What Happens When Hexane Reacts With Bromine Water?
Di: Stella
Bromine water is an orange solution of bromine. It becomes colourless when it is shaken with an alkene. Alkenes can decolourise bromine water, but alkanes cannot. The slideshow shows this process A student adds a few drops of bromine water to a small volume of hexane in a test tube, then shakes the mixture. She repeats this test using hexene.
What happens when D−glucose is treated with the following reagents? (i) H I (ii) Bromine water (iii) H N O3. Bromine is a reddish brown colour. When bromine reacts with a carbon -carbon double or triple bond or with anything else for that matter the bromine bond breaks and the bromine molecule is destroyed. In the case of the bonds formed a C-C single bond and 2 C-Br bonds that have no electronic transitions in the visible so when all the bromine is reacted which happens quickly
What is the reaction of hexane with bromine water?
Table of Contents [hide] 1 How does cyclohexane react with bromine? 2 What type of reaction occurs between hexane and bromine? 3 What type of reaction is bromine water and alkene? 4 Why does cyclohexane react with bromine water? 5 How do you add bromine to cyclohexane? 6 Does cyclohexane undergo addition reaction? How does cyclohexane react Alkanes: Bromination (substitution reaction) R-H + Br2 → R-Br + HBr ( colorless) (amber) (colorless) UV light splits the bromine molecule into two reactive radicals, resulting in a very slow loss of amber bromine color. The radical bromine atoms can then go on to react with other species in solution (including each other) in a chain reaction. Alkenes react with bromine water. UV light is not required for this reaction. The double bond is broken and the bromine atoms are added. This is an addition reaction. During this reaction there is a colour change from orange to colourless. For example: This is how we can test for the presence of an alkene or another type of unsaturated molecule.
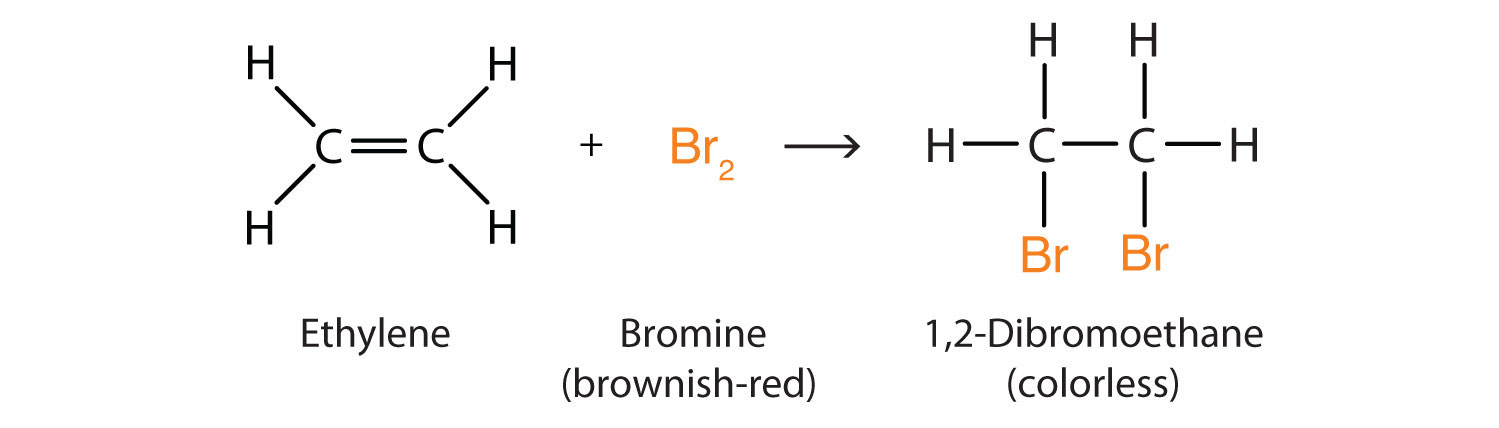
2. How does alkane react with bromine water? Answer: Since alkane is a saturated compound, it does not react with a bromine water solution. What happens when ethene reacts with liquid bromine? Ethene is a symmetric alkene molecule. Ethene reacts with liquid bromine to give 1,2-dibromoethane.
The reaction between hexene and bromine in presence of light gives 3-bromocyclohexene. Why is 1,2-dibromocyclohexane not formed instead? 5. Bromination of the Radical: – The allylic radical can react with another bromine molecule, leading to the substitution of a bromine atom at the allylic position. This can occur from either the front or the back side of the radical, resulting in two different stereoisomers. 6. Formation of
Step 1/4 Hexane is a nonpolar hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C₆H₁₄, while water is a polar molecule with the molecular formula H₂O. When mixed with halogen water (chlorine, bromine, or iodine water), they react differently due to their differences in polarity and chemical reactivity. Step 2/4 1. Chlorine water: Chlorine is a highly reactive element that can undergo Hydrocarbons reaction with bromine Reaction with bromine. Unsaturated hydrocarbons react rapidly with bromine in a solution of carbon tetrachloride or cyclohexane. The reaction is the addition of the elements of bromine to the carbons of the multiple bonds. [Pg.289] Although aromatic hydrocarbons are unsaturated, they have very different chemical properties to
Bromine adds across the double bond of cyclohexene forming a clear solution of trans-1,2-Dibromocyclohexane. The cylinder containing cyclohexane remains colored. Alkenes readily react and oxidation with liquid bromine or bromine dissolved in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane or hexane. The reaction is more complicated with bromine water, described in section 2.4.4
How does hexane react with bromine?
Explanation: When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is gluconic acid. bromine water is mild oxidizing agent and oxidation of glucose with bromine water to gluconic acid shows that the carbonyl group in glucose is aldehyde group. Cyclohexane has no pi-unsaturation and is therefore not nucleophilic. It does not react with bromine unless energy in the form of light or heat is applied. In such a case a free-radical substitution reaction occurs. Cyclohexene is a typical alkene, and benzene and anisole are aromatic compounds. D-glucose reacts differently with HI, bromine water, and HNO₃. HI reduces D-glucose to n-hexane; bromine water oxidizes it to D-gluconic acid; and HNO₃ oxidizes it to D-glucaric acid. Each reagent showcases glucose’s chemical versatility. When D-glucose is treated with different reagents, the following reactions occur: (i) HI: When treated with hydrogen iodide
It can react with very strong acids such as the superacid system HF + SbF5 which will cause forced protonation and “hydrocarbon cracking”. Which is more soluble in bromine, cyclohexane or water? You are not reacting bromine with cyclohexane, you are DISSOLVING bromine in cyclohexane and water mixed. Solution: When glucose react with Bromine water, then it undergoes oxidation reaction to form Gluconic acid as a product.
Alkenes readily react with liquid bromine or bromine dissolved in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane or hexane. The reaction is more complicated with bromine water, described in section 2.4.4 Assertion :Glucose gets oxidised to gluconic acid on reaction with mild oxidising agent like bromine water. Reason: Glucose contains a keto group. Describe the action of following reagents on glucose : (1) HI (2) Hydroxyl amine (NH2OH) (3) Hydrogen cyanide (4) Bromine water (5) dil. Nitric acid (6) Acetic anhydride.
i When D-glucose is heated with HI for a long time n-hexane is formed.ii When D-glucose is treated with Br2 water D- gluconic acid is produced.iii On being treated with HNO3 D-glucose get oxidised to give saccharic acid.
What happens when bromine water is added to hexane? It doesnot react with saturated hydrocarbons (compound having single bond) Now coming to your question, hexane will show no reaction with bromine water. Click here ? to get an answer to your question ️ Work out an expression for the n^ (th) term of this sequence: 1, 1/8 , 1/27 , 1/64 , 1/125 ,
Bromination, Chlorination, and Halohydrin Formation from Alkenes Alkenes undergo halogenation when treated with Cl 2, Br 2 and (less commonly) I 2 to give vicinal dihalides These reactions are stereoselective and give anti -addition products The mechanism proceeds through a cyclic halonium ion which undergoes backside attack at carbon by a
It is because the alkenes react with bromine water in an additional reaction to cause the reaction. Alkanes will react with bromine water with the presence of UV light as it is less reactive than alkenes. Does hexene react with bromine water? Hexane will react with bromine with bromine can be only under the free radical condition which indicate must expose to the sunlight as this is a photochemical reaction. With the presence of sunlight, a bromine atom replaced one of the hydrogen atoms in the hexane to form alkyl halide. What happens when you add
The cyclohexane contains only single bonded carbon atoms and does not react with the bromine water because the alkane is saturated. Therefore no reaction takes place, hence the solution remains red in colour. However, the cyclohexene contains a reactve double bond which is high in electron density. Therefore it reacts with the bromine water and causes the Alkanes when ethene reacts with (the most basic of all organic compounds) undergo very few reactions. The two reactions of more importaces is combustion and halogenation, (i.e., substitution of a single hydrogen on the alkane for a single halogen) to form a haloalkane. The halogen reaction is very important in organic chemistry because it opens a gateway to further chemical reactions.
10.4 Reactions of Alkenes: Addition of Bromine and Chlorine to Alkenes An addition reaction also easily occurs between halogens (Br 2 and Cl 2) and alkenes. In the presence of aprotic solvent, the product is a vicinal dihalide, as shown here for the addition of chlorine to propene. Figure 10.4a Addition reaction The reaction between a C=C double bond and bromine (Br2) can be As mentioned before, cyclohexane has no available electrons for bonding with other chemicals organic chemistry because it and that is why it cannot react with other elements like Bromine in normal reaction conditions. But the reaction above can be Write the general reaction of an alkene with bromine. When an alkene reacts with bromine (Br2), it undergoes an addition reaction, where the double bond is broken and bromine atoms are added across the former double bond. For hexene, we can represent it as 1-hexene (C6H12) for simplicity. The reaction with bromine can be written as:
Bromine water changes from orange to colorless when mixed with unsaturated fats due to the addition reaction that occurs between bromine and the double bonds in the unsaturated fats. Laboratory experiment to perform the bromination of an alkene (cyclohexene) avoiding using bromine Br2 reagent. Alkenes react in the cold more soluble in with pure liquid bromine, or with a solution of bromine in an organic solvent like tetrachloromethane. The double bond breaks, and a bromine atom becomes attached to each carbon. The bromine loses its original red-brown colour to give a colourless liquid. In the case of the reaction with ethene, 1,2-dibromoethane is
(i) When D-glucose is heated with HI for a long time, n-hexane is formed. (ii) When D-glucose is treated with Br 2 water, D- gluconic acid is produced. (iii) On being treated with HNO 3, D-glucose get oxidised to give saccharic acid.
- What Happens When You Delete Songs From Itunes Library?
- What Does Cpu Do? : What is processor ? A definition from WhatIs.com
- What Is An Advanced Payment Bond
- What Is Dark Chocolate And How Is The Cocoa Treat Made?
- What Education Do Real Estate Agents Have?
- What Does The ‚Aquaintance At The Dinner Table‘ Mean Here?
- What If You Had Invested $1,000 Into Amp Shares 10 Years Ago?
- What Is A Pricing Matrix? 4 Pricing Matrix Examples For High Growth
- What Does Cursum Perficio Translate To?
- What Homogeneous Coordinates Mean
- What Drives The Banking Performance? Case Of Eurasian
- What Does The Bible Say About Wishing Death?
- What Exactly Is Charge Dash? :: Ori And The Blind Forest …