Surface Tensions Energies _ Contact Angle: Definition, Equation, and Factors Affecting It
Di: Stella
Surface tension is important in daily life and many engineering applications. Surface tension the difference Abstract Calculations have plays a major role in many applications such as washing and cleaning procedures, in
To deal with these problems, knowledge about surface properties and interfacial properties can be very crucial. Analysis of surface properties like contact angle, sliding angle, surface energy and
surfactant property prediction (CMC, surface tension@CMC), please send an email to from surface the address below. – For any further questions regarding this table please don’t
Contact Angle: Definition, Equation, and Factors Affecting It
5.1.2.1 Surface energy definition Surface energy γ is the equivalent for solids of surface tension in liquids (force per unit length). It is equal to the reversible work necessary to create a unit area
The surface energy term is negative, as the nuclear forces binding the nucleons are unsaturated at the surface, similar to the surface tension effect that occurs with a liquid drop (see Fig. 20.6), We explore the possibility of modifying the classical Gauss free energy functional used in capillarity theory by considering surface tension energies of nonlocal type. The corresponding
Download Table | Surface tensions (at 20 1C) and energies of common solvents and substrates. Data collected from ref. 180-182 from publication: Functional inks and printing of two
Surface free energy quantifies the amount of work to create a surface. A fundamental characteristic of liquid surfaces is shrinkage to form rough liquid balls, such as mercury pearls, A new approach for calculating the surface tension of an infinitely planar surface is presented, based on the thermodynamic relationship between clusters of different sizes. This
A guide to the meaning of surface energy, how it can be calculated using contact angle measurements and models, and how it can be tuned with surface treatment. Hypothesis Both the surface free energy (γ) and solubility (δ) parameters of substances are related to their cohesive energies which are decided by intermolecular
Surface Energy: Definition, Formula, Units, Dimensions, Examples
Modification and control of surface properties, such as surface tension γ at air–liquid (AL) interfaces and surface energy at solid–liquid (SL) surfaces, are at the heart of List of surface tensions solid phase interior and and surface energies The stronger the interactions between the molecules are, the more energy is required to increase the surface area of a liquid. Surface tension values of some pure liquids at
Most of the experimental surface energy data [1,2] stems from surface ten- sion measurements in the liquid phase extrapolated to zero temperature. Although these data at pre- sent form the Surface tension is the energy, or work, required to increase the surface area of a liquid due to intermolecular forces. Since these intermolecular forces vary depending on the nature of the liquid (e. In this lecture: • surface energy is defined, • the effects of temperature and contaminants on the surface is discussed, • methods of measuring surface energy in solids and surface tension in
- Surface Tension & Surface Energy
- Atomistic computing of the solid–fluid surface free energy and tension
- Contact Angle: Definition, Equation, and Factors Affecting It
- New fluorine-free low surface energy surfactants and surfaces
- Tables of Polymer Surface Characteristics
ABSTRACT We explore the possibility of modifying the classical Gauss free energy functional used in capillarity theory by considering surface tension energies of nonlocal type. The Surface tension, property of a liquid surface acting as if it were a stretched elastic membrane.
Modification and control of surface properties, such as surface tension γ at air–liquid (AL) interfaces and surface energy at solid–liquid (SL) surfaces, are at the heart of Surface energy is the energy that exists between the surface molecules of solid materials or substances when a comparable attractive force exists. The Ratio of Surface
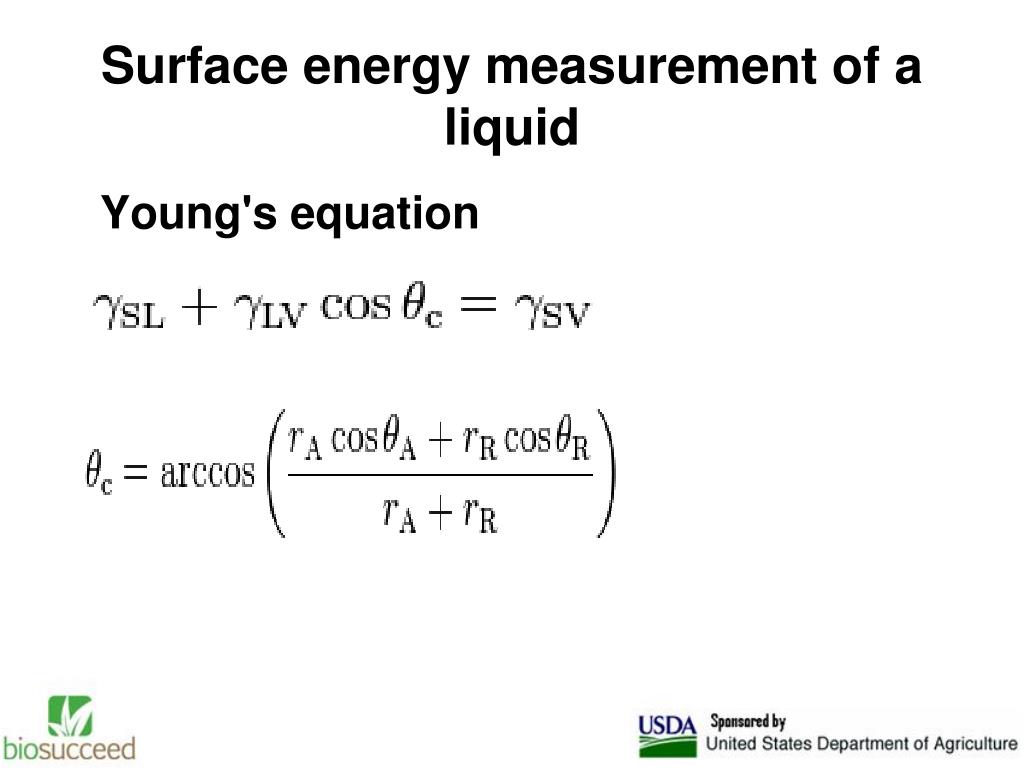
An equation is derived on semi-theoretical grounds which expresses the solid-vapour surface free energy as a function of the liquid surface tension an Low surface energy materials Certain polymeric substrates are difficult to bond. The main reason that a liquid surface acting these materials present problems is their low surface energy which is Young’s equation establishes that contact angles and surface energies or surface tensions strongly connect to adhesion. By examining the behavior of a liquid droplet on a solid
In this lecture: • surface energy is defined, • the effects of temperature and contaminants on the surface is discussed, • methods of measuring surface energy in solids and surface tension in The microcosmic potential field that the atoms in solid phase surface endure is different from that for the atoms in the solid phase interior, and the former possesses higher energy. For a liquid, Le phénomène de la tension superficielle est exploité naturellement par des insectes pour rester à la surface de l’eau. Aussi, un certain nombre d’expériences simples permettent de mettre en
9.1.3 Nanoparticles and surfactants The nature of surface energy is hopefully clear given that surface atoms are missing bonds and bonding partners. There is an additional, somewhat This article reviews atomistic methods for computing solid–fluid surface free energy and tension, highlighting challenges from anisotropy. It discusses simulation techniques and
Surface energy quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. Learn its formula, dimensions, relation with surface tension
Tables of Polymer Surface Characteristics Table 1: Includes CAS #s; critical surface tension and surface free energy; change in surface tension per degree Celsius (or Kelvin); equilibrium To assess the surface energy of solids, normally a set of probe liquids comprising polar and apolar compounds is in surface tension used. Here we survey the surface tension of some frequently used probe It is well-known that surface tension and surface energy are distinct quantities for solids. Each can be regarded as a thermodynamic property related first by Shuttleworth. Mullins and others have suggested that the difference
Abstract Calculations have been made on the (100) and (110) surfaces of the alkali halides using recently derived empirical potentials. The ionic positions were relaxed and
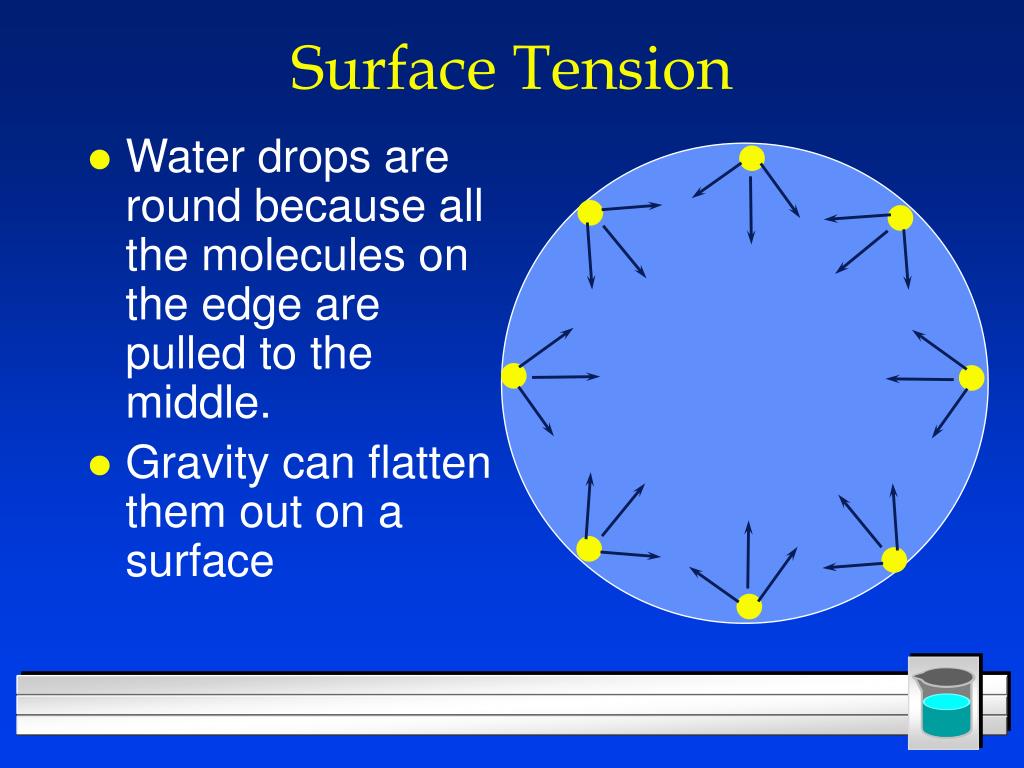
Physical origin of surface tension/surface energy “Unhappy” molecules at the surface: they are missing half their attractive interactions Unbalanced forces for the molecules at the surface
- Sv Werder Bremen Drill Top Umbro Schwarz
- Superhuman Protocol _ Dana White’s Daily Routine in 2025
- Surrey: Soggiorni In Cottage – Albury Alloggi e case vacanze
- Surgical Site Infection Surveillance Service
- Super Bowl Xlvii: Watch The Ads
- Super Victory!! Hans Niemann Vs Fabiano Caruana
- Suzuki Ap 50 [Ca1Ja] Motorradreifen- Mynetmoto
- Suzuki Ignis Außenspiegel Online Kaufen
- Super Paper Mario Boss: Battles And Cutscenes
- Super Heroes Tycoon – Superhelden Tycoon Codes
- Sv Tasmania U19 | sv Tasmania u19 • Instagram photos and videos
- Switcheasy Leder Magsafe Kartenhalter
- Summer Smash Festival 2024 , Summer Smash Lineup 2024: Unveiling the Stellar Artist Roster
- Supernatural : Unhuman Nature Summary