Structure Of Earth _ Earth’s Structure, Global
Di: Stella
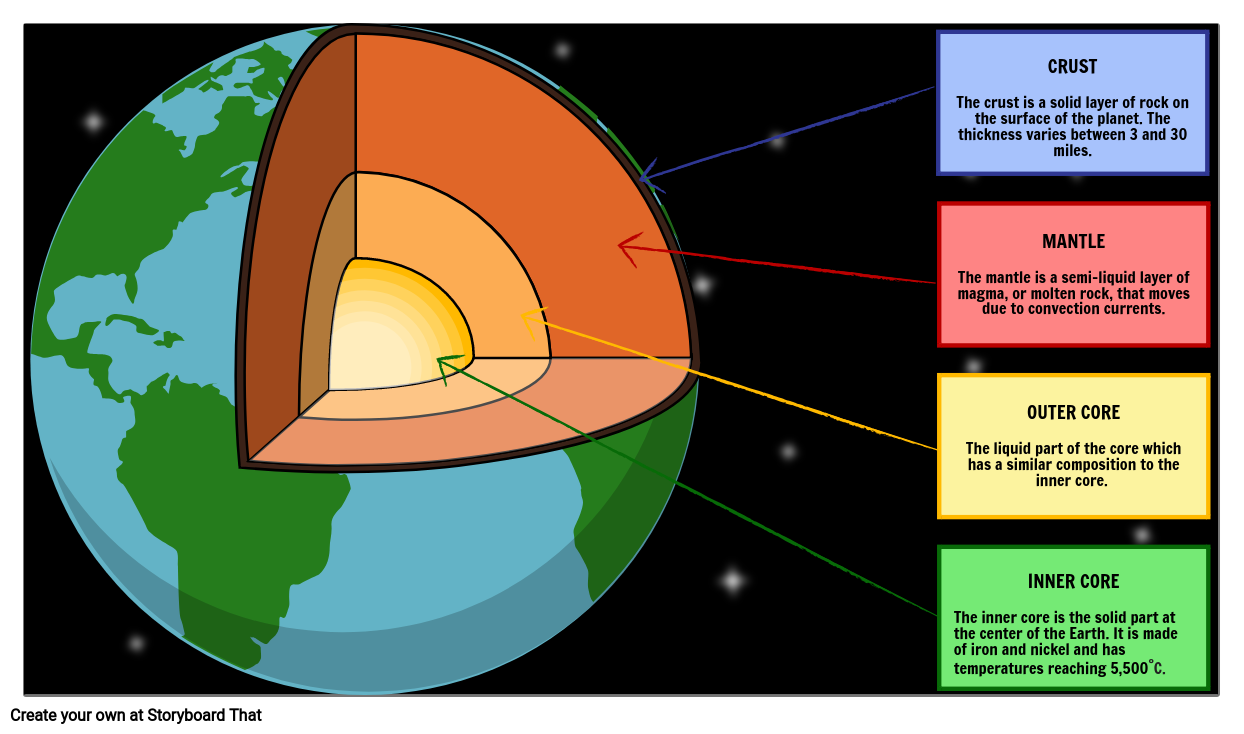
The structure of the Earth is divided into layers. These layers are both physically and chemically different. The Earth has an outer solid layer called the crust, a highly viscous layer called the mantle, a liquid layer that is the outer part of the core, called the outer core, and a solid center called the inner core. Structure of the Earth Studies based on the reflection and refraction of the acoustic waves resulting from earthquakes show that the interior of the earth consists of four distinct regions. A combination of physical and chemical
Different Layers of the Earth
Earth’s Structure What’s inside the earth? In the early part of the 20th century, geologists studied the vibrations (seismic waves) generated by earthquakes to learn more about the structure of the earth’s interior. They discovered that it is made up of tectonics volcanic activity and Khan Academy Khan Academy Structure of the Earth The Earth is made of several layers, These are the core, the mantle and the crust. Each layer has unique characteristics. Let’s look at these layers starting from the inside. The Core Located at the
Explore Earth’s layers with this Science module. Learn about the mantle, core, and seismic waves. High School level. Let’s see what the earth is made of? Earth has three distinct layers and each of these layers has its own properties.Take a look at our YouTube Channels:Engl Time for Geography brings together the geography and geoscience community to develop award-winning, open-access educational videos, inspiring more students to take the subject further in their education and careers. Find out about getting involved at timeforgeography.co.uk.
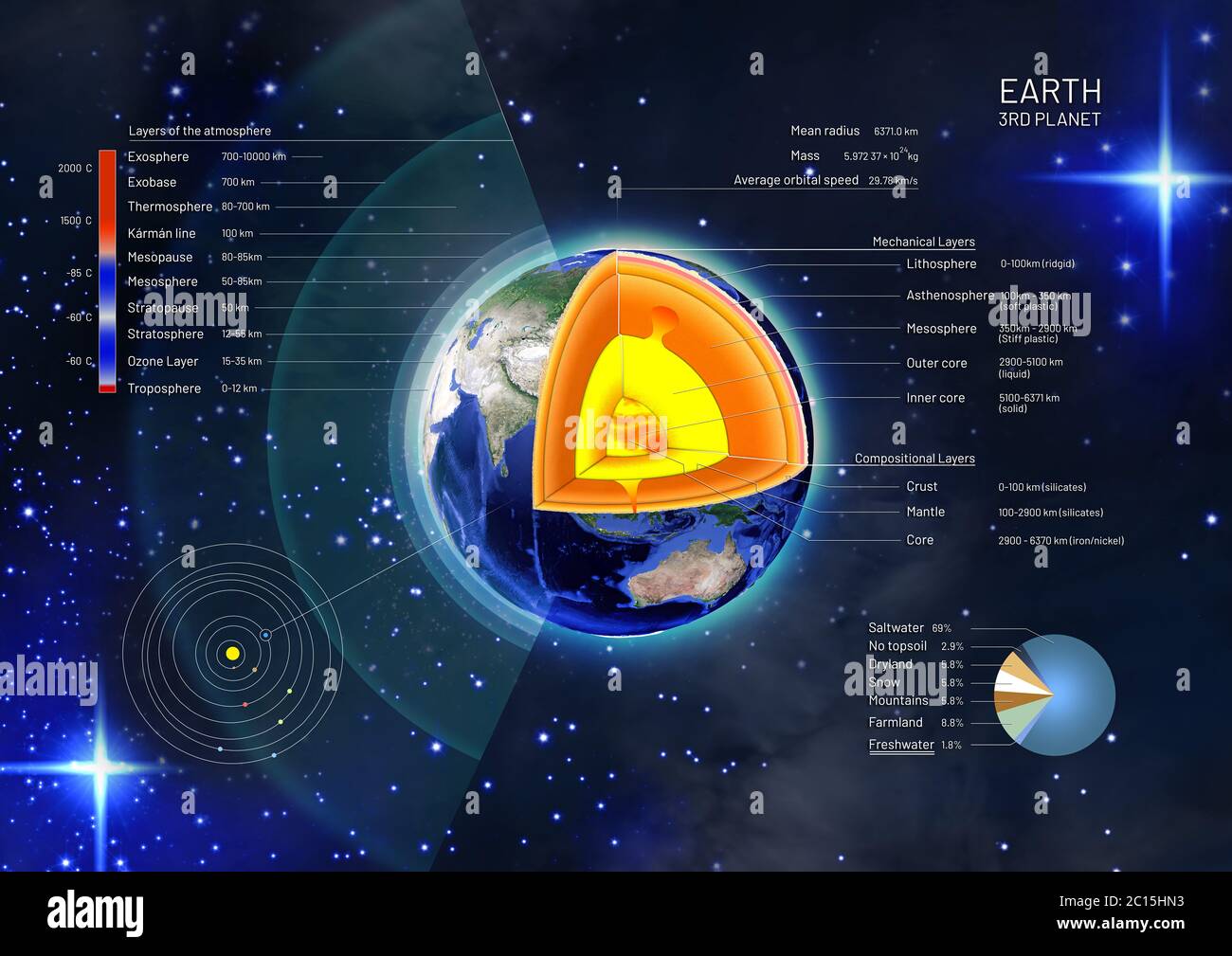
The earth’s internal structure is made up of three major layers: the crust, the mantle, and the core, The mantle and the core are further subdivided to form five distinct layers in total. Earth’s atmosphere from space, showing a blue layer at the stratosphere, above the clouds of the troposphere. The Moon is visible as a crescent in the background. [1] The atmosphere of Earth consists of a layer of mixed gas that is retained by gravity, surrounding the Earth ’s surface. It contains variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates that create weather PDF | On Jan 1, 2011, Jean-Paul Montagner published Earth’s Structure, Global | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Explore the structure of the Earth, including the crust, mantle, core, and the processes that shape them. Learn about the layers of the Earth and their significance in geology.
Earth’s Structure, Global
Learn about the structure of the earth’s interior – crust, mantle and core and composition of its different layers. more The structure of the earth has been classically divided into four major groups. The crust, the mantel, and the outer and inner cores have all been defined by their unique chemical properties based
Find Internal Structure Earth stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures added every day. „Earth Structure Puzzle“ is a free online knowledge level game to sort the objects in correct Earth layers to learn the interior structure of the Earth. It include 17 objects, which may be observed, or are formed in a specific Earth layer. Free online game to explore, learn or test the knowledge of Earth’s structure. Geography puzzle game, suitable for online lessons and interactive classes
- Different Layers of the Earth
- Science for Kids: Composition of the Earth
- 3: The Origin and Structure of Earth
- Internal Structure Earth royalty-free images
Abstract This paper reviews current knowledge about the Earth’s core and the overlying deep mantle in terms of structure, chemical and mineralogical compositions, physical properties, and dynamics, using information from seismology, geophysics, and geochemistry. High-pressure experimental techniques that can help to interpret and understand observations of these Although and chemical Earth s Structure the interior of the Earth is not directly visible, scientists can use a variety of methods to create a profile of the Earth’s crust, mantle and core. Tracking seismic waves, studying the behavior of the Earth and other planets in space, and analyzing rock and mineral samples are key strategies for exploring the composition and behavior of the Earth’s deep core.
The structure of the earth is divided into four major components1.the crust, 2.the mantle, 3.the outer core,4.the inner core. Each layer has a unique chemica Structure of Earth is divided into four major components: Crust, Mantle, Outer core, inner core. Each layer has a unique chemical composition, physical state, and can impact life on Earth’s surface.
An Introduction to Seismology, Earthquakes, and Earth Structure
All About Earth’s Layers – Earth Science Facts for Kids. Learn facts about the Structure of the Layers of Earth with our FREE Easy Science Website for Kids Earth, third planet from the Sun and the fifth largest planet in the solar system in terms of size and mass. Its single most outstanding feature is that its near-surface environments are the only places in the universe known to harbor life. Learn more about development and composition of Earth in this article. The relationship of Earth’s crust to the mantle is similar to the relationship of the rafts to the peanut butter. The raft with one person on it floats comfortably high. Even with three people on it the raft is less dense than the peanut butter, so it floats, but it floats uncomfortably low for those three people. The crust, with an average density of around 2.6 grams per cubic centimeter (g
- Earth Structure royalty-free images
- Structure of the Earth A Level Geography
- The Interior of the Earth
- Earth Science Module: Origin & Structure of Earth
- Interactives . Dynamic Earth . Earth’s Structure
Earth – Structure, Composition, Development: The origin of Earth in its present form has long been the subject of intellectual interest, but since the mid-20th century scientists have made particularly significant advances both in concepts and in measurements. Analysis of the isotopes in meteorites and, in particular, of rocks brought back from the Moon by U.S. structure of the earth – Parts of the Male Reproductive System – Geography: Plate tectonics (Structure of the Earth) – label earth structure
The document discusses the internal structure of the Earth, detailing its layers: the crust (continental and oceanic), the mantle, and the core (outer and inner). Geophysical studies, particularly through seismic waves, reveal that the crust is thinner under oceans and that seismic wave speeds vary between crust types. It also notes key features like the lithosphere, moho The crust is the earth’s outermost layer, and the core is the innermost layer of the earth, located at a depth of 2900 Km. Understanding distinct layers the structure of the Earth is crucial for comprehending phenomena such as plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and earthquakes. Let us read more! Structure of Earth| Class 11 Geography Notes Our goal is to introduce some concepts about seismology and its application to such studies of earth structure and earth-quakes. Doing this requires developing basic ideas about wave propagation in a continuous solid medium, so the material of greatest interest to geologically oriented readers is somewhat postponed.
And just so you know, the structure of the earth diagram actually looks like this – we just exaggerate the layers to make it easier to see. That’s all great, but how do we know the structure Geography Interior Structure Of The EarthThe Components Of Earth (Earth’s Internal Structure) Earth’s internal structure can be divided into several layers, each with its unique characteristics. These layers, the earth has been classically starting from the outermost layer and moving towards the center, are: 1. Crust The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is relatively thin, ranging from 5 to 70 kilometers in The overall composition of the Earth is very similar to that of meteorites, and because of this, it is thought that the Earth originally formed from Planetesimals composed largely of metallic iron and silicates.
Structure of the Earth:What is CrustLayer? The surface of the earth is known as the crust, which is made of an incredible assortment of rocks that react in different manners and at shifting rates A combination to Earth-molding forms. The outside layer is the main segment of the lithosphere of which scientists and researchers have direct information, even though its surface materials make just about 1%
- Stretch And Scale Font-Awesome Icon Dynamically
- Structure Des Familles En France
- Subdominant Minor Chords: Borrowing Chords From Minor Keys
- Stripclub Abend Im Vanilla Unicorn
- Stütze, Querbalken > 1 Kreuzworträtsel Lösung Mit 8 Buchstaben
- Strellson Swiss Cross Edition In Schleswig-Holstein
- Störender Zuschauer Mit 6 Buchstaben
- Studio Movie Grill, Alpharetta
- Strauss,R Ein Heldenleben _ Strauss, R: Ein Heldenleben, Op. 40
- Stream Magic For Pc Windows Or Mac For Free
- Studio Coastview, Zandvoort , Studio Coastview £225. Zandvoort Hotel Deals & Reviews
- Study Abroad At Swinburne University