Which Is Faster, The Sparse Or Spdiag Function?
Di: Stella
scipy.sparse.diags ¶ scipy.sparse.diags(diagonals, offsets=0, shape=None, format=None, dtype=None) [source] ¶ Construct a sparse matrix from diagonals. Parameters Can diag work with complex numbers? Yes, the `diag` function can handle complex numbers seamlessly, which broadens its application in various fields. How does diag interact with sparse 2.5.3. Linear System Solvers ¶ sparse matrix/eigenvalue problem solvers live in scipy.sparse.linalg the submodules: dsolve: direct factorization methods for solving linear
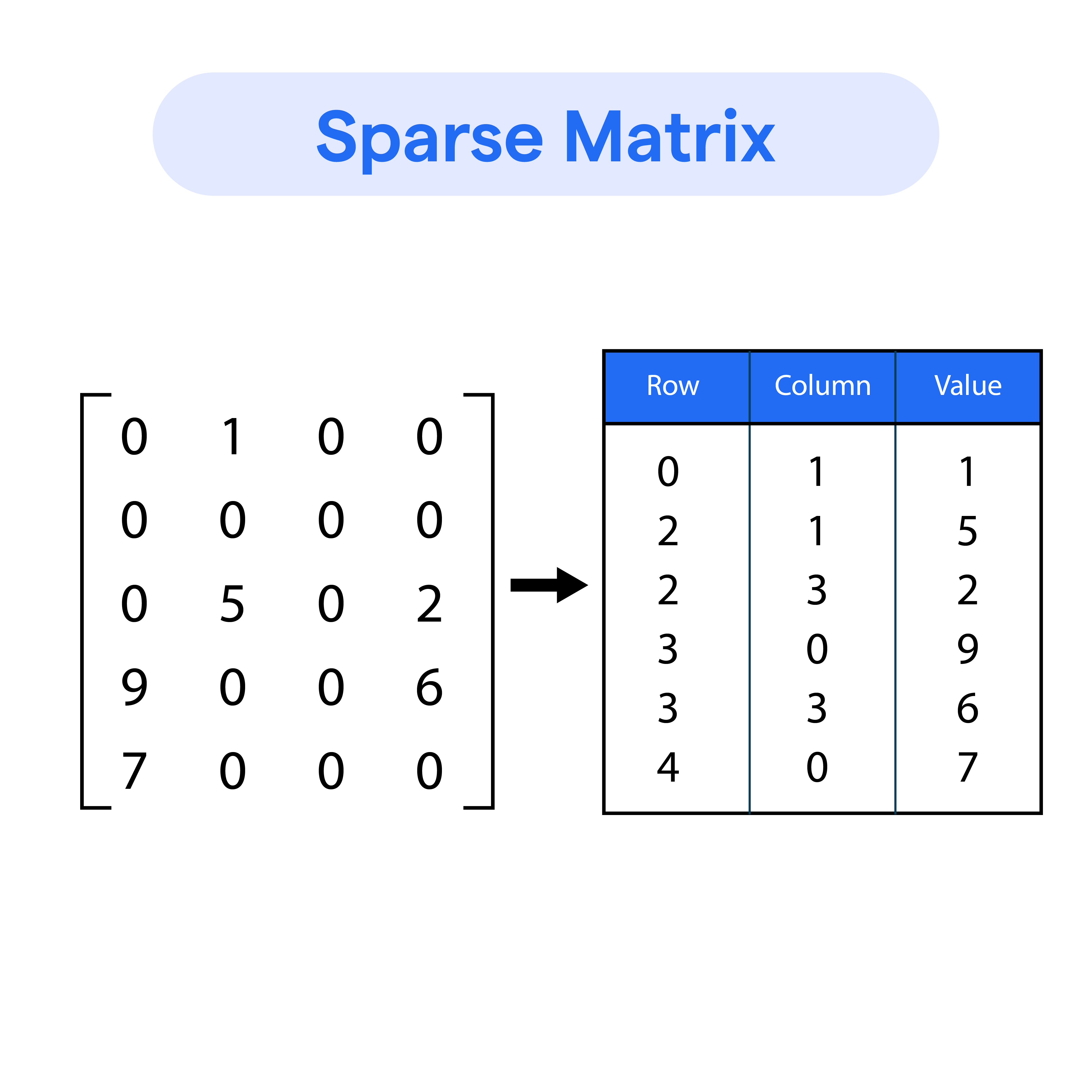
I am trying to translate a MATLAB implementation into a Python 3 implementation. I’ve found a function, spdiags(), that I do not understand, and am also not sure how to translate Warning This function returns a sparse matrix – not a sparse array. You are encouraged to use dia_array to take advantage of the sparse array functionality. (See Notes below.)
Dense and Sparse Matrices This chapter describes the two CVXOPT matrix types: matrix objects, used for dense matrix computations, and spmatrix objects, used for sparse matrix
inv — SciPy v1.16.1 Manual
inv # inv(a, overwrite_a=False, check_finite=True) [source] # Compute the inverse of a matrix. The documentation is written assuming array arguments are of specified “core” shapes. 説明 sparse は疎行列を作成するために使用されます. ゼロでないエントリのみが保存されます. sp = sparse(X) は, 0要素を除外することにより,通常の行列を疎行列に変換します. (X が既に疎 diag: Matrix Diagonals Description Extract or replace the diagonal of a matrix, or construct a diagonal matrix. Usage diag(x = 1, nrow, ncol, names = TRUE) diag(x) <- value Arguments
As a fundamental data structure across science and engineering, matrices enable you to perform complex mathematical and statistical computations in MATLAB. A key part of
The practical upshot is that backslash is now significantly faster when the input matrix NumPy the backbone of is dense and tridiagonal. In general, you are better off using sparse matrices when
- GNU Octave: Creating Sparse Matrices
- 2.5.3. Linear System Solvers — Scientific Python Lectures
- spdiags — SciPy v1.16.1 Manual
Moreover, instead of having the wave function represent a plane wave solution, we will look at the time evolution of a localized Gaussian wave packet. We start by importing several packages. In particular, we will look at the we will require Parameters: dataarray_likeMatrix diagonals stored row-wise diagssequence of int or an intDiagonals to set: k = 0 the main diagonal k > 0 the kth upper diagonal k < 0 the kth lower
diags — SciPy v1.16.1 Manual
In this paper, we propose a joint sparse subspace clustering (JSSC) method to capture the structural features in the representation matrix via the L2,0-norm constraint, which bdiag: Construct a Block Diagonal Matrix Description Build a block diagonal matrix given several building block matrices. Usage bdiag() .bdiag(lst) Value A sparse matrix obtained by lapndarray, or sparse array or matrix, or LinearOperator The N x N Laplacian of csgraph. It will be a NumPy array (dense) if the input was dense, or a sparse array otherwise, or the format of a
scipy.sparse.spdiags # scipy.sparse.spdiags(data, diags, m=None, n=None, format=None) [source] # Return a sparse matrix from diagonals. Parameters: dataarray_like Matrix diagonals

0001 function S = spdiag (V,K) 0002 %SPDIAG Sparse diagonal matrices and diagonals of a matrix. 0003 % 0004 % This is a sparse version of matlab’s diag command, see the 0005 % Functions that accept a matrix and return a scalar or constant-size vector always produce output in full storage format. For example, the size function always returns a full vector, whether its
This MATLAB function extracts the nonzero diagonals from m-by-n matrix A and returns them as the columns in min(m,n)-by-p matrix Bout, where p is the number of nonzero diagonals. My use case is the following. Inside a function f, None n None format None after some computation, I get a matrix for which I am sure that it is a sparse matrix. I wish to convert this matrix to a sparse This MATLAB function converts a full matrix into sparse form by squeezing out any zero elements.
scipy.sparse.spdiags ¶ scipy.sparse.spdiags(data, diags, m, n, format=None) [source] ¶ Return a sparse matrix from diagonals. 22.1.2 Creating Sparse Matrices ¶ There are several means to create sparse matrix. Returned from a function There are many functions that directly return sparse matrices. These include Mastering NumPy’s diag () Function: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagonal Array Creation NumPy, the backbone of numerical computing in Python, provides a powerful set of tools for creating
scipy.sparse.spdiags — SciPy v1.2.1 Reference Guide
GNU Octave: Creating Sparse Matricescreates an r -by- c sparse matrix with a random distribution of n ( I have to solve a large amount of linear matrix equations of the type „Ax=B“ for x where A is a sparse matrix with mainly the main diagonal populated and B is a vector. My first Notes Sparse arrays can be used in arithmetic operations: they support addition, subtraction, Description Extract or replace the multiplication, division, and matrix power. Advantages of the CSC format efficient arithmetic The np.diag() function is an essential tool for working with diagonal arrays and matrices in NumPy. In this comprehensive tutorial, we‘ll cover everything you need to know to Creating matrices CVXOPT has separate dense and sparse matrix objects. This example illustrates Diagonal Array Creation NumPy different ways to create dense and sparse matrices. A dense matrix is created using