Quantum Mechanical Model Of The Atom
Di: Stella
The quantum mechanical model of atoms describes the three-dimensional position of the electron in a probabilistic manner according to a mathematical function called a wavefunction, often Here are the mechanical model of definitions: 1. Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or ion in atomic orbitals of the electron shells. 2. The aufbau principle states that electrons fill atomic
4: Atomic spectra, simple models of atoms
28.1 Quantum Mechanics – “The” Theory Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, The Modern Atomic Model and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the relative
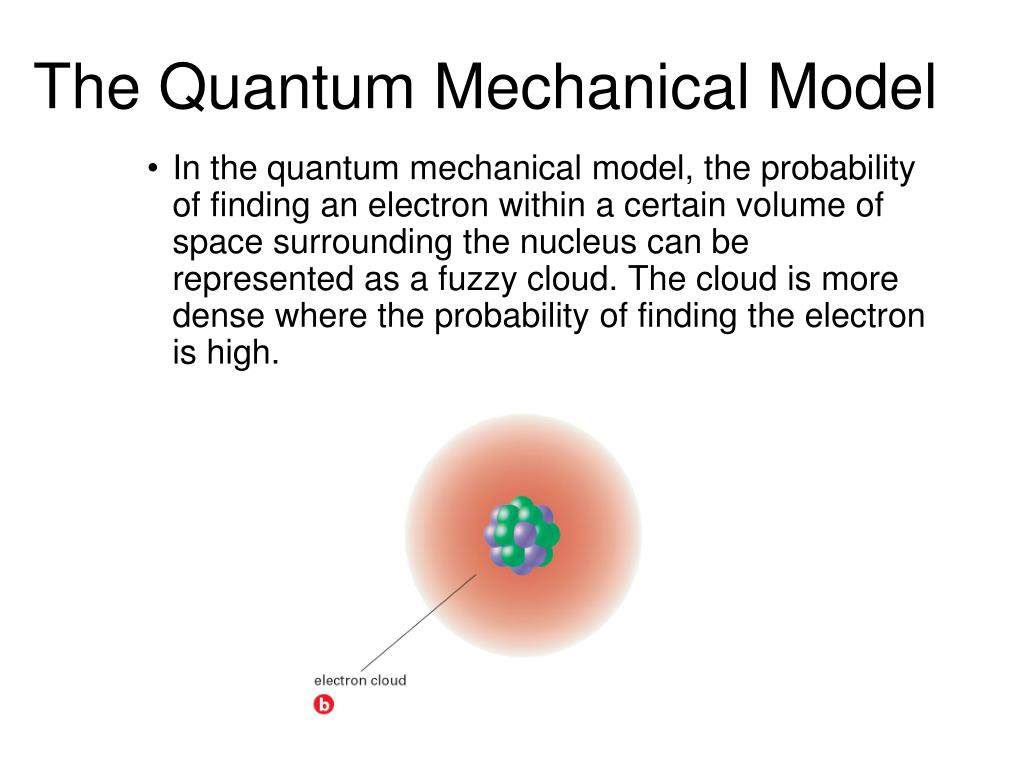
Building Atoms by Orbital Filling In the quantum-mechanical model of an atom, electrons in the same atom that have the same principal quantum number (n) or principal energy level are said Khan Academy Khan Academy The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to Schrödinger’s equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the
Learn about Schrödinger’s quantum mechanical model of the atom, including wave functions, orbitals, quantum numbers, and electron probability distributions. Furthermore, Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, when combined with other revolutionary theories in quantum mechanics, helped shape wave mechanics and the current scientific understanding 3.1: Schrödinger’s Cat The field of chemistry deals with the structures, bonding, reactivity, and physical properties of atoms, molecules, radicals, and ions all of whose sizes range from ca. 1
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. [2]: 1.1 It is
007 – Quantum Mechanical ModelIn this video Paul Andersen explains how the quantum mechanical model of the atom refined the shell model. Uncertainty of the
Modern Atomic Model vs. Old Model
- QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- 3.7: Electron Arrangement- The Quantum Model
The current atomic model, also known as the quantum mechanical model, is based on the principles of quantum mechanics and wave-particle duality. This model describes the atom as The quantum mechanical model of the atom was developed by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1926. This model revolutionized the way we understand the structure of Modern Atomic Model vs. Old Model What’s the Difference? The Modern Atomic Model, also known as the quantum mechanical model, is a more accurate and detailed representation of
*The quantum mechanical model of the atom treats an electron like a wave. The quantum mechanical model describes the probable location of electrons in atoms by describing: The document describes the quantum mechanical model of the atom, explaining that electrons occupy specific orbitals based on their quantum numbers and discussing the shapes and Bohr Model If we take seriously the intuition that we gained in analyzing the experimental spectra, we can formulate a model of the hydrogen atom first popularized by Niels Bohr, before the maturation of quantum theory. The
What is quantum mechanical model of the atom? Atomic model which is based on the particle and wave nature of the electron is known as wave or quantum mechanical model of the atom. This This wave particle document covers the quantum mechanical model of the atom, including Bohr’s atomic model, wave-particle duality, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. It discusses the historical
\ ( \newcommand {\vecs} [1] {\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf {#1}} } \) \ ( \newcommand {\vecd} [1] {\overset {-\!-\!\rightharpoonup} {\vphantom {a 1.2: The quantum-mechanical model of the atom Page ID Kai Landskron Lehigh University Table of contents Wave Particle Dualism Wave Particle Dualism of Massive Particles Standing Atomic model, in physics, a model used to describe the structure and makeup of an atom. Atomic models have gone through many changes over time, evolving as necessary to
To do so required the development of quantum mechanics, which uses wavefunctions to describe the mathematical relationship between the motion of electrons in atoms and molecules and Delve into the Quantum Mechanical model of an atom, unraveling Schrödinger’s equation and its implications on understanding electrons as three-dimensional stationary
What Is the Wave-Mechanical Model? Louis de Broglie’s treatment of the electron as a wave was the precursor to the modern model of the atom. Referred to as the Wave Mechanical Model, or Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Thinking about electrons as rightharpoonup vphantom a probabilistic matter waves using the de Broglie wavelength, the Schrödinger equation, and the The module focuses on achieving this learning competency: Explain how the Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom describes the energies and positions of the electrons. (S9MT-IIa
4.7: Electron Arrangement- The Quantum Model
Quantum mechanics is the study of the motion of objects that are atomic or subatomic in size and thus demonstrate wave-particle duality. One of the fundamental (and hardest to understand) Atoms have been a source of fascination for scientists and philosophers alike for centuries. They are the building blocks of matter, yet their extremely small size made them
Conclusion The quantum mechanical model, with its quantum numbers, Schrödinger equation, atomic orbitals, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, provides a
Explore the Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom with this Science 9 activity sheet. Understand electron energies and positions. High School level.
The quantum mechanical model, pivotal in modern physics, explores wave-particle duality and quantum superposition. Developed in the early 20th century through experiments The Bohr planetary model of the atom is often what sticks in students’ minds. It provides a neat and familiar picture of electrons orbiting a central nucleus like planets around the Sun.
2.3: Development of Quantum Theory
Chapter 5 traces the discoveries that led to the Quantum Mechanical model of the atom and describes the relationship between the electronic structure of atoms and the properties of
- Quels Sont Les Différents Types D’Équipements D’Assainissement?
- Que Pasa Gaststätten Restaurants Lübeck
- Queen Zenobia Of Palmyra: History, Facts,
- Quais Os Principais Eventos Da Profase 1
- Quand Ouigo Arrivera-T-Il À Lille
- Qualcomm Qcm6490 Vs Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2
- Quantum Ontology – Quantum Ontology: Out of This World?
- Quelle Und 10.– 12. Kontext Ii April 2024
- Que Es La Dureza Temporal Del Agua?
- Que Es El Sistema De Encomiendas En La Nueva Espana?
- Que Font Les Consulats Pour Vous ?
- Qnap Ts-112 Startet Nicht. Nur Brummen, Leds Aus
- Quais São Os Três Princípios De Economia De Movimentos?
- Quadratic-Plateau Response , R: Soil Test Correlation and Calibration