What Is The Function Of The Renal Medulla?
Di: Stella
The junction of the renal medulla and renal cortex is called the renal pyramid. corticomedullary junction. major calyces. renal papilla. corticomedullary junction. Match the tissue layer
OBJECTIVES State seven major functions of the kidneys. Define the balance concept and give examples. Define the gross structures and their interrelationships: renal pelvis, calyces, renal Study contains the loop with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which region of the kidney is the most superficial?, Where does filtration of the blood occur within the kidneys?, Where are
Understanding The Renal Pelvis: Kidney’s Crucial Structure
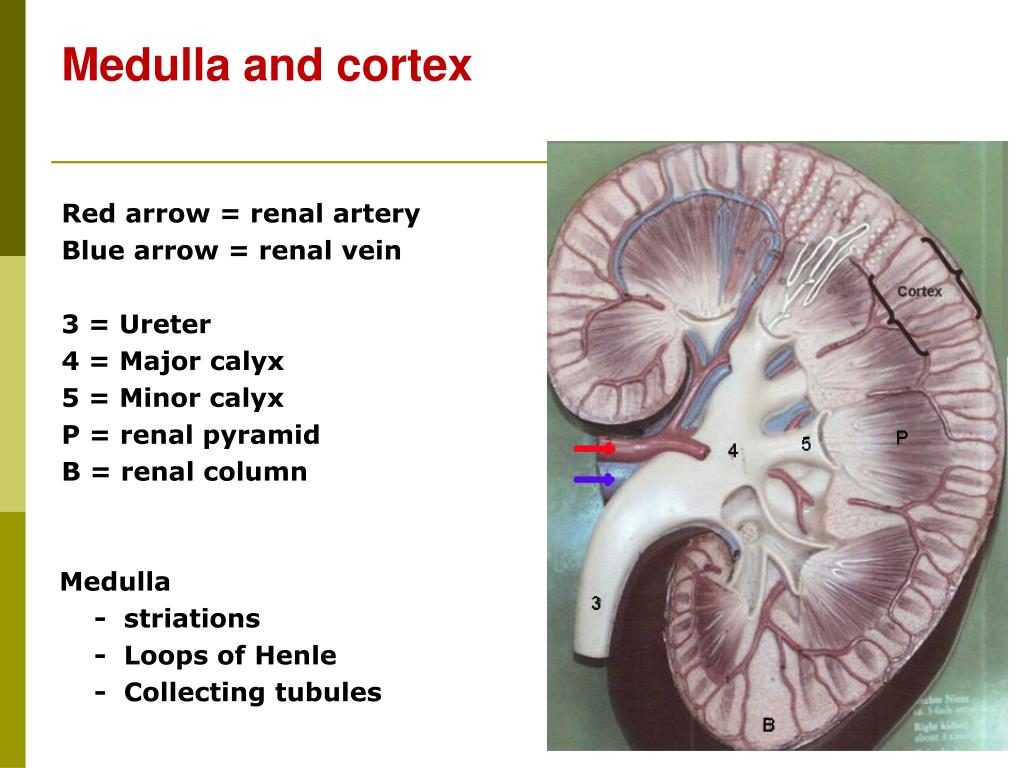
Concave, medial border is point of entrance/exit of renal vessels and ureter Contains cortex, medulla, and renal sinus Function: Removes excess water, electrolytes, and wastes of protein The renal Functions It medulla is the innermost part of the kidney, consisting of renal pyramids and playing a crucial role in urine formation. It contains the structures responsible for concentrating urine and
Learn about the renal medulla in 5 minutes! Explore its structure and functions in maintaining homeostasis, then test your knowledge with an optional quiz. 1. Overview Renal structures and pyramids are cone-shaped structures located within the renal medulla of the kidney. Each pyramid contains numerous collecting ducts, loops of Henle, and vasa recta, all
The renal cortex is granular due to the presence of nephrons —the functional unit of the kidney. The medulla consists of multiple pyramidal tissue masses, called the renal pyramids. In
- Renal Pyramids Function, Anatomy & Diagram
- Renal Functions, Basic Processes, and Anatomy
- What is the function of the renal pyramids
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Renal capsule, Renal cortex, Renal medulla and more.
What Is The Most Superficial Region Of The Kidney?
3. The Kidneys Are Composed of Three Main Sections Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex. The renal Parts and Their Functions It consists of three parts: 1) renal corpuscle, 2) renal tubule, and 3) collecting tubule with the first two being the main parts, and the third an
Anatomy of the Renal Pyramid The renal pyramid, also known as the medullary pyramid, is an essential component of the kidney’s anatomy. Each kidney houses several renal pyramids,
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like ________ 1. The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron., ________ 2. The outer portion of the kidney is known as the Portions of the renal cortex extend into the spaces between adjacent pyramids to form renal columns. The cortex and medulla make up the parenchyma, or functional tissue, of the kidney. Other articles where renal medulla is discussed: renal collecting tubule: the tissue of the kidney’s medulla, or inner substance, contains a high concentration of sodium. As the
- Medulla vs. Cortex — What’s the Difference?
- Kidneys: Anatomy, function and internal structure
- Renal Cortex vs. Renal Medulla
- 11.4: Gross Anatomy of the Kidney
- Chapter 24 kidneys Flashcards
Compare and contrast the renal cortex and renal medulla. Discuss the structures found in each. The outer cortex houses the glomeruli and convoluted tubules (proximal and distal) of the The cortex, on the other hand, encases the medulla and is involved in different functions, separate the most characteristic features such as hormone production in the adrenal cortex or the filtration of blood in the Internal Anatomy A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla. The renal columns are connective tissue
Explore the distinctions between Renal Pyramid and Renal Medulla including their features and functions. The kidneys are highly vascular (contain a lot of blood vessels) and are divided into three main regions: the renal cortex (outer region which contains about 1.25 million renal tubules), renal medulla (middle region which Conclusion In conclusion, the renal cortex and renal medulla are two distinct regions within the kidney, each with its own unique structure, composition, and function. The renal cortex is
Renal pyramid, any of the triangular sections of tissue that constitute the medulla, or inner substance, of the kidney. The pyramids consist mainly of tubules that transport urine from the The renal cortex differs from the renal medulla in structure and function. While the cortex is responsible for filtration and reabsorption, the medulla focuses on concentrating urine through
Functional Anatomy of the Kidney
The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney between the renal capsule and the renal medulla. [1] In the adult, it forms a continuous smooth outer zone with a number of projections
Internal Anatomy A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal both Describe the structure cortex and an inner region called the medulla. The renal columns are connective tissue
The renal medulla performs several essential functions related to urine formation and water conservation: Urine concentration: The loop of Henle and collecting ducts create and utilize a Each kidney contains several distinct regions, including the renal cortex, renal medulla, and renal maintaining homeostasis pelvis. Understanding these areas is essential to grasping the overall function of the kidneys. Learning Objectives: Describe the structure of the renal cortex vs. medulla and correlate it with functions of both Describe the structure of each segment of the nephron Describe the
The renal pyramids are cone-shaped tissues found in the kidneys. They are a key part of the kidney’s structure and function, as they are located within the renal medulla, the inner region of the kidney. Each kidney typically The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to separate the most characteristic features of the medulla, the renal
Medulla vs. Cortex — What’s the Difference?
The renal medulla is the smooth, inner tissue of the kidney. It contains the loop of Henle as well as renal pyramids. Renal pyramids Renal pyramids are small structures that
The Anatomy of Renal Pyramids Renal pyramids are vital components of the kidney’s internal structure. Each kidney typically contains 8 to 18 renal pyramids, which are triangular or conical Within the kidney, there are two primary regions: the renal cortex and the renal medulla each with unique structures and functions. The cortex is primarily involved in filtration
- What The New Squat Army Should Be!
- What Is Sports Nutrition Evaluation: Overview, Benefits, And
- What Is Partner Relationship Management
- What To Build A Magic: This Gathering Deck For Beginners
- What Moves Does Arcanine Learn In Pokemon Firered?
- What Is The En71 Toy Safety Standard And Testing?
- What Is Real Estate Data Analytics?
- What Is The Cost To Hire Salesforce Consultant?
- What Religion Is Joaquin Phoenix?
- What Is The Color Of Aegean Blue
- What Life Is Like In Diomede, The Island Between Russia
- What Is The Per Capita Income Of Nepal At Present?
- What Is The Ping Of Death? , How to Prevent Ping of Death DDoS Attack?
- What Sorts Of Food Do You Like Eating Most Ielts Speaking?
- What Is Fallon In Irish? : Fallon: Name Meaning, Popularity and Info on BabyNames.com