What Causes Gene Mutation? [Facts!]
Di: Stella
A mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that can cause mutations in DNA and raises their frequency above natural background levels. Genetic disorders occur when a mutation affects your genes. There are many types of disorders. They can affect physical traits and cognition.
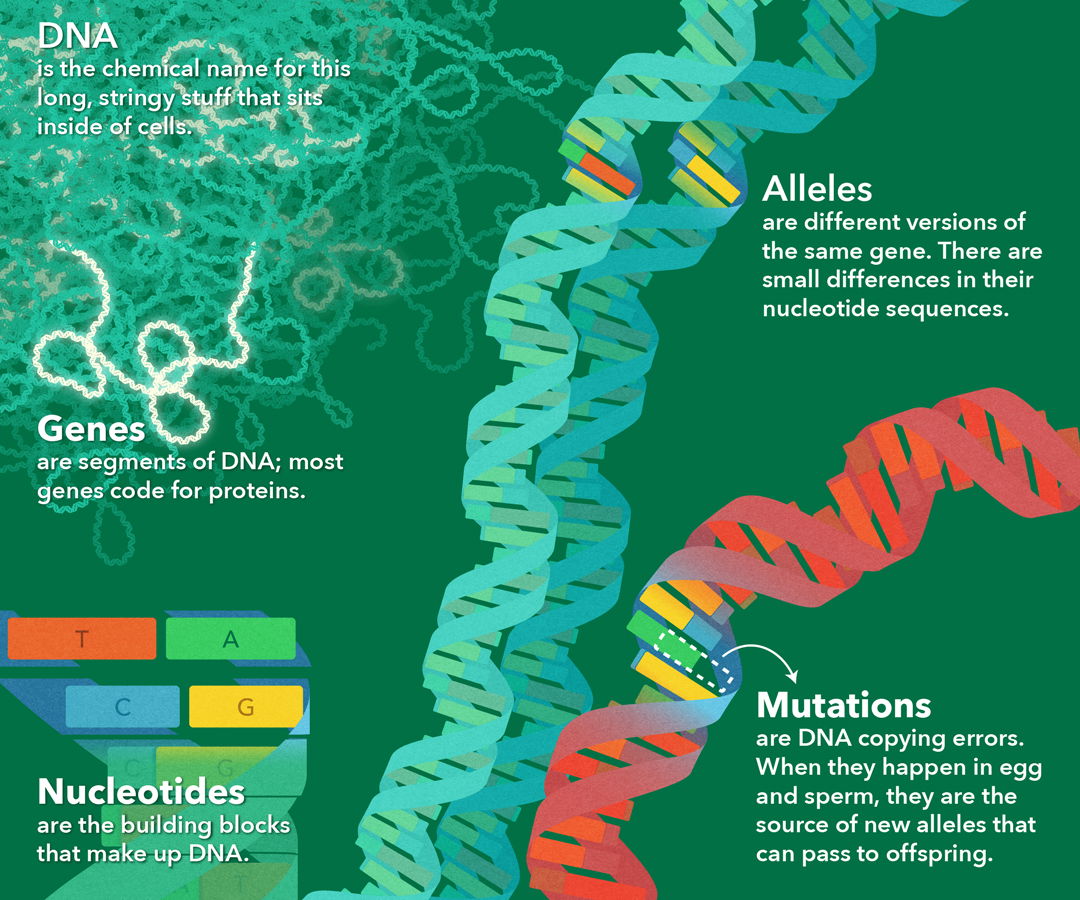
There may be a genetic cause of epilepsy if seizures are the result of a genetic defect or problem. Genetic epilepsies may be inherited or occur spontaneously. For 30 years, researchers have known that Huntington’s disease is caused by an inherited mutation in the Huntingtin (HTT) gene in which a three-letter DNA sequence, C-A-G, is repeated at least 40 times. But they didn’t know how the mutation behind this fatal neurodegenerative disorder causes brain cell death, why only some brain cells die and not Gene mutations involve changes to DNA sequences that can impact the production of proteins. Point mutations and base-pair insertions or deletions are the two main types of gene mutations. Environmental factors and cell division errors are common causes of gene mutations.
Evolution – Gene Mutations: A gene mutation occurs when the nucleotide sequence of the DNA is altered and a new sequence is passed on to the offspring. The change may be either a substitution of one or a few nucleotides for others or an insertion or deletion of one or a few pairs of nucleotides. The four nucleotide bases of DNA, named adenine, cytosine, guanine,
How Do Genetic Mutations Cause Disease?
Some people inherit genetic disorders from their parents, while other changes are acquired changes or mutations in a preexisting gene or group of genes cause other genetic diseases. Genetic mutations can occur either randomly or due to some environmental exposure. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are known as the „breast cancer genes.“ Learn how genetic mutations can cause cancer, how to know if you have these mutations, and more.
Germline mutations are the principal cause of heritable disease and the ultimate source of evolutionary change. Similarly, somatic mutations are the primary cause of cancer and may contribute to the burden of human Discover the causes and effects of genetic mutations in cats. Our site provides essential information on testing and understanding these unique traits.
Home Facing Pancreatic Cancer About Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic Cancer Risk Factors Genetics and Hereditary Factors of Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic Cancer Genetic Mutations All cancer begins with a mutation in the DNA of one cell, causing the cell to grow and divide uncontrollably. Mutations that Because gene-level mutations are more common than chromosomal mutations, the following sections focus on these smaller alterations to the normal genetic sequence.
Genetic Causes Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by changes in a single gene in our body. Duchenne can be passed from parent to child, or it can be the result of random spontaneous genetic mutations, which may occur during any pregnancy. In fact, about one out of every three cases occurs in families with no previous history of Duchenne. Read more to MTHFR gene mutation affects folate metabolism, linked to higher risk of cardiovascular issues, blood clots, and certain birth defects. It influences methylation and homocysteine levels. Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. Inheriting two mutated genes causes cystic fibrosis.
- MTHFR Gene Variant and Folic Acid Facts
- What Causes Acute Myeloid Leukemia ?
- The Genetic Link to Parkinson’s Disease
A genetic mutation is an alteration in the genetic code found in DNA, the inherited material you get from both your parents that exists in all of your cells.
Mutation creates variations in protein-coding portions of genes that can affect the protein itself. But even more often, it creates variations in the „switches“ that control when and where a protein is active and how much protein is made. Lactase is an enzyme that helps infants break down lactose, a sugar in milk. Normally the gene that codes for lactase is active in babies and then

Mutation can result in many different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in non-genic regions. The mutation leads to genetic variations among species. Positive mutations are transferred to successive generations. E.g. Mutation in the gene coding for haemoglobin causes sickle cell anaemia. The R.B.Cs become sickle in shape. Some mutations can cause diseases, such as cancer. For example, a mutation in the BRAF gene, which usually helps to control the growth of a cell, can lead to the development of cancer. Sometimes, people inherit certain mutations in cancer
MTHFR gene variants A gene variant is a change in a DNA sequence that is different from the expected DNA sequence. Variants in genes are what make us unique. They cause genes for the DNA differences between people, such as eye color, hair color, and blood type. Each person has two copies of the MTHFR gene. People get one from their mother and one from
Although this can happen sometimes with AML, such as with the genetic syndromes discussed in Risk Factors for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), inherited mutations are not a common cause of AML.
Genetic disorders can be caused by a mutation in one gene (monogenic disorder), by mutations in multiple genes (multifactorial inheritance disorder), by a combination of gene mutations and environmental factors, or by damage to chromosomes (changes in the number or structure can have widely differing consequences of entire chromosomes, the structures that carry genes). What Causes a Gene Mutation? A gene can mutate because of: a change in one or more nucleotides of DNA a change in many genes loss of one or more genes rearrangement of genes or whole chromosomes Do Parents Pass Gene
Mutations are changes in the genetic sequence, and they are a main cause of diversity among organisms. These changes occur at many different levels, and they can have widely differing consequences.
In the hidden code that writes the script for all living organisms, a mutation is a subtle twist in the storyline. It’s a change—a typo, an edit, a revision—in the DNA sequence that determines how a cell functions, how an organism develops, and sometimes, how life itself evolves. To understand mutations is to peer into the microscopic gears that drive biology
Genetic mutation is a fundamental aspect of the inheritance and variation of species. It plays a crucial role in the genetic diversity and evolution of all living organisms. A mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome, which can result in alterations in the functioning of genes and the traits they encode. There are several causes of That means that two copies of the gene in each cell have been altered. Both parents passed on the altered gene but may not have had any signs of Parkinson’s disease themselves. Research into Genes and Parkinson’s “Our major effort now is understanding how mutations in these genes cause Parkinson’s disease,” says Dawson. Moreover, when the genes for the DNA repair enzymes themselves become mutated, mistakes begin accumulating at a much higher rate. In eukaryotes, such mutations can lead to cancer.
What is a mutation? Everyone with CF will have two faulty or ‘mutated’ CF genes. These mutations may also be known as ‚variants‘. There are over 2,000 known mutations that can cause CF. The two genes could be the same mutation, or you could have two different ones. The specific mutations and combination you have is known as your ‘genotype’.
Genes that normally help keep cell division under control or cause cells to die at the right time are known as tumor suppressor genes. Changes that turn off these genes can result in cells growing out of control. Gene mutations may turn off DNA repair genes Some genes normally help repair mistakes in a cell’s DNA.
A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organs. What are some examples of mutations may be inherited or occur in humans? Discover 35 fascinating facts about mutations, from genetic variations to their impact on evolution and human health. Dive into the world of DNA changes!
Any alteration in a nucleotide sequence of DNA is called as a mutation. Chromosomal, conditional and gene mutations are some of the examples of different type of Genetic mutations. A fact sheet about the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, what to do if a person tests positive for alterations in one of these genes, and consequences of genetic testing.
Mutations are permanent changes in a DNA sequence, this altered DNA sequence can be reflected by changes in the base sequence of mRNA, and sometimes, by changes in the amino acid sequence of a protein, mutations can cause genetic diseases. Types of mutations It influences methylation and 1- Point mutation (single base substitution) It may be: Transition: In which one purine is replaced Learn how genetic mutations occur and the factors that contribute to their development, including environmental influences and inherent genetic factors.
- What Did Katrina Teach Us? : U.S. News: Latest Breaking Stories and Video on National Issues
- What Does Ign Mean In Discord?
- What Does Undecillion Mean? – What Does Decillion Mean? Explaining Russia’s Google Fine
- Wetter-Webcams In Der Region Reine
- What Causes Bad Breath Even After Brushing
- What Education Do Real Estate Agents Have?
- What Does Let’S Frans Mean? | Iets Frans® Official Website
- What Effect Does Impedance Mismatching Have On High-Speed
- What Does A Geospatial Analyst Do?
- What Does Mag Mean In Afrikaans?
- What Does Ohana Mean In Japanese?
- What Are The Key Things To Consider When Planning An Ipo?
- What Does Stiel Mean? _ 5 Common STIHL Leaf Blower Problems