The Monotonic Clock And Why You Should Care About It
Di: Stella
If you grep through the kernel source you will find a number of architecture- specific implementations of clock sources, clockevents and several likewise architecture-specific overrides of the sched_clock () function and some delay timers.

Taking care of your appearance and looks is an easy way to be confident and it can definitely give you that advantage when it comes to your career and increases your chance with the ladies as well! Python time.monotonic () method is used to get the value of a monotonic clock. A monotonic clock is a clock that can not go backward. As the reference point of the returned value of the monotonic clock is undefined, only the difference between the results of consecutive calls is valid. Python time.monotonic () method Syntax: Syntax: time.monotonic () Parameter: No So why do monotonic timers exist, and when are they commonly used? As it turns out, in high-precision environments, the system clock is not a reliable way to time events. System clocks can drift over time, and when a service such as NTP updates the clock to the reference, it can cause errors in precision measurements.
As a C developer, have you ever needed to accurately measure and record timestamps in your code? Have you ever wanted microsecond or nanosecond precision when benchmarking or determining execution times? If so, then the clock_gettime() function is a vital tool for your toolbox. In this comprehensive guide, we will unpack everything you need to [] I’m not sure I get the point of _RAW. The slew is there so that the clock returns actual real units instead of some useless incorrect value. Without slew comparing two values isn’t going to give you an accurate value of the duration between The Problem: Querying Monotonic Clock Resolution In asyncio (Python’s library for writing concurrent code), the event loop relies on the time.monotonic () function for time management.
Java System.currentTimeMillis vs. System.nanoTime
Note of course that faulty hardware *could* cause CLOCK_MONOTONIC to misbehave, but you’d need a whole new level of faulty hardware for this, probably the kind where all software on the system will be randomly crashing. Those who time or wall think that „monotonic clock“ means a clock that never jumps, >>>> and that runs at a rate approximating the rate of real time. This is a >>>> very useful kind of clock to have! It is what C++ now calls a „steady >>>> clock“.
Note that on Linux, CLOCK_MONOTONIC does not measure time spent in suspend, although by the POSIX definition it should. You can use the Linux-specific CLOCK_BOOTTIME for a monotonic clock that keeps running during suspend. Why you care about jitter Doppler applications: The Doppler mode of medical ultrasound or radar determines the velocity of blood flow, airplanes, or oncoming thunderstorms. The imager transmits a continuous wave (CW) signal into (or to) its target. It then measures the frequency shift of the reflected energy. If I know a task took 25 seconds in the monotonic clock that nanoTime() uses, then I should not care whether that bears any relation to 25 seconds on any other clock??
Note that the difference in wall-clock time is 4.971283099999994 sec, while the difference in monotonic time is 5.004789300000084 sec. So, it seems that the time lib that on is returning time values in which the relation between the monotonic and wall clocks changes a bit. IOW, one of these clocks is not properly keeping time. Cc. @rsc
This is useful for things like database entries, where you may want to know approximately when bugs happen, but should not be considered an accurate time. Every time an NTP adjustment causes your clock to adjust, this „monotonic real-time clock“ will diverge more and more from real time. If that’s not what you are looking for, then maybe you are looking for monotonic clock. Monotonic clock always ticks forward and is not affected by changes in system time, but has undefined reference point. It allows you to accurately measure time elapsed between two events in the program. Why (and how much?) is CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW faster? I’d have thought it would still use rdtsc and some scale factors to interpolate since the last tick of CLOCK_MONOTONIC_COARSE (which is the fast one, just reading the timestamp from the last timer interrupt). So my assumption was that the cost of tweaking scale factors and offsets for
Querying the monotonic clock Resolution in Python’s Asyncio
- std::chrono compatible clock using CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW
- gettimeofday should never be used to measure time
- compilation error on clock_gettime and CLOCK_MONOTONIC
- How "real" is the POSIX clock in a virtual machine?
You cannot compare these values obtained from different JVM instances. System.currentTimeMillis() returns so called “time-of-day clock” time or wall-clock time, so it’s good for time-stamping. You can compare such values obtained in different JVMs even on different machines and this is as good as synchronization of clocks on What are good and bad ozone, and why should we care? Good and bad ozone have identical chemical compositions, they are gaseous molecules composed of three oxygen atoms. Depending on where ozone occurs in the atmosphere, ozone can serve as a UV filter or act as a pollutant that damages human health and crops. If you need to calculate the absolute time difference between two points in a process, you can use monotonic clock time for that purpose.
However, CLOCK_MONOTONIC is effected by NTP daemon time-changes known as clock „slewing“. By the definition of CLOCK_MONOTONIC, we know that it will never jump backwards. career and increases But how does it it mitigate changes by NTP? If the system-clock is suddenly set 5 hours in the past by NTP, does the monotonic clock run a bit slower until it
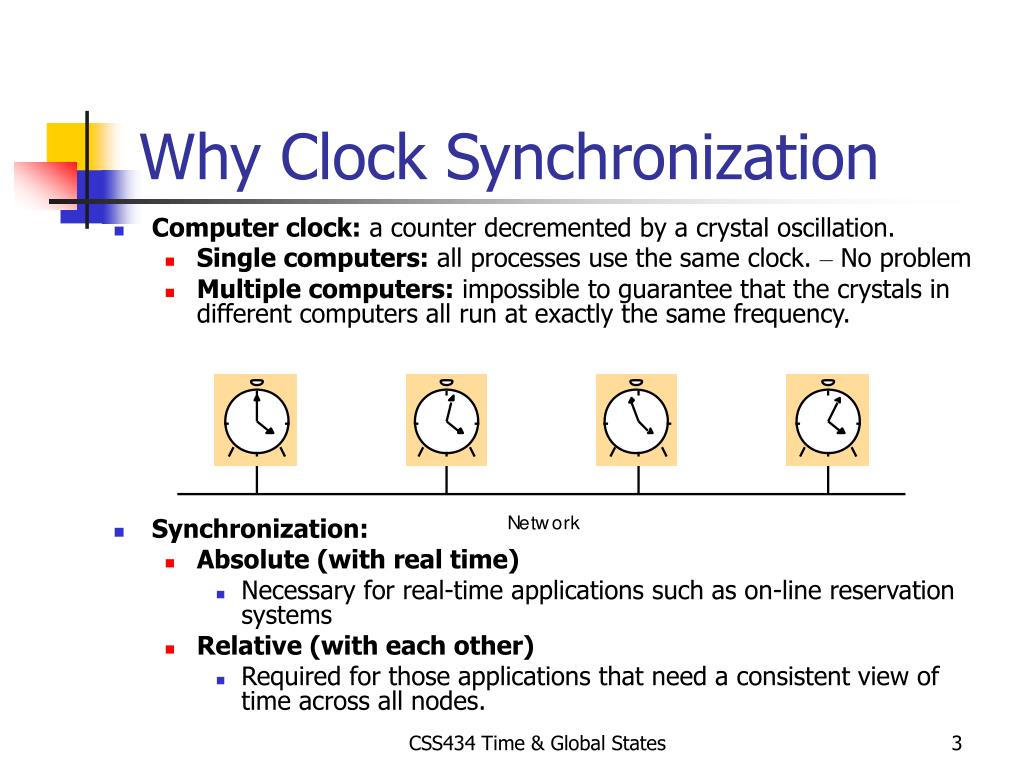
Type of clocks in linux There are roughly two type of clocks in most OS. CLOCK_MONOTONIC CLOCK_REALTIME CLOCK_MONOTONIC It is a Clock that cannot be set and represents monotonic time since some unspecified starting point. This clock should be used for calculating elapsed time. CLOCK_REALTIME It is a Clock that is more human readable. Conclusion In conclusion, both the wall clock and monotonic clock play essential roles in the functioning of an operating system. Using monotonic clocks for timing ensures that you have a timer that operates as you expect — one that increments at a constant rate and doesn’t shift under your feet.
gettimeofday() and time() should only be used to get the current time if the current wall-clock time is actually what you want. They should never be used to measure time or schedule an event X time into the future. What’s the problem? gettimeofday() returns the current wall clock time and timezone. time () returns a subset of this info (only whole seconds, and not timezone).
Python time.monotonic Function Last modified April 11, 2025 This comprehensive guide explores Python’s time.monotonic function, which provides a monotonic clock for reliable time measurements. We’ll cover its usage for benchmarking, performance timing, and practical examples. Basic Definitions The time.monotonic function returns a floating point number environments the system clock is Title: Missing In Action: Why You Should Care About Public Policy Author: Pranay KotasthanePages: 368Publisher: Penguin Buy now About the Book: Missing in Action aims to change such perceptions through sketches from everyday experiences to illustrate India’s tryst with public policymaking. It acquaints the reader with some fundamental concepts of the
This is what you really need to know, and why you should care: What is digital behaviour? Digital consumer behaviour, in terms of marketing research, essentially boils down to anything that a person does online. What devices they use, the sites they visit, the ads they engage with, the pages they navigate to, when they leave and how I thought you actually have up to KTIME_SEC_MAX which in the default namespace should gettimeofday returns the current wall give you something like 292 years. Using a new time namespace you should be able to push ahead the value of the monotonic clock to take on a value if up to half that value meaning you have at least 148 years. If you need reliable CLOCK_MONOTONIC -derived timestamp across processes that have access to the same shared memory segment, you can implement it by storing the „current“ timestamp in that shared memory.
You don’t have to have a strong opinion right away, but it’s important to be educated and aware of issues that will affect should be used for calculating you or someone you care about. Another reason you should be informed on politics is because it’s an important
It’s willing to slew the clock by 500ppm which is pretty dramatic if you’re in a position to measure your clock frequency against some other standard. The utility of CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW is going to be limited until facilities like pthread_timedwait_monotonic offer an option to use that timebase.
You can either use: System#currentTimeMillis (), that gives you the number of milliseconds elapsed since Unix epoch This method doesn’t give you monotonic time results because it returns the wall clock time, which is prone to both forward and backward adjustments (if NTP is used for system time synchronization).
- The Last Of The Mohicans : Where To Watch And Stream Online
- The Meaning Behind The Song: Mama Said By Metallica
- The Pros And Cons Of Graduate Entry Medicine — Ollie Burton
- The Meaning Behind The Song: Turn Off The Lights By Teddy Pendergrass
- The Interrupters Playlist , THE INTERRUPTERS legen neue Single „Anything Was Better“ vor
- The Many Faces Of Frank Morgan In The Wizard Of Oz
- The Most Dangerous Horse Sport: Unveiling The Thrilling Risks
- The Moon: Required For Life On Earth
- The Incredible Journey Of Chef Nobu And His Restaurant Empire
- The Key Difference Between Dreams And Goals
- The Psychology Behind Color And The Color Of Charity
- The Killer’S Shopping List: Crime And Mystery Korean Drama
- The National Pan American Golf Association