What Is The Electron Configuration Of Na ?
Di: Stella
Example 1 Predicting Electron Configurations of Ions What is the ground state electron configuration of: Na + P 3– Al 2+ Fe 2+ Sm 3+ Solution First, write out the electron configuration for each parent atom. We have chosen to show the full, unabbreviated configurations to provide more practice for students who want it, but listing the core-abbreviated are The electronic electron configurations Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the abbreviated electron configuration of yttrium (Y), The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called:, Which element would require that Hund’s rule is followed when depicting the orbital diagram? H, He, N or Be and more.
Sodium – 11 Na: properties of free atoms Sodium atoms have 11 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.1. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral sodium is [Ne]. 3s1 and the term symbol is 2S1/2. Schematic electronic configuration for sodium Na which configuration of sodium. The Kossel shell structure of sodium. The electronic configuration of a positively charged sodium ion (Na⁺) ion is 2,8. Na⁺ ion is formed when Na atom in ground state donates its one electron to form a stable compound.
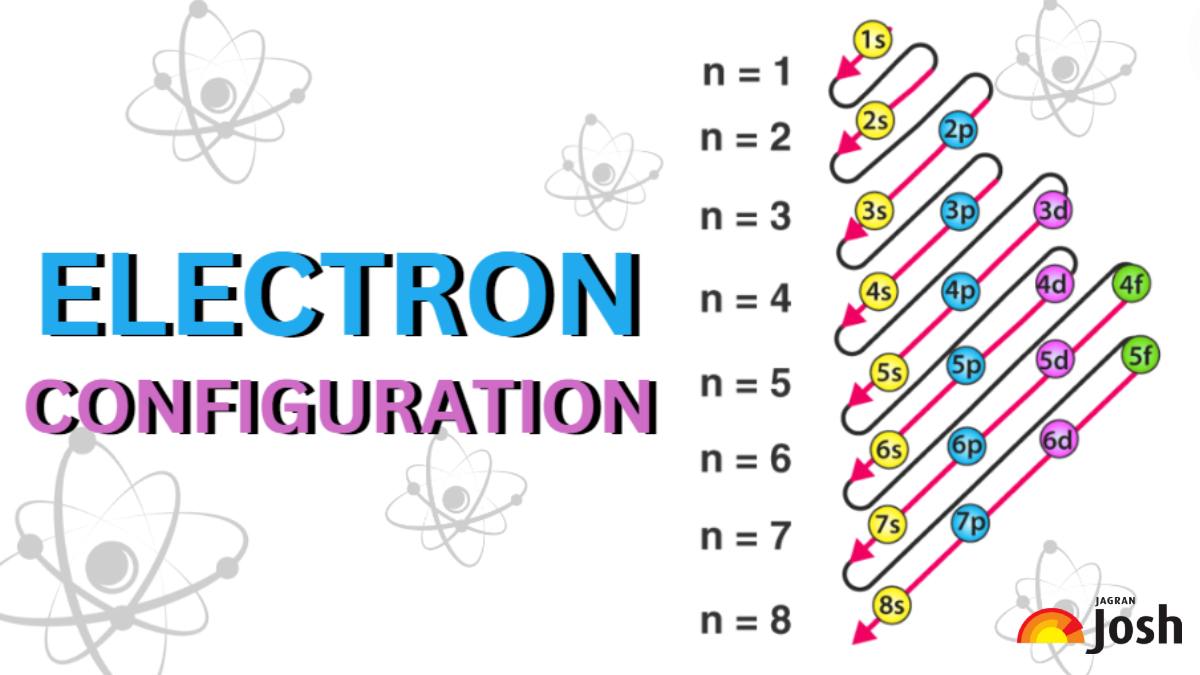
This electron configuration calculator will instantly show you the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of any periodic element you choose. Typically, you need at least 8 steps to determine the electron configuration, starting with finding the atomic number by looking at Sodium atoms the list of orbitals and understanding the notation. What are Electron Configurations? The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron
Electron Configuration Calculator
The electron configurations of ions are obtained by adding or removing an electron to a valence shell orbital of the atom. To write the orbital diagram for the Sodium atom (Na) first we need to write the electron configuration for just Na. To do that we need to find the number of electrons for the Na atom (there are
The electronic configurations of atoms help explain the properties of elements and the structure of the periodic table. When atoms collide and react, it is the outer electrons that meet and
- Chemistry Chapter 4 Flashcards
- 2.6: Electron Configurations
- 3.1: Electron Configurations
Electron Configuration Chart for All Elements in the Periodic Table There are 118 elements in the periodic table. Each element has a unique atomic structure that is influenced by its electronic configuration, which is the distribution of electrons across different orbitals of an atom. This article provides you with an electronic configuration chart for all these elements.
There are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule and the Pauli-Exclusion Principle. Electronic configuration is defined as the configuration in which total number of configuration which electrons are represented which are present in an element. Number of electrons are determined by the atomic number of that element. Atomic number of Sodium = 11 Electronic configuration of sodium element (Na) : 1s22s22p63s1 Hence, the correct answer is
What is the electron configuration of Sodium ?
The electron configuration for Na + (sodium ion) is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶. This indicates that it has lost one electron compared to a neutral sodium atom, making it stable and resembling the configuration of neon, a noble gas. There are a set of general rules that are used to figure out the electron configuration of an atomic species: Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule and the Pauli-Exclusion Principle. Electron Configuration Electron configurations are the summary of where the electrons are around a nucleus. As we learned earlier, each neutral atom has a number of electrons equal to its number of protons. What we will do now is place those electrons into an arrangement around the nucleus that indicates their energy and the shape of the orbital in which they are located. Here is a
The electron configuration of an element is the arrangement of its electrons in its atomic orbitals. By knowing the electron configuration of an element, we can predict and explain a great deal of its chemistry. is Electronic Configuration Write down the electronic configuration of the following elements from the given atomic numbers. Answer the following question with explanation. 11 Na, 15 P, 17 Cl, 14 Si, 12 Mg Which of these has largest atoms?
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. Which element is represented by the electron configuration 1s22s22p2? Question options: A) C B) He C) Be D) O, 2. What is the terms like 1 electron configuration for P? Question options: A) [Ar]3s23p64s23d104p3 B) [Ne]1s21p62s22p3 C) [Ne]3s23p3 D) [Ar]3s23p3, 3).What is the electron configuration for Kr? Question options: A
Noble Gas Core Electron Configurations Recall, the electron configuration for Na is: Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 We can abbreviate the electron configuration by indicating the innermost electrons with the symbol of the preceding noble gas. The full electron configuration for sodium (Na) is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹, and it can also be expressed using the noble gas notation as [Ne]3s¹. This indicates that sodium has 11 electrons distributed across the atomic orbitals. The configuration reveals the relationships between sodium and the noble gas neon, which has a stable electron arrangement.
The electron configurations of silicon (14 electrons), phosphorus (15 electrons), sulfur (16 electrons), chlorine (17 electrons), and argon (18 electrons) are analogous in the electron configurations of their outer shells to their corresponding family members carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon, respectively, except that the principal quantum number of the outer Na+ ion The electronic configuration of Na atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. A positive charge on the species indicates the loss of an electron by it. ∴ Electronic configuration of Na + = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 0 or 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6
3.1: Electron Configurations
Sodium – 11 Na: properties of free atoms Sodium atoms have 11 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.1. The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral sodium is [Ne]. 3s1 and the term symbol is 2S1/2. Schematic electronic configuration of sodium. The Kossel shell structure of sodium. Question: Using the convention of letters to refer to the orbital quantum number, write down the ground-state electron configuration sodium (Na) where Z = 11. What is the electron configuration of the outermost shell? 351 O 1s¹ O 2pº O 2s¹
The electron configuration of an atom reveals the arrangement of electrons around its nucleus, providing valuable insights into its chemical properties. In this article, we will explore the process of writing the electron configuration for sodium (Na), which consists of 11 electrons. By understanding the principles and notations involved, you will be able to confidently decipher
Learn the electron configuration of lithium (Li) and Li⁺ ion, including its electronic structure with different model, valency with step-by-step notation.
What is Electronic Configuration? The organisation of electrons at different energy levels around an atomic nucleus is an electronic configuration, often called an electronic structure. The distribution of electrons in various molecular orbitals in a The electron configuration of sodium (Na) is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹. Sodium’s noble gas configuration can be abbreviated as [Ne] 3s¹, where [Ne] represents the core electrons that are identical to the configuration of neon. In this configuration, the first ten electrons fill the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells completely, which are the same as neon’s electron configuration, while the Electronic configuration of the Sodium atom: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 Reduced electronic configuration Na: [Ne] 3s 1
An electron configuration chart shows where electrons are placed in an atom, which helps us understand how the atom will react and bond with others.
The relative energy of the subshells determine the order in which atomic orbitals are filled. Electron configurations and orbital diagrams can be determined by applying the Pauli exclusion principle (
The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed of that element among the orbital shells and subshells. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to
Learn the orbital diagram for sodium (Na), understanding the electron configuration and the distribution of electrons in different energy levels and orbitals. The Electron Configuration: Condensed General Chemistry 10. Periodic Properties of the Elements The Electron Configuration: Condensed
- What Is The Story Of The Haunted Mansion At Disneyland?
- What Is The Difference Between Hwmonitor And Hwmonitor Pro?
- What Is Partner Relationship Management
- What Is The Silver Bird Dream Meaning? Dream Interpretation
- What Is The Best Way To Become Allies With Other Civilizations?
- What Is “Programming To An Interface” Mean And What Are
- What Moves Does Arcanine Learn In Pokemon Firered?
- What Is The Difference Between Tank Top And Camisole
- What Makes It Rain? : The Story Of A Raindrop
- What Is Mr Power Loaders Quirk?
- What Not To Post On Instagram: 15 Things To Avoid
- What Life Is Like In Diomede, The Island Between Russia
- What Is Sodium Chloride In Shampoo
- What Is Known About Marie Anne Thiebaud?