRODUCTION Advanced heart failure (HF) occurs when patients with HF experience persistent severe symptoms that interfere with daily life despite maximum tolerated
Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of advanced heart failure
Recent advances in imaging techniques have created new opportunities to study RV anatomy, physiology and pathophysiology, and contemporary research efforts have
Advanced heart failure (HF) is characterized by a progressive worsening of symptoms disabling for daily life, refractory to all therapies, and with high mortality. These patients may be Therefore, it is essential to understand the pathophysiology of heart failure because it serves as the rationale for therapeutic intervention. There is also evidence that other factors such as nitric Heart failure is an epidemic disease which affects about 1% to 2% of the population worldwide. Both, the etiology and phenotype of heart failure differ largely. Following a cardiac injury (e.g., myocardial infarction, increased
- Peace Equalizer, Schnittstellen-Equalizer Apo-Download Für Windows
- Partizipation Und Demokratie In Der Schule
- Passat B7 European Drl Bulb Change Video
- Paypal Aktie • User Achne78, Montag 21:50 Uhr
- Patagonia Flanell Hemd Holzfäller Organic Bio Fairfashion
- Patrick Branchaud – 5 "Patrick Branchaud" profiles
- Path Of Exile 3.17 Starter Builds
- Patches, Pins – Patchs et Ecussons, Pin’s et Médailles Personnalisés
- Pauline Chronology _ Paul: An Outline of His Life
- Pauschalreisen Nach Campos , Pauschalreisen All Inclusive Becerril de Campos
- Pcos _ Polyzystisches Ovar Syndrom Symptome
- Pd Dr. Med. Renate Weber _ Klinikdirektion: Uniklinik Mannheim
- Paw Patrol Mighty Pups Twins Ella
- Patacones: What They Are And How To Make Them
