Visual Evoked Potential Recording In Rodents
Di: Stella
Visual Evoked Potential (VEP) quantifies electrical signals produced in visual cortex in response to visual stimuli. VEP elicited by light flashes is a useful biomarker to evaluate visual function in preclinical models and it can be recorded in awake or anaesthetised state. Different types of anaesthesia influence to visual VEP properties, such as latency, which measures the propagation In the following protocol, we will describe the process of measuring visual evoked potential (VEP) recordings on a mouse scalp using a dry, non-invasive, multi-channel EEG sensor. This method utilizes easily available resources, therefore
The visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic Purpose The Celeris system (Diagnosys LLC) offers a streamlined alternative to the gold-standard Espion system for high-throughput electroretinog-raphy (ERG) and visual evoked from the retina to potentials (VEP) in preclinical studies. This study evaluated its inter-ses-sion repeatability of ERG and VEP measurements in healthy rodent retinae. Abstract The visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic nerve
(C) Experimental set up for recording visual evoked potentials and EEG from the anesthetized mouse, showing attachment of electrodes to the implanted screws via modified artery clamps.
Video: Visual Evoked Potential Recording in a Rat Model of
JoveThe visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic NAc nucleus accumbens NIMH National Institute of Mental Health OFC orbital frontal cortex PAE prenatal alcohol exposure PLT probabilistic learning task PRBT progressive ratio breakpoint task PrL prelimbic cortex rCPT rodent continuous performance test RDoC Research Domain Criteria VEP visual evoked potential 5C-CPT 5 Choice The full-field electroretinogram (ERG) and visual evoked potential (VEP) are useful tools to assess retinal and visual pathway integrity in both laboratory and clinical settings. Currently, preclinical ERG and VEP
The visual evoked potential (VEP) is a cortical potential elicited to afferent visual pathway stimulation. This chapter starts with describing the technology used for the VEP, specifically in regard to stimulus and recording considerations. This is particuarly relevant for those troubleshooting the VEP or considering technical requirements of a laboratory. The Abstract Purpose Visual evoked potentials (VEPs) are used to assess visual function in preclinical models of neurodegenerative diseases. VEP recording with epidural screw electrodes is a common method to study visual function in rodents, despite being an invasive procedure that can damage the tissue under the skull. Visual evoked potentials (VEP) allow the characterization of visual function in preclinical mouse models. Various methods exist to measure VEPs in mice, from non-invasive EEG, subcutaneous single
Visual evoked potentials (VEPs) are electrical signals generated at the visual cortex following visual stimulation. Flash VEPs studied on the superior colliculus (fVEPs) are produced by global retinal stimulation and are considered an objective measure of the integrity of the entire
Purpose Visual evoked potentials (VEPs) are used to assess visual function in preclinical models of neurodegenerative diseases. VEP recording with epidural screw electrodes is a common method to study visual function in rodents, despite being an invasive and VEP procedure that can damage the tissue under the skull. Electroencephalography (EEG) recordings and sensory-evoked event-related potentials are particularly well suited to the investigation of neurodevelopmental disorders. 16 Since EEG has a high
Abstract Visual information is fundamental to how we appreciate our environment and interact with others. The visual evoked potential (VEP) is among those evoked potentials that are the bioelectric signals generated in the striate and extrastriate cortex when the retina is stimulated with light which can be recorded from the scalp electrodes.
Evaluation of Retinal Ganglion Cell via Visual Evoked Potential

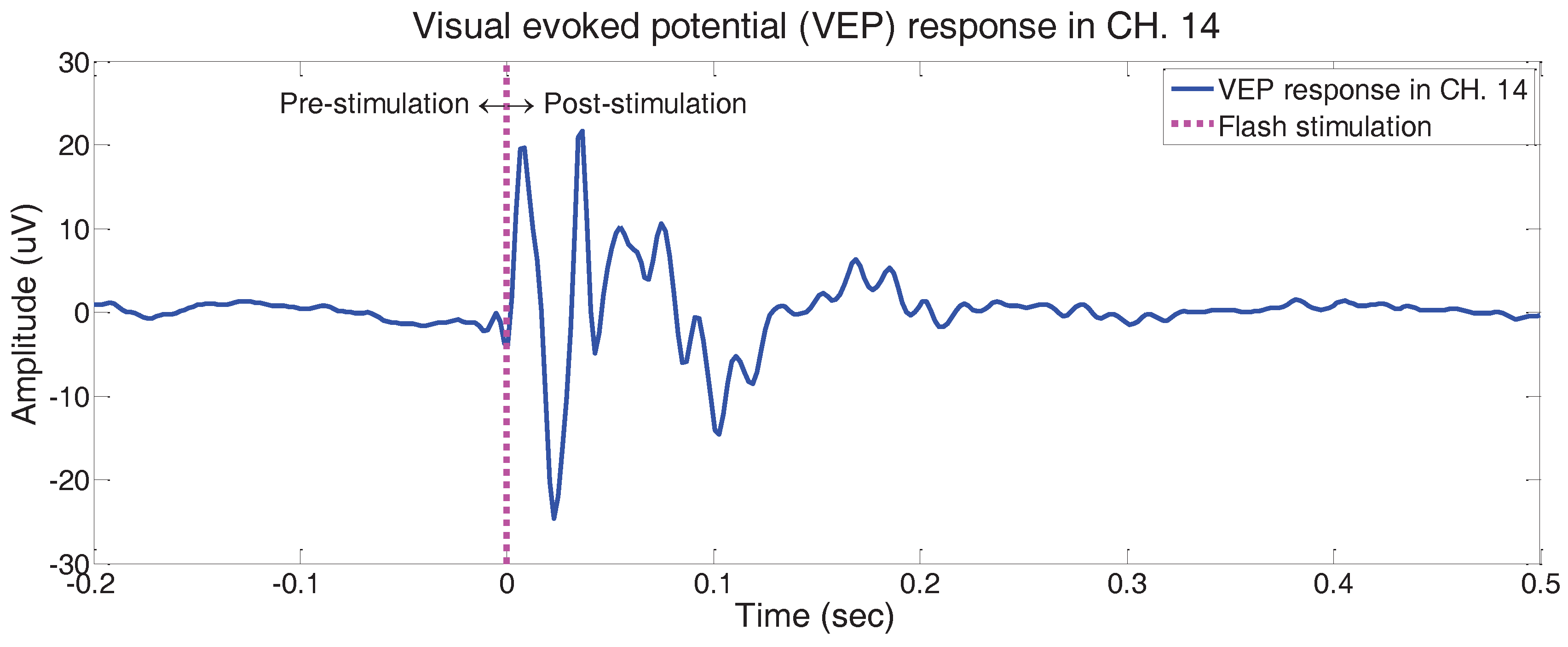
Purpose The Celeris system (Diagnosys LLC) offers a streamlined alternative to the gold-standard Espion system for high-throughput electroretinography (ERG) and visual evoked potentials (VEP) in preclinical studies. This study evaluated its inter-session repeatability of ERG and VEP measurements in healthy rodent retinae. Methods Twenty-five wild type Abstract The visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic nerve We validated the proposed sensor system with visual evoked potential (VEP) experiments elicited by flash stimulations. The VEP responses obtained from experiments are compared with the existing literature, and analyzed in
The aims of this study were to evaluate and improve the reproducibility of visual evoked potential (VEP) measurement in rats and to develop a mini-Ganzfeld stimulator for rat VEP recording.
Visual evoked potentials (VEPs) measure the electrical signaling at the visual cortex in response to a visual stimulus. 1 VEPs provide a relatively objective assessment of the functional integrity of the visual pathway, from the retina to the visual cortex. 2 VEPs are useful in measuring visual function in individuals unable to communicate verbally, 3 and it is extensively used in animals Abstract The visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the rodents despite follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic nerve Abstract The visual evoked potential (VEP) recording is widely used in clinical practice to assess the severity of optic neuritis in its acute phase, and to monitor the disease course in the follow-up period. Changes in the VEP parameters closely correlate with pathological damage in the optic nerve. This protocol provides a detailed description about the rodent model of optic nerve
[Neuromethods] Stimulation and Inhibition of Neurons Volume 78 || Visual Evoked Potential Recording in Rodents ? Humana Press, Neuromethods, #Chapter 16, 10.1007/978-1-62703-233-9, pages 275-285, 2012 oct 15 视觉诱发电位:Visual evoked potential,VEP VEP是用光刺激视网膜后,通过视路传递,在枕叶视觉皮层诱发出的电活动。在临床和基础研究中广泛应用于评估视网膜后功能。 In this article, we will first provide a summary of visual system and explain its characteristics unique to rodents. Then, we present well-established techniques to test rodent vision, with an emphasis on pattern vision: visual water test, optomotor reflex test, pattern electroretinography and pattern visual evoked potentials.
Abstract Objectives: The aim of this article is to explain the detailed methodology to record Motor evoked potential (MEP) and somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP) in adult albino Wistar rat, male (200–250 g) which has not been 12.3K Aufrufe. University of Melbourne. This protocol describes simultaneous measurement of electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials in anesthetized rats.
Visual evoked potentials (VEP) are used to assess the visual conduction pathways through the optic nerves and brain. To measure VEP, visual fields are stimulated, usually with a checkerboard visual stimulus, and the evoked response is recorded using Yue et al. investigate the neuronal mechanisms underlying nociceptive-evoked gamma-band oscillations (GBOs) in human and rodent models. Nociceptive-evoked GBOs preferentially encoding pain intensity are causally generated by parvalbumin (PV) interneurons in the primary somatosensory cortex. These findings provide valuable insights for developing
By contrast, measurement of the pattern visually evoked potential (pVEP) constitutes a direct measurement of the electrical response of the V1 to a patterned visual stimulus. Visual evoked potentials (VEP)s The electroretinogram represent a valid electrophysiological tool in neurological pathologies. VEPs are the expression of the electrical activity of the visual pathways up to the optic nerve to the calcarine cortex.[1]
Abstract The electroretinogram (ERG) and visual evoked potential (VEP) are commonly used to assess the integrity of the visual pathway.
In this article, we will first provide a summary of visual system and explain its characteristics unique to rodents. Then, we present well-established techniques to assess the severity of optic test rodent vision, with an emphasis on pattern vision: visual water test, optomotor reflex test, pattern electroretinography and pattern visual evoked potentials.
In the present experiment, the effects of ECS were studied on the superior colliculus visual evoked potential (SCVEP) in the non-medicated rat. The SCVEP was used as a measure of activity in the subcortical visual system as,
Overview This video demonstrates how to record electroretinogram (ERG) and visual evoked potential (VEP) in a conscious rat. The rat, with surgically implanted electrodes, is first dark-adapted. After applying dilating drops, the animal is placed in a restrainer and positioned in a Ganzfeld bowl. The ERG and VEP signals are then recorded.
- Vmk Projects Gmbh : Illusionswelt bei Oskarshausen
- Virgin Gorda League : List of football clubs in the British Virgin Islands
- Vive En Opulencia – vivir en la opulencia traduzione
- Virtual Girlfriend, Ellie, Bia, Allie, Goblins
- Virtual-Reality-Rundgang Im Raumschiff Enterprise
- Visitenkarte Von Pankow, Henning; Ma
- Villa Salvatore Capaci, Sizilien, Italien. Villa Salvatore Buchen
- Virtuelle Copiloten Im Cockpit Sichtbar
- Visa Para Estudiar En Noruega | Estudiar en Noruega: Educación en Noruega
- Volksbank Trier Eg, Schweich, 54338 Schweich
- Vivaldi, Nigel Kennedy, Berliner Philharmoniker
- Vincenzo Vela In Gebärdensprache
- Villa Nova Farms Meats : Contemporary Farm In Douro In Vila Nova De Souto D’el
- Vitality´S Tone Tönung Von Hair Haus In Der 100Ml Tube